Abstract
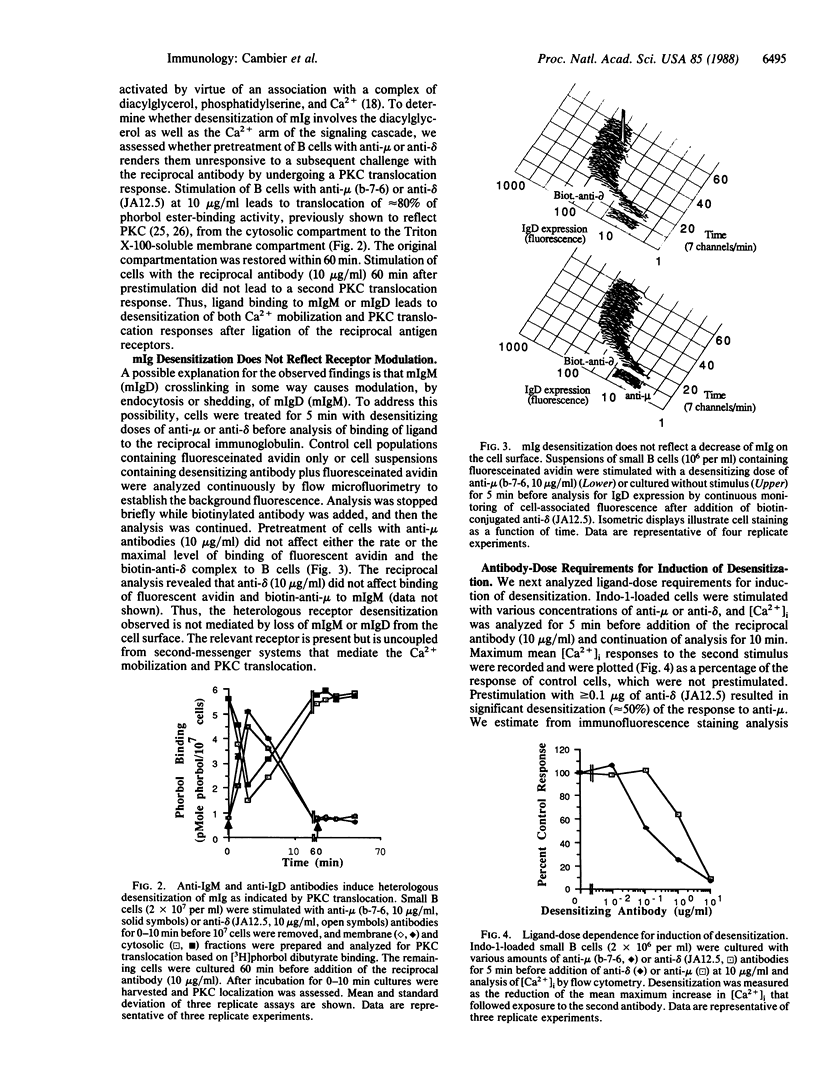
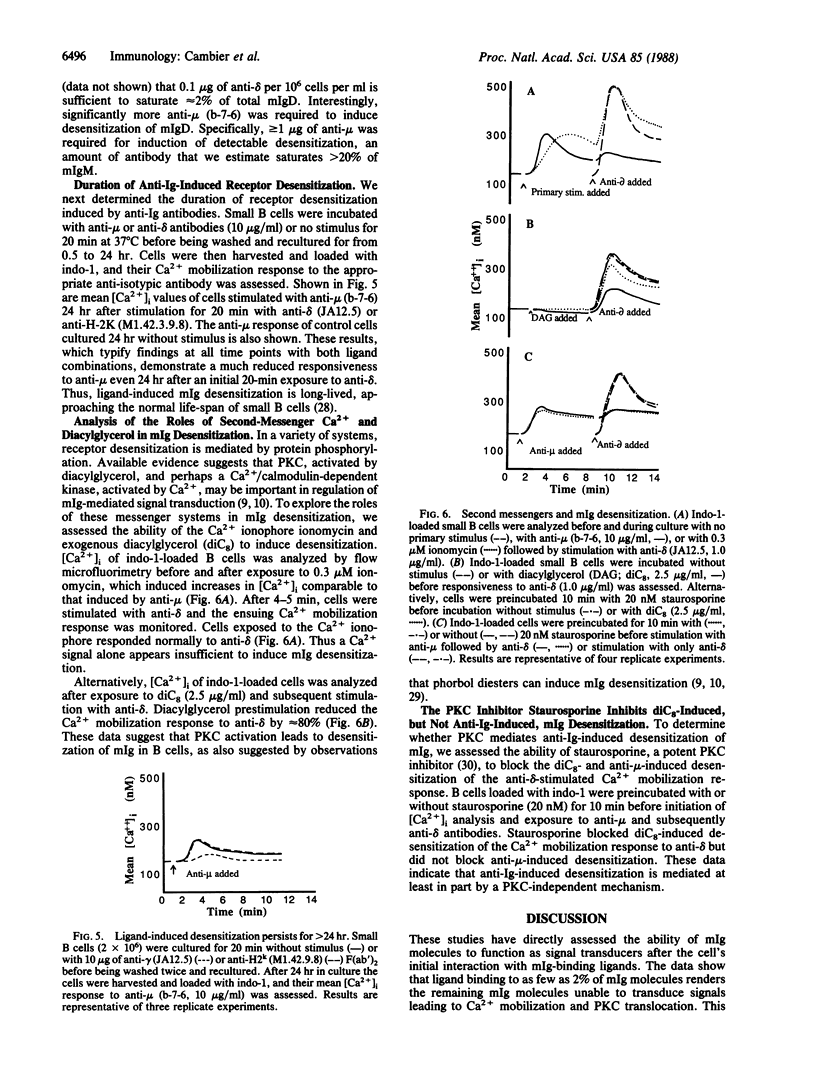
Binding of ligand to B-cell membrane immunoglobulin (mIg) can lead to activation of a number of distinct biologic responses, including altered expression of genes encoding c-fos, c-myc, and Ia, as well as proliferation and immunologic tolerance. Tolerance could reflect a functional uncoupling of receptors from systems that generate intracellular second messengers (i.e., receptor desensitization). To better understand the molecular basis of immune regulation, we examined the ability of mIg to function as a signal transducer after the cell's initial contact with mIg-binding ligand. The results show that ligand binding to as little as 2-10% of mIgM or mIgD renders the cell unresponsive to ligand binding to the reciprocal isotype as judged by Ca2+ mobilization and protein kinase C translocation responses. This heterologous receptor desensitization lasts longer than 24 hr and does not reflect loss of receptor from the cell surface. Studies with the calcium ionophore ionomycin, 1,2-dioctanoyl-sn-glycerol, and the protein kinase inhibitor staurosporine indicate that both protein kinase C-dependent and protein kinase C-independent (staurosporine-insensitive) mechanisms mediate heterologous desensitization after mIg crosslinking.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Meade C. J., Turner G. A., Klaus G. G. B lymphocyte receptors and polyphosphoinositide degradation. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Rigley K. P., Klaus G. G. Cross-linking of surface immunoglobulin on B lymphocytes induces both intracellular Ca2+ release and Ca2+ influx: analysis with indo-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):500–506. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Sha'afi R. I., Unanue E. R. Crosslinking by ligands to surface immunoglobulin triggers mobilization of intracellular 45Ca2+ in B lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):755–766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Heusser C. H., Julius M. H. Abortive activation of B lymphocytes by monoclonal anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3140–3146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Newell M. K., Justement L. B., McGuire J. C., Leach K. L., Chen Z. Z. Ia binding ligands and cAMP stimulate nuclear translocation of PKC in B lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):629–632. doi: 10.1038/327629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Ransom J. T. Molecular mechanisms of transmembrane signaling in B lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:175–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Z., Coggeshall K. M., Cambier J. C. Translocation of protein kinase C during membrane