Abstract
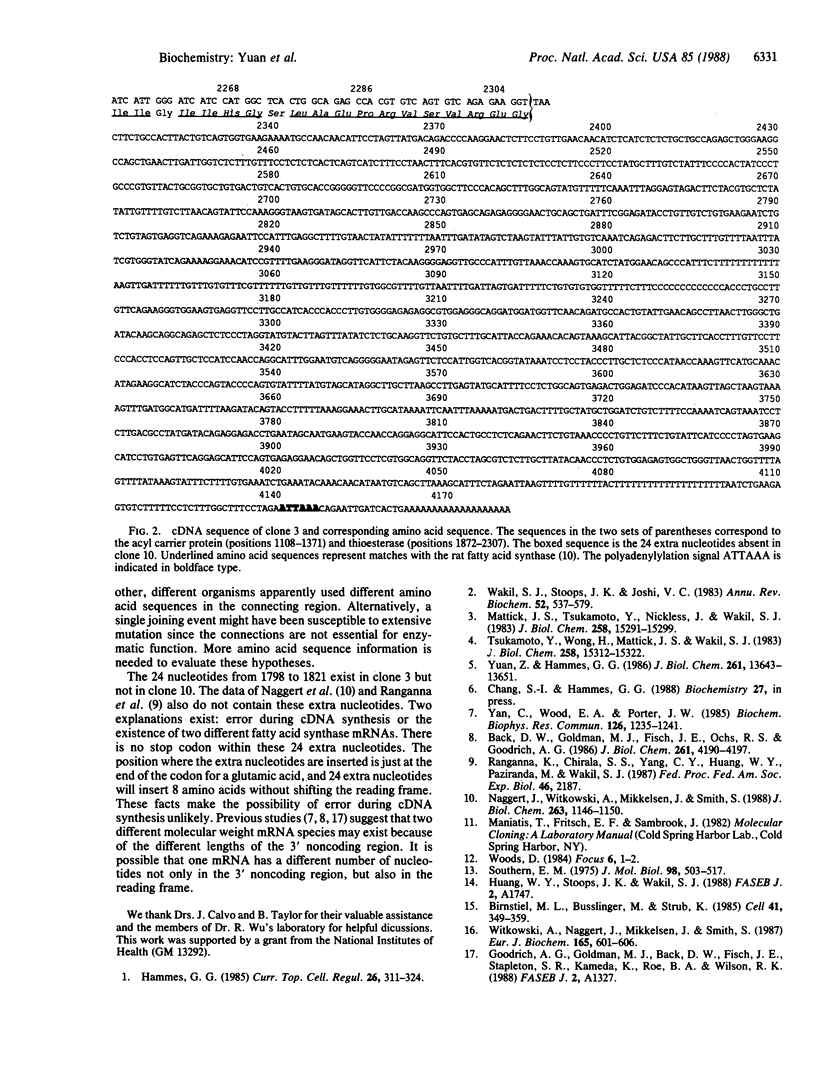
The cDNA corresponding to 4.18 kilobases (kb) of the mRNA of chicken liver fatty acid synthase has been cloned and sequenced. The cDNA corresponds to the 3' end of the mRNA and consists of a 1.87-kb noncoding tail and a 2.31-kb region encoding 769 amino acids of the C terminus of the enzyme. The thioesterase at the C terminus, preceded by the acyl carrier protein, can be identified from known amino acid sequences. However, the identity of the enzymes N terminal to the acyl carrier protein could not be ascertained. The partial amino acid sequence of the chicken liver fatty acid synthase shows greater than 70% similarity with the rat mammary gland enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Back D. W., Goldman M. J., Fisch J. E., Ochs R. S., Goodridge A. G. The fatty acid synthase gene in avian liver. Two mRNAs are expressed and regulated in parallel by feeding, primarily at the level of transcription. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4190–4197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammes G. G. Fatty acid synthase: elementary steps in catalysis and regulation. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1985;26:311–324. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152826-3.50030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattick J. S., Tsukamoto Y., Nickless J., Wakil S. J. The architecture of the animal fatty acid synthetase. I. Proteolytic dissection and peptide mapping. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15291–15299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naggert J., Witkowski A., Mikkelsen J., Smith S. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding the thioesterase domain of the rat fatty acid synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1146–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto Y., Wong H., Mattick J. S., Wakil S. J. The architecture of the animal fatty acid synthetase complex. IV. Mapping of active centers and model for the mechanism of action. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15312–15322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakil S. J., Stoops J. K., Joshi V. C. Fatty acid synthesis and its regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:537–579. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkowski A., Naggert J., Mikkelsen J., Smith S. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding the acyl carrier protein and its flanking domains in the mammalian fatty acid synthetase. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 15;165(3):601–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan C., Wood E. A., Porter J. W. Characterization of fatty acid synthetase cDNA clone and its mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 15;126(3):1235–1241. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90318-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Z. Y., Hammes G. G. Fluorescence studies of chicken liver fatty acid synthase. Segmental flexibility and distance measurements. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13643–13651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



