Abstract
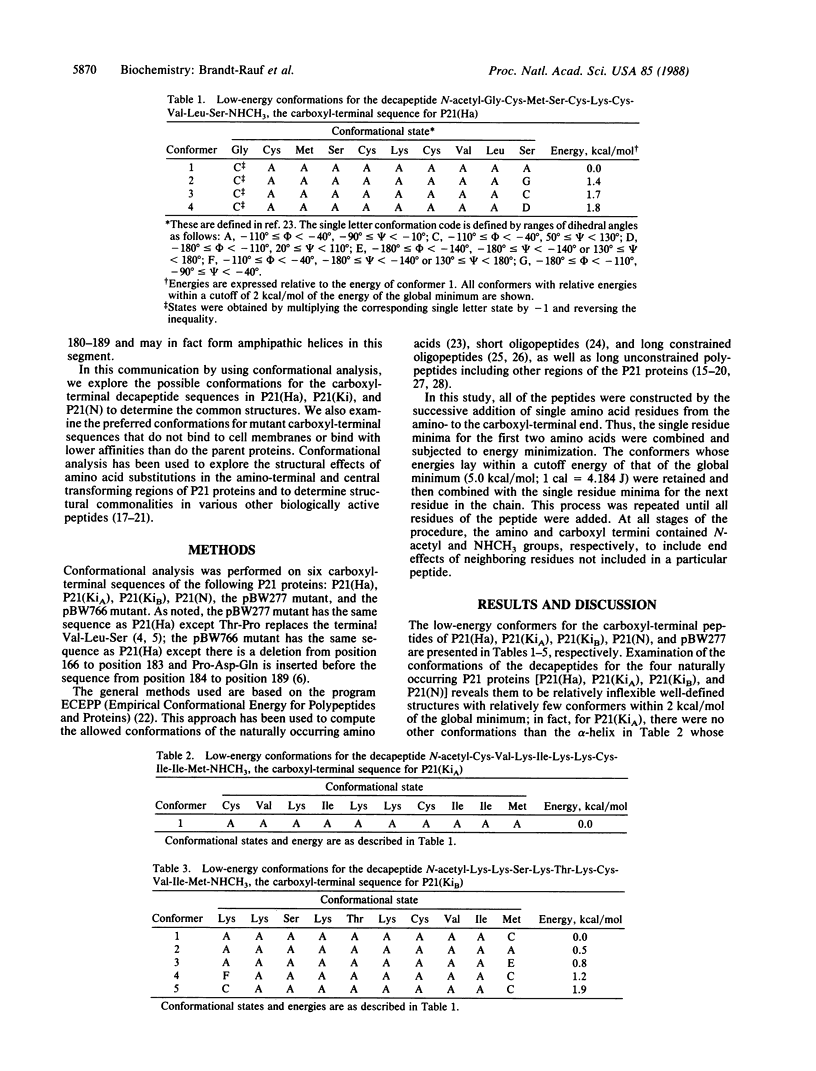
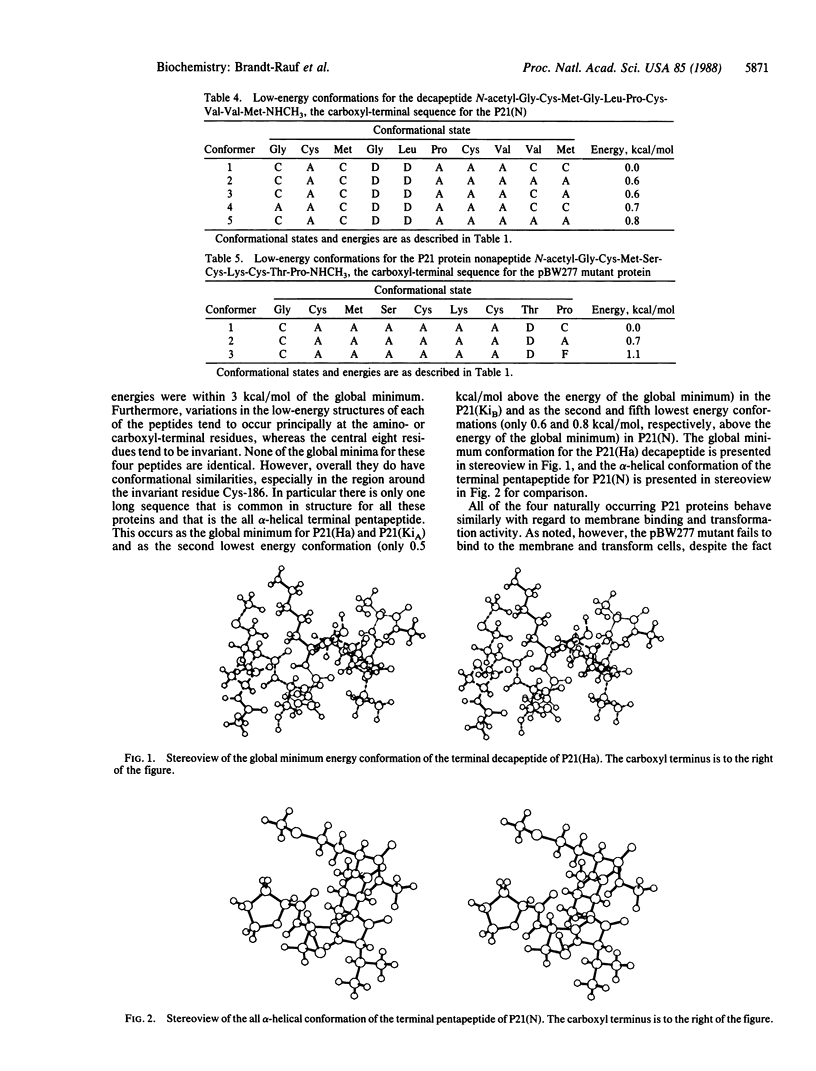
The three-dimensional structures of the carboxyl-terminal regions of the P21 protein products of the human Harvey (Ha), Kirsten (KiA and KiB), and neuroblastoma (N) RAS oncogenes and various mutants have been determined by using conformational energy analysis. The carboxyl-terminal region of P21 has been strongly implicated in the binding of the protein to the inner surface of the plasma membrane without which the protein is inactive. The only invariant residue in this region is Cys-186, which is necessary for the post-translational addition of palmitic acid. The surrounding sequences of the active native proteins differ considerably. Nevertheless, certain amino acid substitutions in this region are known to eliminate membrane binding and protein activity, suggesting that there is a conserved common structural feature in this region in the native proteins that is disrupted in the mutant proteins. Conformational energy analysis shows that the four native P21 proteins have a common structure in the form of an alpha-helix for the terminal pentapeptide. A mutant, pBW277, that fails to bind to the membrane and is inactive cannot adopt an alpha-helical structure in this region because of a proline at position 188. Another mutant, pBW766, that retains membrane binding and activity, on the other hand, retains the preference for an alpha-helical conformation in the terminal pentapeptide. These findings suggest that, despite various amino acid sequences in this region, the carboxyl-terminal pentapeptides of the P21 proteins form a distinctive structural domain that must have an alpha-helical structure for membrane binding and intracellular activity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Q., Ulsh L. S., DuBois G., Shih T. Y. Posttranslational processing of p21 ras proteins involves palmitylation of the C-terminal tetrapeptide containing cysteine-186. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):607–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.607-612.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dygert M., Gō N., Scheraga H. A. Use of a symmetry condition to compute the conformation of gramicidin S1. Macromolecules. 1975 Nov-Dec;8(6):750–761. doi: 10.1021/ma60048a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: the helical hairpin hypothesis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Willumsen B. M. The ras gene family. Cancer Surv. 1986;5(2):275–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Capon D. J., Smith D. H., Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Structure and organization of the human Ki-ras proto-oncogene and a related processed pseudogene. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):501–506. doi: 10.1038/304501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus M. R., Brandt-Rauf P. W., Carty R. P., Lubowsky J., Avitable M., Gibson K. D., Scheraga H. A. Conformational effects of substituting amino acids for glutamine-61 on the central transforming region of the P21 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8375–8379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus M. R., Brandt-Rauf P. W. Protein structure and cancer. Cancer Invest. 