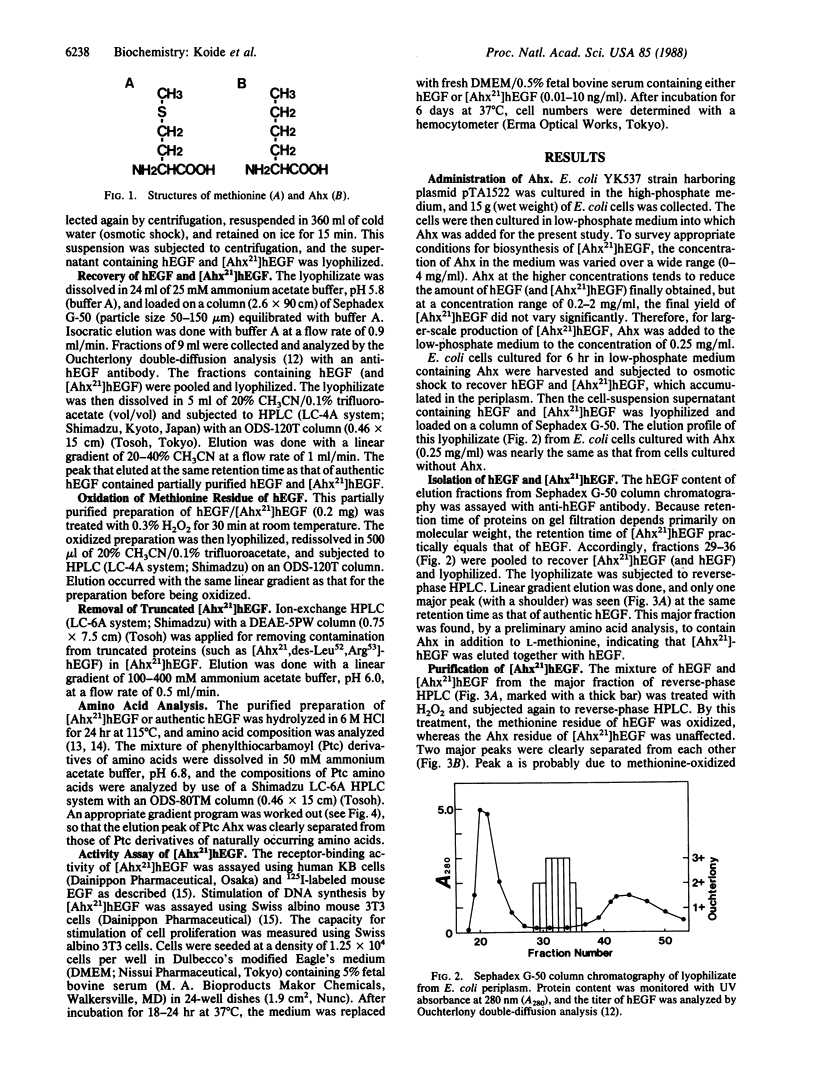
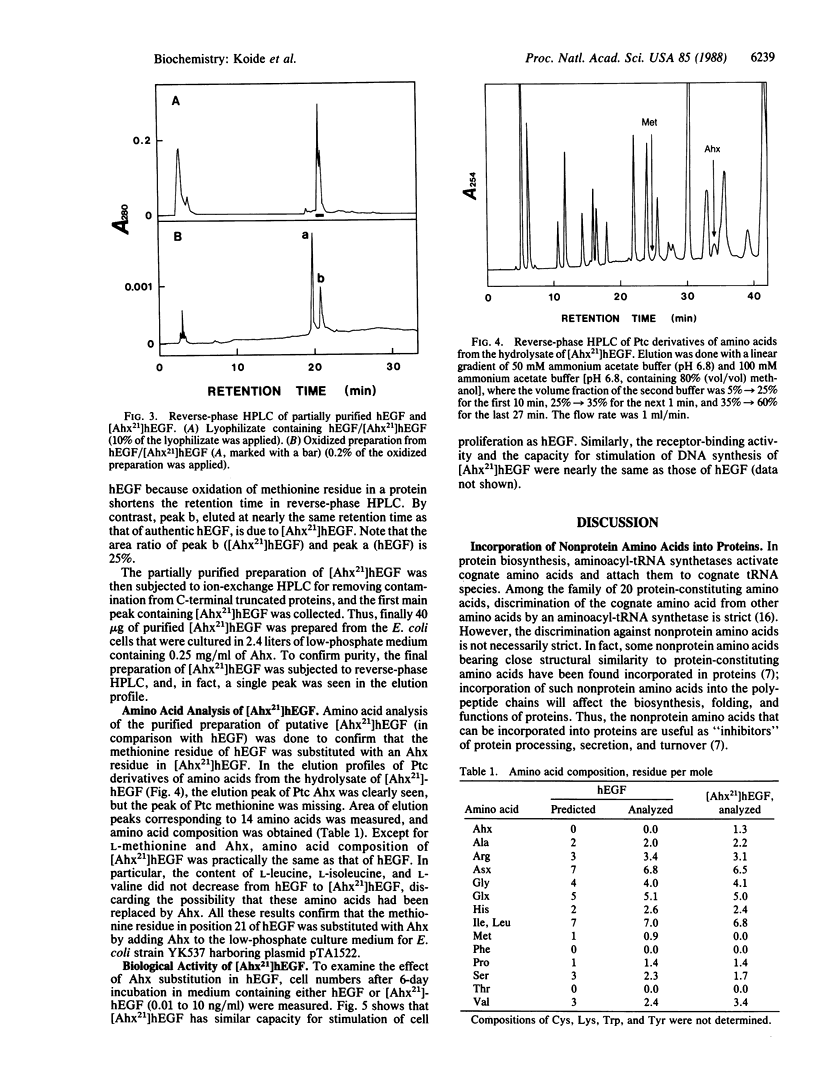
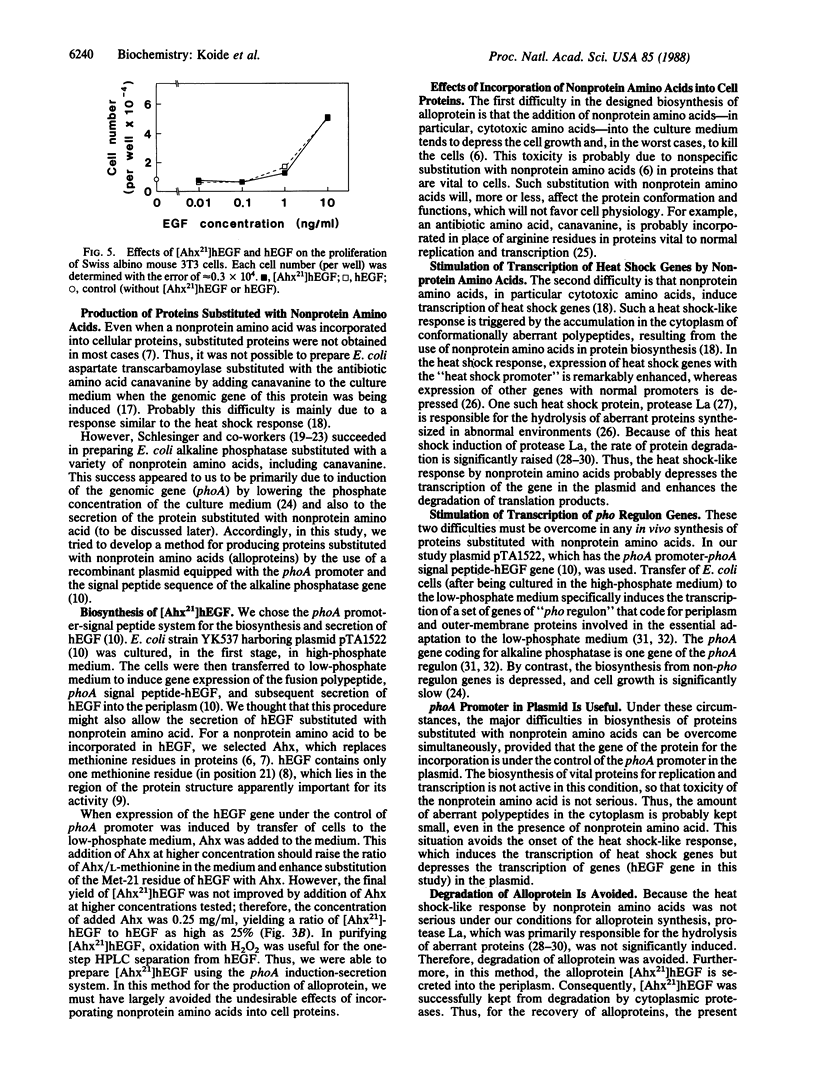
Abstract
Endeavoring to develop a method to biosynthesize proteins substituted with nonprotein amino acids, we attempted the incorporation of L-2-aminohexanoic acid (Ahx) into human epidermal growth factor (hEGF). Escherichia coli YK537 strain harboring plasmid pTA1522, which has the phoA promoter-phoA signal peptide-hEGF gene, was used. Cells were cultured first in high-phosphate medium and then, for induction of the hEGF-encoding gene, transferred to low-phosphate medium containing Ahx (0.25 mg/ml). hEGF and Ahx-substituted hEGF, [Ahx21]hEGF, secreted into the periplasm were recovered. After treatment with H2O2, [Ahx21]-hEGF was clearly separated from methionine-oxidized hEGF by one-step reverse-phase HPLC. Substitution of the methionine residue of hEGF with Ahx was confirmed by the amino acid analysis of [Ahx21]hEGF. The three biological activities of [Ahx21]hEGF were the same as those of hEGF. From the successful production of [Ahx21]hEGF, a basic strategy was established for preparing proteins substituted with nonprotein amino acid (alloprotein). Induction of the phoA promoter of pho regulon and secretion of the product to the periplasm may depress heat shock-like responses and subsequent hydrolysis of the product by cytoplasmic protease.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attias J., Schlesinger M. J., Schlesinger S. The effect of amino acid analogues on alkaline phosphatase formation in Escherichia coli K-12. IV. Substitution of canavanine for arginine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 25;244(14):3810–3817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne D. T., Otvos J. D. 4-Fluorotryptophan alkaline phosphatase from E. coli: preparation, properties, and 19F NMR spectrum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 9;68(3):907–913. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari A. I., Zipser D. Mutants of Escherichia coli with a defect in the degradation of nonsense fragments. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 20;243(129):238–241. doi: 10.1038/newbio243238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver J. A., Cooke R. M., Esposito G., Campbell I. D., Gregory H., Sheard B. A high resolution 1H NMR study of the solution structure of human epidermal growth factor. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 1;205(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80869-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowden L., Lewis D., Tristram H. Toxic amino acids: their action as antimetabolites. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:89–163. