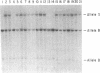
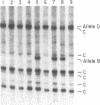
Abstract
Mouse trisomy 16 has been proposed as an animal model of Down syndrome (DS), since this chromosome contains homologues of several loci from the q22 band of human chromosome 21. The recent mapping of the defect causing familial Alzheimer disease (FAD) and the locus encoding the Alzheimer amyloid beta precursor protein (APP) to human chromosome 21 has prompted a more detailed examination of the extent of conservation of this linkage group between the two species. Using anonymous DNA probes and cloned genes from human chromosome 21 in a combination of recombinant inbred and interspecific mouse backcross analyses, we have established that the linkage group shared by mouse chromosome 16 includes not only the critical DS region of human chromosome 21 but also the APP gene and FAD-linked markers. Extending from the anonymous DNA locus D21S52 to ETS2, the linkage map of six loci spans 39% recombination in man but only 6.4% recombination in the mouse. A break in synteny occurs distal to ETS2, with the homologue of the human marker D21S56 mapping to mouse chromosome 17. Conservation of the linkage relationships of markers in the FAD region suggests that the murine homologue of the FAD locus probably maps to chromosome 16 and that detailed comparison of the corresponding region in both species could facilitate identification of the primary defect in this disorder. The break in synteny between the terminal portion of human chromosome 21 and mouse chromosome 16 indicates, however, that mouse trisomy 16 may not represent a complete model of DS.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Búcan M., Herrmann B. G., Frischauf A. M., Bautch V. L., Bode V., Silver L. M., Martin G. R., Lehrach H. Deletion and duplication of DNA sequences is associated with the embryonic lethal phenotype of the t9 complementation group of the mouse t complex. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):376–385. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Eustachio P., Fein B., Michaelson J., Taylor B. A. The alpha-globin pseudogene on mouse chromosome 17 is closely linked to H-2. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):958–963. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J., Varsanyi-Breiner A., Kao F. T., Jones C., Puck T. T., Keys C., Orkin S., Housman D. Precise localization of human beta-globin gene complex on chromosome 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5239–5242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeijer A., Smit E. M. Partial trisomy 21. Further evidence that trisomy of band 21q22 is essential for Down's phenotype. Hum Genet. 1977 Aug 31;38(1):15–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00295803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallewell R. A., Masiarz F. R., Najarian R. C., Puma J. P., Quiroga M. R., Randolph A., Sanchez-Pescador R., Scandella C. J., Smith B., Steimer K. S. Human Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase cDNA: isolation of clones synthesising high levels of active or inactive enzyme from an expression library. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2017–2034. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B., Bućan M., Mains P. E., Frischauf A. M., Silver L. M., Lehrach H. Genetic analysis of the proximal portion of the mouse t complex: evidence for a second inversion within t haplotypes. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90468-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye N. W., Church R. L., Piatigorsky J., Petrash J. M., Lalley P. A. Assignment of the mouse alpha A-crystallin structural gene to chromosome 17. Curr Eye Res. 1985 Dec;4(12):1263–1268. doi: 10.3109/02713688509017685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., O'Brien S. J., Créau-Goldberg N., Davisson M. T., Roderick T. H., Echard G., Womack J. E., Graves J. M., Doolittle D. P., Guidi J. N. Report on the committee on comparative mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;46(1-4):367–389. doi: 10.1159/000132486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meo T., Douglas T., Rijnbeek A. M. Glyoxalase I polymorphism in the mouse: a new genetic marker linked to H-2. Science. 1977 Oct 21;198(4314):311–313. doi: 10.1126/science.910130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Neve R. L., Colletti-Feener C., Bertelson C. J., Kurnit D. M., Kunkel L. M. Isolation of candidate cDNAs for portions of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):646–650. doi: 10.1038/323646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münke M., Kraus J. P., Ohura T., Francke U. The gene for cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) maps to the subtelomeric region on human chromosome 21q and to proximal mouse chromosome 17. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Apr;42(4):550–559. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau J. H., Phillips S. J., Egorov I. K. Recombination between the t6 complex and linked loci in the house mouse. Genet Res. 1985 Jun;45(3):251–264. