Abstract
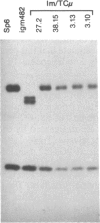
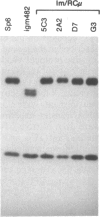
We report here the occurrence of homologous recombination between transferred and chromosomal immunoglobulin genes. Specifically, we have corrected a chromosomal immunoglobulin gene mutation by transferring pSV2neo vectors encoding the constant region of the immunoglobulin mu heavy chain to mutant hybridoma cells that bear a 2-base-pair deletion in the third constant region exon of their chromosomal mu gene. After DNA transfer, we detected G418-resistant transformants that produce normal IgM. Analysis of the DNA structure of the mu gene in these transformants indicates that in four of five cases the mu gene has been restored as a result of the integration of a single copy of the transfer vector by a reciprocal homologous recombination event; the fifth case seems to have resulted from gene conversion or double crossover. These results suggest that this technology might be adapted for mapping immunoglobulin gene mutations by marker rescue and for more convenient engineering of specifically altered immunoglobulin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker M. D., Wu G. E., Toone W. M., Murialdo H., Davis A. C., Shulman M. J. A region of the immunoglobulin-mu heavy chain necessary for forming pentameric IgM. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1724–1728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann B., Potash M. J., Köhler G. Consequences of frameshift mutations at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus of the mouse. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):351–359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilofsky H. S., Burks C., Fickett J. W., Goad W. B., Lewitter F. I., Rindone W. P., Swindell C. D., Tung C. S. The GenBank genetic sequence databank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):1–4. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calame K. L. Mechanisms that regulate immunoglobulin gene expression. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:159–195. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T., Gregg R. G., Maeda N., Hooper M. L., Melton D. W., Thompson S., Smithies O. Targetted correction of a mutant HPRT gene in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):576–578. doi: 10.1038/330576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K., Henry C., Nordin A. A., Fuji H., Koros A. M., Lefkovits I. Plaque forming cells: methodology and theory. Transplant Rev. 1974;18:130–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb01588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Potash M. J., Lehrach H., Shulman M. J. Deletions in immunoglobulin mu chains. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):555–563. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01208.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leptin M., Potash M. J., Grützmann R., Heusser C., Shulman M., Köhler G., Melchers F. Monoclonal antibodies specific for murine IgM I. Characterization of antigenic determinants on the four constant domains of the mu heavy chain. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jun;14(6):534–542. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi A., Hawley R. G., Hawley T., Shulman M. J., Traunecker A., Köhler G., Hozumi N. Functional immunoglobulin M production after transfection of cloned immunoglobulin heavy and light chain genes into lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6351–6355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M. J., Hawley R. G., Ochi A., Baczynsky W. O., Collins C., Pennell N., Potash M. J., Köhler G., Hozumi N. Biochemical genetics of the mouse IgM system. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;62(4):217–224. doi: 10.1139/o84-031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M. J., Heusser C., Filkin C., Köhler G. Mutations affecting the structure and function of immunoglobulin M. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1033–1043. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M. J., Pennell N., Collins C., Hozumi N. Activation of complement by immunoglobulin M is impaired by the substitution serine-406----asparagine in the immunoglobulin mu heavy chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7678–7682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gregg R. G., Boggs S. S., Koralewski M. A., Kucherlapati R. S. Insertion of DNA sequences into the human chromosomal beta-globin locus by homologous recombination. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):230–234. doi: 10.1038/317230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song K. Y., Schwartz F., Maeda N., Smithies O., Kucherlapati R. Accurate modification of a chromosomal plasmid by homologous recombination in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6820–6824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Introduction of homologous DNA sequences into mammalian cells induces mutations in the cognate gene. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):34–38. doi: 10.1038/324034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Folger K. R., Capecchi M. R. High frequency targeting of genes to specific sites in the mammalian genome. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble W. S., Baker M. D., Boulianne G. L., Murialdo H., Hozumi N., Shulman M. J. Analysis of hybridoma mutants defective in synthesis of immunoglobulin M. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Sep;12(5):467–477. doi: 10.1007/BF01539918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]