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Goldberg A. L. Production of abnormal proteins in E. coli stimulates transcription of lon and other heat shock genes. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):587–595. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Zipser D. Deg phenotype of Escherichia coli lon mutants. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):844–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.844-851.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory H. Isolation and structure of urogastrone and its relationship to epidermal growth factor. Nature. 1975 Sep 25;257(5524):325–327. doi: 10.1038/257325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gueguen P., Padron M., Perbal B., Hervé G. Incorporation of amino acid analogs during the biosynthesis of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 9;615(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. S., Weiner J. H., Sykes B. D. Fluorotyrosine M13 coat protein: fluorine-19 nuclear magnetic resonance study of the motional properties of an integral membrane protein in phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 5;17(18):3860–3866. doi: 10.1021/bi00611a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Meredith S. C. Amino acid analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: precolumn derivatization with phenylisothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarema M. A., Lu P., Miller J. H. Genetic assignment of resonances in the NMR spectrum of a protein: lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2707–2711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohda D., Kawai G., Yokoyama S., Kawakami M., Mizushima S., Miyazawa T. NMR analyses of the conformations of L-isoleucine and L-valine bound to Escherichia coli isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 6;26(20):6531–6538. doi: 10.1021/bi00394a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komoriya A., Hortsch M., Meyers C., Smith M., Kanety H., Schlessinger J. Biologically active synthetic fragments of epidermal growth factor: localization of a major receptor-binding region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1351–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowit J. D., Goldberg A. L. Intermediate steps in the degradation of a specific abnormal protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8350–8357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H., Schlesinger M. J. Effects of proline analogues on the formation of alkaline phosphatase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):203–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.203-210.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa S., Yoshida S., Hirao Y., Kasuga S., Fuwa T. Biological effects of biosynthetic human EGF on the growth of mammalian cells in vitro. Differentiation. 