immunoglobulin-mediated transmembrane signaling in B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2300–2304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Raveche E. S., Paul W. E. Separate control of B lymphocyte early activation and proliferation in response to anti-IgM antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):87–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas A. A., Rocha B., Coutinho A. A. Lymphocyte population kinetics in the mouse. Immunol Rev. 1986 Jun;91:5–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Jakway J. P., DeFranco A. L. Involvement of a guanine-nucleotide-binding component in membrane IgM-stimulated phosphoinositide breakdown. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3604–3613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K., Haaijman J., Herzenberg L. A. B-cell subpopulations identified by two-colour fluorescence analysis. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):589–591. doi: 10.1038/297589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havran W. L., DiGiusto D. L., Cambier J. C. mIgM:mIgD ratios on B cells: mean mIgD expression exceeds mIgM by 10-fold on most splenic B cells. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1712–1716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornbeck P., Paul W. E. Anti-immunoglobulin and phorbol ester induce phosphorylation of proteins associated with the plasma membrane and cytoskeleton in murine B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14817–14824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Heusser C. H., Hartmann K. U. Induction of resting B cells to DNA synthesis by soluble monoclonal anti-immunoglobulin. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Aug;14(8):753–757. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., O'Garra A., Bijsterbosch M. K., Holman M. Activation and proliferation signals in mouse B cells. VIII. Induction of DNA synthesis in B cells by a combination of calcium ionophores and phorbol myristate acetate. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jan;16(1):92–97. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuguchi J., Beaven M. A., Li J. H., Paul W. E. Phorbol myristate acetate inhibits anti-IgM-mediated signaling in resting B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuguchi J., Ji Y. Y., Nakabayaschi H., Huang K. P., Beaven M. A., Chused T., Paul W. E. Protein kinase C activation blocks anti-IgM-mediated signaling BAL17 B lymphoma cells. