Abstract
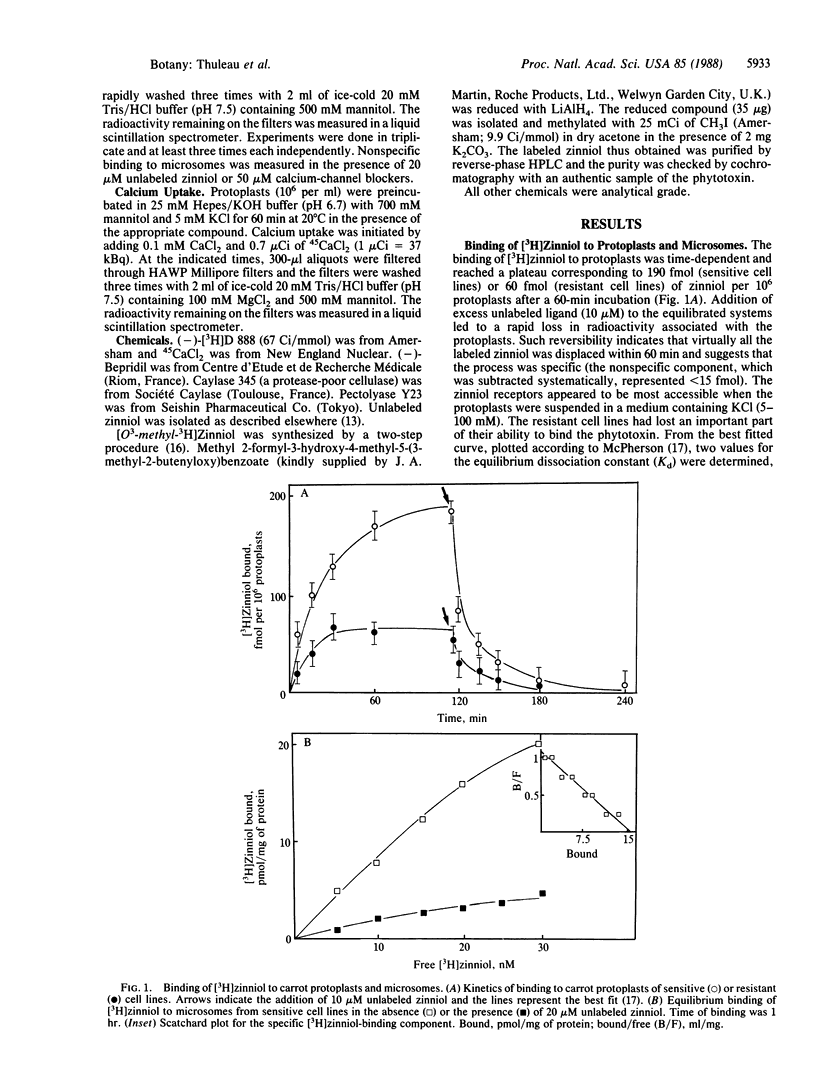
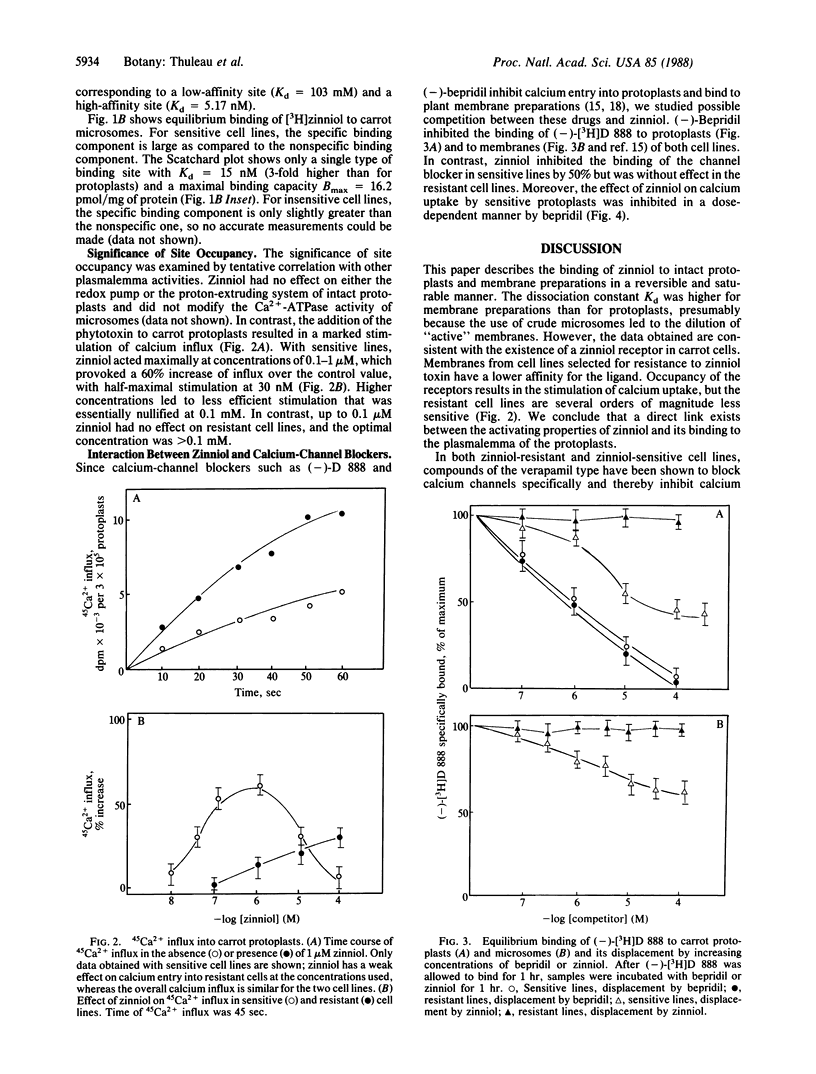
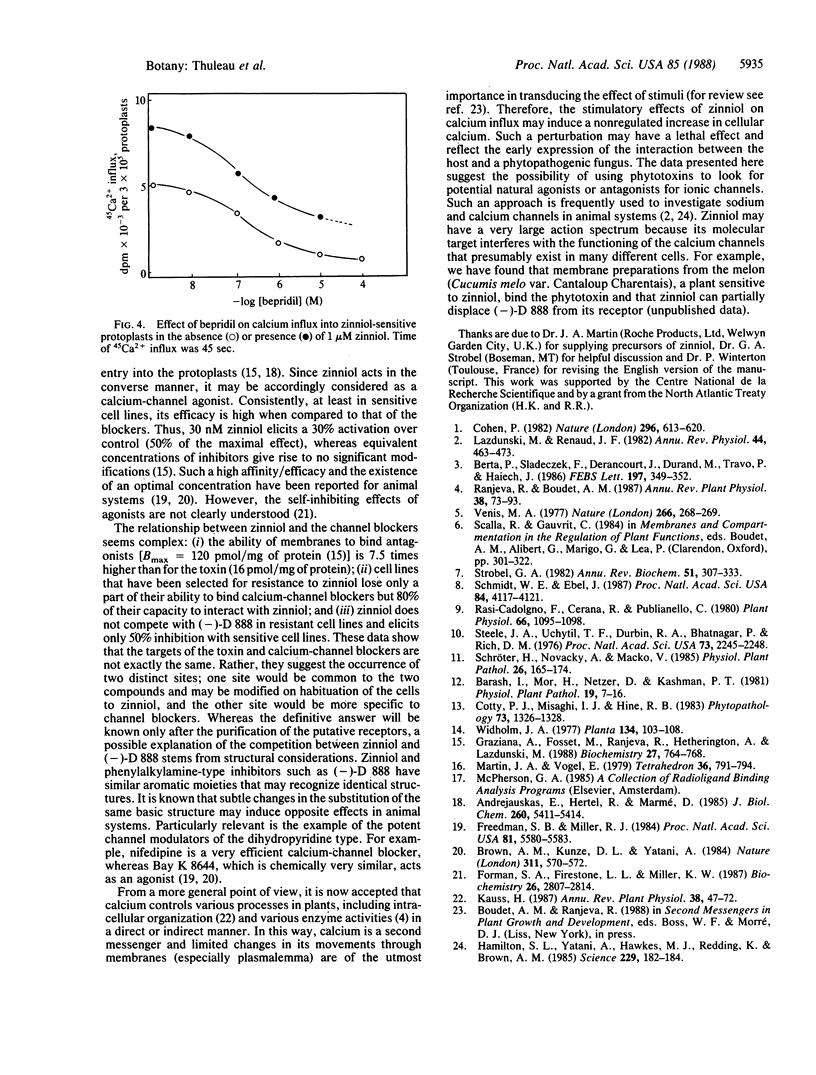
Zinniol [1,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)-3-methoxy-4-methyl-5-(3-methyl-2-butenyloxy)benzene], a toxin produced by fungi of the Alternaria group, causes symptoms in plants that resemble those induced by the fungi. The phytotoxin binds to carrot protoplasts and isolated membranes in a saturable and reversible manner. Receptor occupancy stimulates entry of calcium into protoplasts. Zinniol can partially reverse the effects and binding of the calcium-channel blockers desmethoxyverapamil and bepridil. Selected cell lines that are insensitive to zinniol lose part of their binding capacity and sensitivity to the action of the agonist-like compound but are still able to bind calcium-channel blockers. We conclude that zinniol acts on calcium entry but that the targets of the toxin and of calcium-channel blockers are dissimilar, suggesting the occurrence of sites affected both by zinniol and by channel blockers and of sites affected only by zinniol.
Keywords: receptor, calcium-channel agonist
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrejauskas E., Hertel R., Marmé D. Specific binding of the calcium antagonist [3H]verapamil to membrane fractions from plants. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5411–5414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berta P., Sladeczek F., Derancourt J., Durand M., Travo P., Haiech J. Maitotoxin stimulates the formation of inositol phosphates in rat aortic myocytes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 3;197(1-2):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Kunze D. L., Yatani A. The agonist effect of dihydropyridines on Ca channels. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):570–572. doi: 10.1038/311570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman S. A., Firestone L. L., Miller K. W. Is agonist self-inhibition at the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor a nonspecific action? Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2807–2814. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman S. B., Miller R. J. Calcium channel activation: a different type of drug action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5580–5583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. L., Yatani A., Hawkes M. J., Redding K., Brown A. M. Atrotoxin: a specific agonist for calcium currents in heart. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):182–184. doi: 10.1126/science.3160111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdunski M., Renaud J. F. The action of cardiotoxins on cardiac plasma membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:463–473. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasi-Caldogno F., Cerana R., Pugliarello M. C. Relationship between ATP Level and Activity of Fusicoccin-stimulated H/K-Exchange System in Plant Tissues. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1095–1098. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. E., Ebel J. Specific binding of a fungal glucan phytoalexin elicitor to membrane fractions from soybean Glycine max. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4117–4121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele J. A., Uchytil T. F., Durbin R. D., Bhatnagar P., Rich D. H. Chloroplast coupling factor 1: A species-specific receptor for tentoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2245–2248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel G. A. Phytotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:309–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



