Abstract
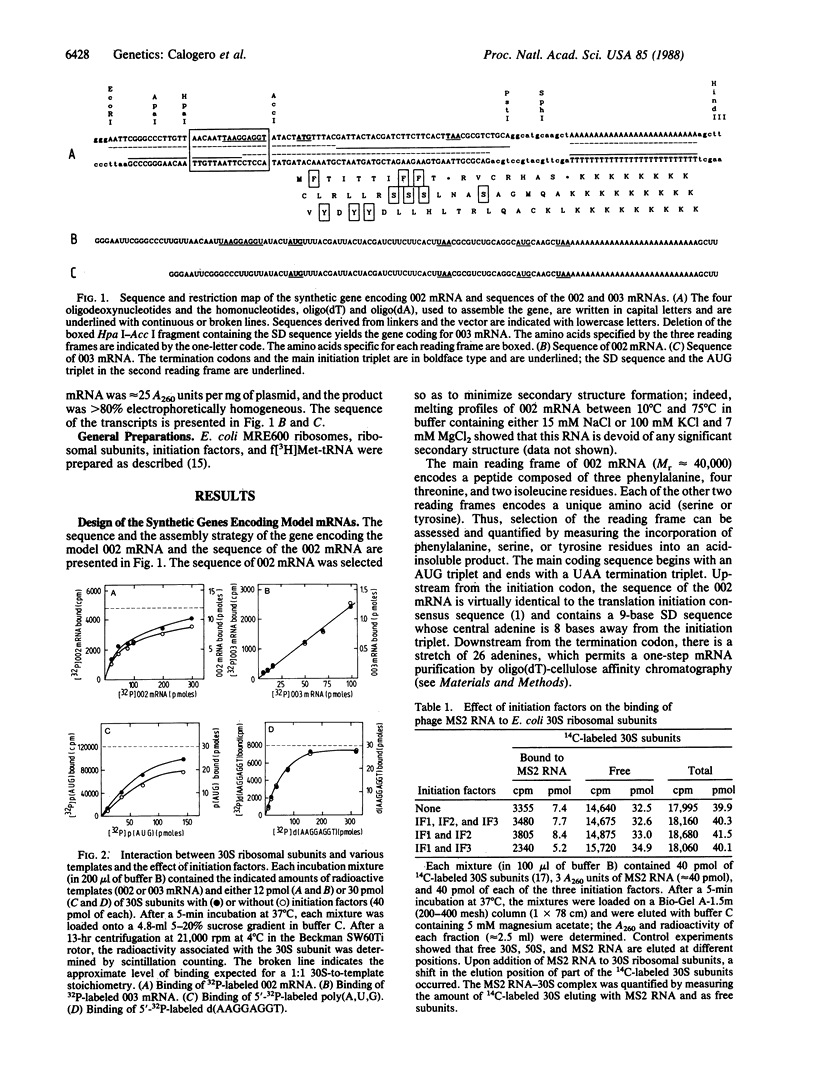
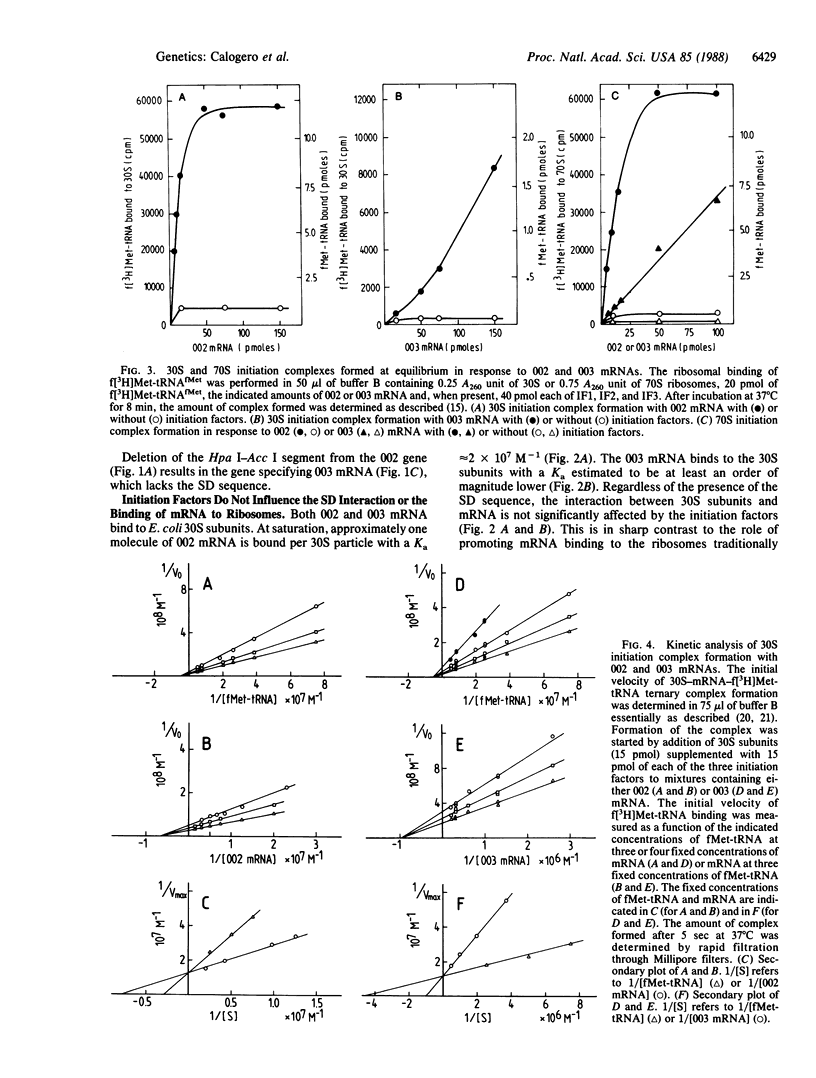
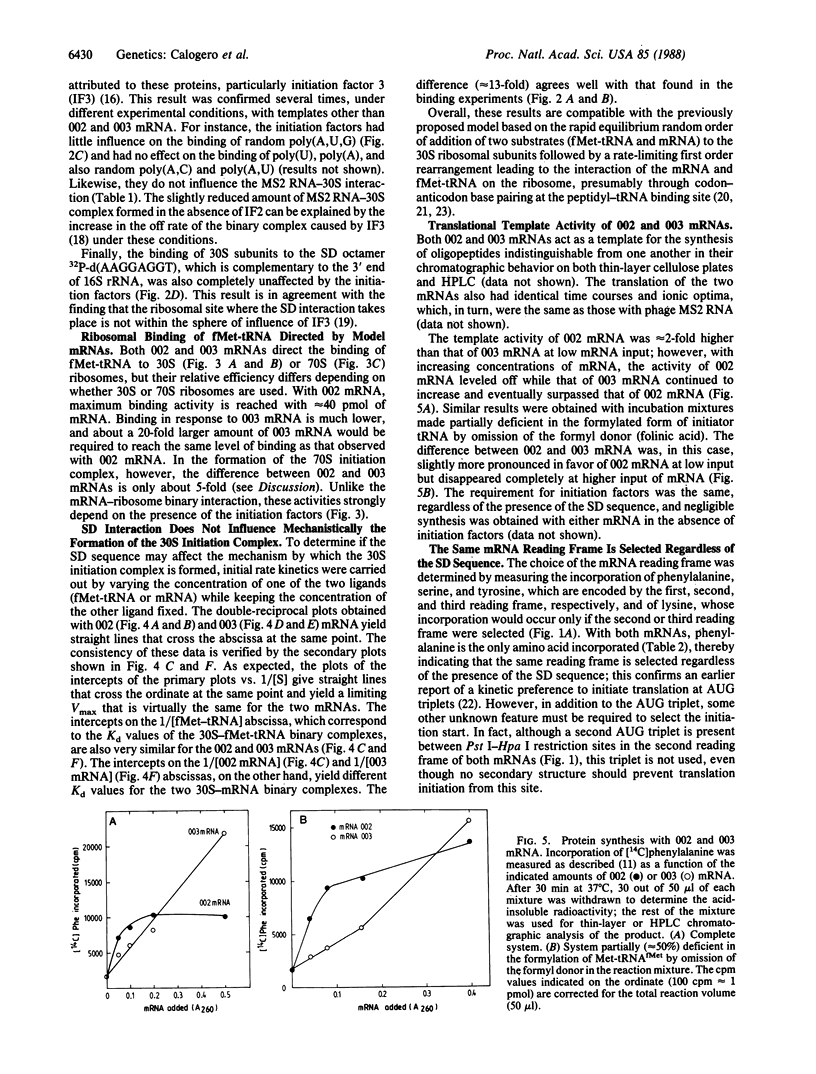
Two genes specifying model mRNAs of minimal size and coding capacity, with or without the Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence, were assembled, cloned, and transcribed in high yields. These mRNAs, as well as synthetic polynucleotides, phage MS2 RNA, and a deoxyoctanucleotide complementary to the 3' end of 16S rRNA were used to study the mechanism of translation initiation in vitro. Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunits interact with all these nucleic acids, albeit with different affinities; the affinity for the mRNA with the SD sequence (Ka approximately 2 x 10(7) M-1) is more than an order of magnitude higher than that for the mRNA lacking this sequence. The initiation factors are equally required, regardless of the presence of the SD sequence, for 30S and 70S initiation complex formation and for mRNA translation, but the initiation factors do not affect the SD interaction or the binding of the mRNAs to the ribosomes. The SD interaction is also mechanistically irrelevant for 30S initiation complex formation and is not essential for translation in vitro or for the selection of the mRNA reading frame. It is suggested that the function of the SD interaction is to ensure a high concentration of the initiation triplet near the ribosomal peptidyl-tRNA binding site, whereas the selection of the translational start is achieved kinetically, under the influence of the initiation factors, during decoding of the initiator tRNA.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. C., Doty P. Kinetic preference for initiation of protein synthesis at AUG codons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 11;228(3):746–748. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90740-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calogero R. A., Pon C. L., Gualerzi C. O. Chemical synthesis and in vivo hyperexpression of a modular gene coding for Escherichia coli translational initiation factor IF1. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):63–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00330423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonaco M. A., Pon C. L., Pawlik R. T., Calogero R., Gualerzi C. O. Relationship between size of mRNA ribosomal binding site and initiation factor function. Biochimie. 1987 Sep;69(9):957–963. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90229-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gren E. J. Recognition of messenger RNA during translational initiation in Escherichia coli. Biochimie. 1984 Jan;66(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(84)90188-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualerzi C., Pon C. L. Radioactive chemical labeling of ribosomal proteins and translational factors in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:782–795. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualerzi C., Risuleo G., Pon C. L. Initial rate kinetic analysis of the mechanism of initiation complex formation and the role of initiation factor IF-3. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 19;16(8):1684–1689. doi: 10.1021/bi00627a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualerzi C., Risuleo G., Pon C. Mechanism of the spontaneous and initiation factor 3-induced dissociation of 30 S.aminoacyl-tRNA.polynucleotide ternary complexes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):44–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui A., de Boer H. A. Specialized ribosome system: preferential translation of a single mRNA species by a subpopulation of mutated ribosomes in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4762–4766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob W. F., Santer M., Dahlberg A. E. A single base change in the Shine-Dalgarno region of 16S rRNA of Escherichia coli affects translation of many proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4757–4761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H., Kutter E., Nakanishi M. A restriction map of the bacteriophage T4 genome. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(2):421–435. doi: 10.1007/BF00425473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa H., Gualerzi C. Chemical modification in situ of Escherichia coli 30 S ribosomal proteins by the site-specific reagent pyridoxal phosphate. Inactivation of the aminoacyl-tRNA and mRNA binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):150–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa H., Herrlich P., Gualerzi C. In vitro template activity of 0.3 mRNA from wild type and initiation mutants of bacteriophage T7. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(1):53–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00334091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pon C. L., Gualerzi C. O. Mechanism of protein biosynthesis in prokaryotic cells. Effect of initiation factor IF1 on the initial rate of 30 S initiation complex formation. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 1;175(2):203–207. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80737-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G. F., Walkinshaw M. D., Arnott S., Morré D. J. The ribosome binding sites recognized by E. coli ribosomes have regions with signal character in both the leader and protein coding segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3895–3907. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintermeyer W., Gualerzi C. Effect of Escherichia coli initiation factors on the kinetics of N-Acphe-tRNAPhe binding to 30S ribosomal subunits. A fluorescence stopped-flow study. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):690–694. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