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1054–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Seghal E., Kung J., Finkelman F. D. Increased expression of I-region-associated antigen (Ia) on B cells after cross-linking of surface immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):881–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Cellular mechanisms of immunologic tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:33–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike B. L., Nossal G. J. Requirement for persistent extracellular antigen in cultures of antigen-binding B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):568–571. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch P. S., June C. H., Grossmann A., Ledbetter J. A. Heterogeneity among T cells in intracellular free calcium responses after mitogen stimulation with PHA or anti-CD3. Simultaneous use of indo-1 and immunofluorescence with flow cytometry. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):952–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom J. T., Harris L. K., Cambier J. C. Anti-Ig induces release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, which mediates mobilization of intracellular Ca++ stores in B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):708–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe M. J., Julius M. H. H-2-restricted T-B cell interactions involved in polyspecific B cell responses mediated by soluble antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Aug;12(8):634–641. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Molecular mechanisms of receptor desensitization using the beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase system as a model. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):124–129. doi: 10.1038/317124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow E. C., Fetherston J. D., Zimmer S. Induction of the c-myc protooncogene after antigen binding to hapten-specific B cells. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):944–949. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Filburn C. R. Affinity chromatography of protein kinase C-phorbol ester receptor on polyacrylamide-immobilized phosphatidylserine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12311–12314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against mouse macrophage and lymphocyte Fc receptors. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):580–596. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Hardy K., Manger B., Terhorst C., Stobo J. The role of the T3/antigen receptor complex in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:593–619. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson H. A., Greenblatt D., Taylor C. W., Putney J. W., Tsien R. Y., Finkelman F. D., Chused T. M. The B lymphocyte calcium response to anti-Ig is diminished by membrane immunoglobulin cross-linkage to the Fc gamma receptor. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1712–1718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