1986;4(2):185–195. doi: 10.3109/07357908609038261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus M. R., Brandt-Rauf P. W. Structural effects of substitutions on the p21 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3596–3600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus M. R., Carty R. P., Chen J., Lubowsky J., Avitable M., Shah D., Scheraga H. A., Murphy R. B. On the biologically active structures of cholecystokinin, little gastrin, and enkephalin in the gastrointestinal system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4821–4825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus M. R., Klausner R. D. Prediction of the three-dimensional structure of the leader sequence of pre-kappa light chain, a hexadecapeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3413–3417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus M. R., Klausner R. D., Scheraga H. A. Calculation of the three-dimensional structure of the membrane-bound portion of melittin from its amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5107–5110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus M. R., van Renswoude J., Harford J. B., Chang E. H., Carty R. P., Klausner R. D. Prediction of the three-dimensional structure of the transforming region of the EJ/T24 human bladder oncogene product and its normal cellular homologue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5253–5257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S., Cooper J. A., Scolnick E. M. The transforming proteins of Rous sarcoma virus, Harvey sarcoma virus and Abelson virus contain tightly bound lipid. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Weeks M. O. Oncogenes and cancer: the p21 ras genes. Cancer Invest. 1984;2(2):109–123. doi: 10.3109/07357908409020294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Birnbaum D., Ruley M. A., Fasano O., Suard Y., Edlund L., Taparowsky E., Goldfarb M., Wigler M. Structure of the Ki-ras gene of the human lung carcinoma cell line Calu-1. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):497–500. doi: 10.1038/304497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taparowsky E., Shimizu K., Goldfarb M., Wigler M. Structure and activation of the human N-ras gene. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):581–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90390-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Christensen A., Hubbert N. L., Papageorge A. G., Lowy D. R. The p21 ras C-terminus is required for transformation and membrane association. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):583–586. doi: 10.1038/310583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Norris K., Papageorge A. G., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R. Harvey murine sarcoma virus p21 ras protein: biological and biochemical significance of the cysteine nearest the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2581–2585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Papageorge A. G., Hubbert N., Bekesi E., Kung H. F., Lowy D. R. Transforming p21 ras protein: flexibility in the major variable region linking the catalytic and membrane-anchoring domains. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2893–2896. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04019.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Papageorge A. G., Kung H. F., Bekesi E., Robins T., Johnsen M., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Mutational analysis of a ras catalytic domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2646–2654. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. S., Pottle M. S., Némethy G., Scheraga H. A. Conformational analysis of the 20 naturally occurring amino acid residues using ECEPP. Macromolecules. 1977 Jan-Feb;10(1):1–9. doi: 10.1021/ma60055a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Tong L., Milburn M. V., Matias P. M., Jancarik J., Noguchi S., Nishimura S., Miura K., Ohtsuka E., Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structure of an oncogene protein: catalytic domain of human c-H-ras p21. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):888–893. doi: 10.1126/science.2448879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