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300022242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau J. H., Phillips S. J. The putative oncogene Pim-1 in the mouse: its linkage and variation among t haplotypes. Genetics. 1987 Nov;117(3):533–541. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.3.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau J. H., Taylor B. A. Lengths of chromosomal segments conserved since divergence of man and mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):814–818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niebuhr E. Down's syndrome. The possibility of a pathogenetic segment on chromosome no. 21. Humangenetik. 1974 Jan 22;21(1):99–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00278575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax-Jeuken Y., Quax W., van Rens G., Khan P. M., Bloemendal H. Complete structure of the alpha B-crystallin gene: conservation of the exon-intron distribution in the two nonlinked alpha-crystallin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5819–5823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. H., Gallahan D., O'Hara B. F., Callahan R., Gearhart J. D. Genetic mapping of Prm-1, Igl-1, Smst, Mtv-6, Sod-1, and Ets-2 and localization of the Down syndrome region on mouse chromosome 16. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;44(2-3):76–81. doi: 10.1159/000132347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. H., Gearhart J. D., Littlefield J. W. Genetic basis for a mouse model of Down syndrome. Brain Res Bull. 1986 Jun;16(6):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(86)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert B., Barton P., Minty A., Daubas P., Weydert A., Bonhomme F., Catalan J., Chazottes D., Guénet J. L., Buckingham M. Investigation of genetic linkage between myosin and actin genes using an interspecific mouse back-cross. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):181–183. doi: 10.1038/314181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein P., Vienne K. Genetic control of the quantitative variation of erythrocytic glyoxalase-1(GLO-1) in mice. Biochem Genet. 1982 Feb;20(1-2):153–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00484943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J. Confidence limits for estimates of gene linkage based on analysis of recombinant inbred strains. J Hered. 1985 Nov-Dec;76(6):436–440. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a110140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinet P. M., Couturier J., Dutrillaux B., Poissonnier M., Raoul O., Rethore M. O., Allard D., Lejeune J., Jerome H. Trisomie 21 et superoxyde dismutase-1 (IPO-A). Tentative de localisation sur la sous bande 21Q22.1. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jan;97:47–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90653-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skow L. C., Donner M. E. The locus encoding alpha A-crystallin is closely linked to H-2K on mouse chromosome 17. Genetics. 1985 Aug;110(4):723–732. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.4.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. D., Harris P., Galt J., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Cloned DNA probes regionally mapped to human chromosome 21 and their use in determining the origin of nondisjunction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4125–4132. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., St George-Hyslop P. H., Haines J. L., Polinsky R. J., Nee L., Foncin J. F., Neve R. L., McClatchey A. I., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. The genetic defect in familial Alzheimer's disease is not tightly linked to the amyloid beta-protein gene. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):156–157. doi: 10.1038/329156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. C., Tanzi R. E., Cheng S. V., Gusella J. F. Molecular genetics of human chromosome 21. J Med Genet. 1987 May;24(5):257–270. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.5.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. C., Tanzi R. E., Gibbons K. T., Tricoli J. V., Landes G., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Gusella J. F. Isolation of polymorphic DNA segments from human chromosome 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6075–6088. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams-Smith M. J., Nunn M. F., Duesberg P. H., O'Brien S. J., Papas T. S. The ets sequence from the transforming gene of avian erythroblastosis virus, E26, has unique domains on human chromosomes 11 and 21: both loci are transcriptionally active. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7294–7298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. D., Summitt R. L., Martens P. R., Kimbrell R. A. Familial Down syndrome due to t(10;21) translocation: evidence that the Down phenotype is related to trisomy of a specific segment of chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Jul;27(4):478–485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]