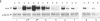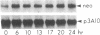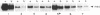Abstract
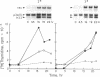
Recent evidence on the transcriptional regulation of the human thymidine kinase (TK) gene raises the possibility that cell-cycle regulatory sequences may be localized within its promoter. A hybrid gene that combines the TK 5' flanking sequence and the coding region of the bacterial neomycin-resistance gene (neo) has been constructed. Upon transfection into a hamster fibroblast cell line K12, the hybrid gene exhibits cell-cycle-dependent expression. Deletion analysis reveals that the region important for cell-cycle regulation is within -441 to -63 nucleotides from the transcriptional initiation site. This region (-441 to -63) also confers cell-cycle regulation to the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (HSVtk) promoter, which is not expressed in a cell-cycle manner. We conclude that the -441 to -63 sequence within the human TK promoter is important for cell-cycle-dependent expression.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artishevsky A., Delegeane A. M., Lee A. S. Use of a cell cycle mutant to delineate the critical period for the control of histone mRNA levels in the mammalian cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2364–2369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artishevsky A., Grafsky A., Lee A. S. Isolation of a mammalian sequence capable of conferring cell cycle regulation to a heterologous gene. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1061–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.4059922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artishevsky A., Wooden S., Sharma A., Resendez E., Jr, Lee A. S. Cell-cycle regulatory sequences in a hamster histone promoter and their interactions with cellular factors. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):823–827. doi: 10.1038/328823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw H. D., Jr Molecular cloning and cell cycle-specific regulation of a functional human thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5588–5591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppock D. L., Pardee A. B. Control of thymidine kinase mRNA during the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2925–2932. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppock D. L., Pardee A. B. Regulation of thymidine kinase activity in the cell cycle by a labile protein. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Aug;124(2):269–274. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041240215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delegeane A. M., Lee A. S. Coupling of histone and DNA synthesis in the somatic cell cycle. Science. 1982 Jan 1;215(4528):79–81. doi: 10.1126/science.7053561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Schimke R. T. Transcriptional regulation of mouse dihydrofolate reductase in the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7675–7680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Bradshaw H. D., Jr, Traina-Dorge V., Slagel V., Deininger P. L. Sequence, structure and promoter characterization of the human thymidine kinase gene. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M. K., Kainz M. S., Merrill G. F. Introns are inconsequential to efficient formation of cellular thymidine kinase mRNA in mouse L cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4576–4581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Casimir C. Post-transcriptional regulation of the chicken thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1427–1446. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenh C. H., Geyer P. K., Johnson L. F. Control of thymidylate synthase mRNA content and gene transcription in an overproducing mouse cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2527–2532. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Jorgensen G. N. Formation of thymidine kinase and deoxycytidylate deaminase in synchronized cultures of chinese hamster cells temperature-sensitive for DNA synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1976 May;88(1):57–64. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040880108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight G. B., Gudas J. M., Pardee A. B. Cell-cycle-specific interaction of nuclear DNA-binding proteins with a CCAAT sequence from the human thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8350–8354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreidberg J. A., Kelly T. J. Genetic analysis of the human thymidine kinase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2903–2909. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Kan Y. W. Direct isolation of the functional human thymidine kinase gene with a cosmid shuttle vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):414–418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. S., Delegeane A. M., Baker V., Chow P. C. Transcriptional regulation of two genes specifically induced by glucose starvation in a hamster mutant fibroblast cell line. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):597–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A., Matkovich D. A. Genetic determinants of growth phase-dependent and adenovirus 5-responsive expression of the Chinese hamster thymidine kinase gene are contained within thymidine kinase mRNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2262–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A., Shimizu K., Zipser D. Isolation and preliminary characterization of the Chinese hamster thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1815–1823. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A. Structure and expression of the Chinese hamster thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1998–2010. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. Y., Lee A. S. Induction of two genes by glucose starvation in hamster fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):988–992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Stauber C., Schindler R., Schümperli D. Faithful cell-cycle regulation of a recombinant mouse histone H4 gene is controlled by sequences in the 3'-terminal part of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4389–4393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melero J. A., Fincham V. Enhancement of the synthesis of specific cellular polypeptides in a temperature-sensitive Chinese hamster cell line (K12) defective for entry into S phase. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Jun;95(3):295–306. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040950307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melero J. A. Isolation and cell cycle analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants from Chinese hamster cells. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Jan;98(1):17–30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040980104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill G. F., Harland R. M., Groudine M., McKnight S. L. Genetic and physical analysis of the chicken tk gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1769–1776. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill G. F., Hauschka S. D., McKnight S. L. tk Enzyme expression in differentiating muscle cells is regulated through an internal segment of the cellular tk gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1777–1784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B., Dubrow R., Hamlin J. L., Kletzien R. F. Animal cell cycle. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:715–750. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Lipsich L., Wigler M. Isolation of the chicken thymidine kinase gene by plasmid rescue. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):207–210. doi: 10.1038/285207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharff D. J., Delegeane A. M., Lee A. S. Characterization of a cell cycle mutant derived from hamster fibroblast: reversion analysis. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):629–633. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlosser C. A., Steglich C., deWet J. R., Scheffler I. E. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of thymidine kinase activity introduced into mouse LMTK- cells by DNA and chromatin-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1119–1123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schümperli D. Cell-cycle regulation of histone gene expression. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):471–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Paterson B. M. Cell cycle regulation of a mouse histone H4 gene requires the H4 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1048–1054. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a common factor with conserved promoter and enhancer sequences in histone H2B, immunoglobulin, and U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6382–6386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. J., Ito M., Conrad S. E. Evidence for transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of the cellular thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1156–1163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travali S., Lipson K. E., Jaskulski D., Lauret E., Baserga R. Role of the promoter in the regulation of the thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1551–1557. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. L., Lee A. S. Polymerization of vector DNA after transfection into hamster fibroblast cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):593–601. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]