1985;29(3):284–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1985.tb00328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Sakamoto S., Miyoshi K., Fuwa T., Yoda K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G., Miyake T. Synthesis and secretion of human epidermal growth factor by Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7212–7216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips T. A., VanBogelen R. A., Neidhardt F. C. lon gene product of Escherichia coli is a heat-shock protein. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):283–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.283-287.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F., Rogers P. Canavanine death in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):474–489. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger S., Schlesinger M. J. The effect of amino acid analogues on alkaline phosphatase formation in Escherichia coli K-12. 3. Substitution of 2-methylhistidine for histidine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 25;244(14):3803–3809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger S., Schlesinger M. J. The effect of amino acid analogues on alkaline phosphatase formation in Escherichia coli K-12. I. Substitution of triazolealanine for histidine. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 25;242(14):3369–3372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger S. The effect of amino acid analogues on alkaline phosphatase. Formation in Escherichia coli K-12. II. Replacement of tryptophan by azatryptophan and by tryptazan. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 25;243(14):3877–3883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. D., Weingarten H. I., Schlesinger M. J. Fluorotyrosine alkaline phosphatase from Escherichia coli: preparation, properties, and fluorine-19 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):469–473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORRIANI A. Influence of inorganic phosphate in the formation of phosphatases by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:460–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. PHO-regulon of Escherichia coli K12: a minireview. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Mar-Apr;133(2):243–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer K. M. Protein engineering. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):666–671. doi: 10.1126/science.6572017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. J., Hatfield D. L. Incorporation of modified amino acids into proteins in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 5;781(3):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



