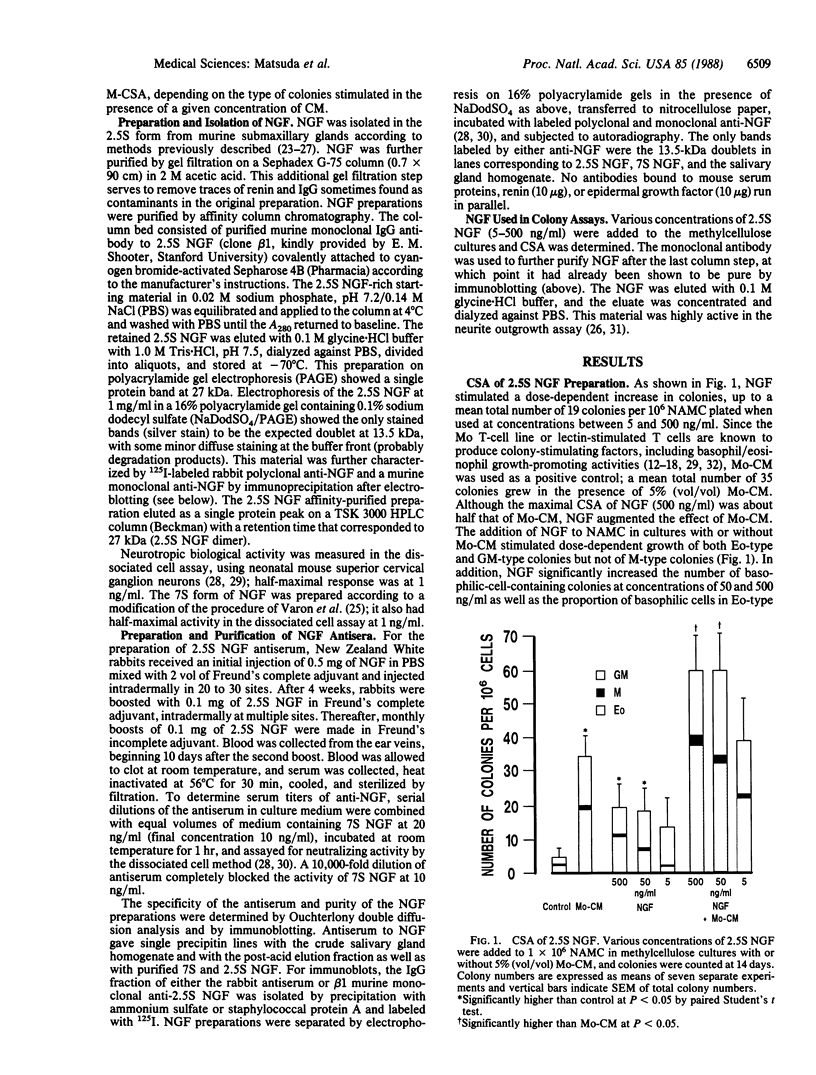
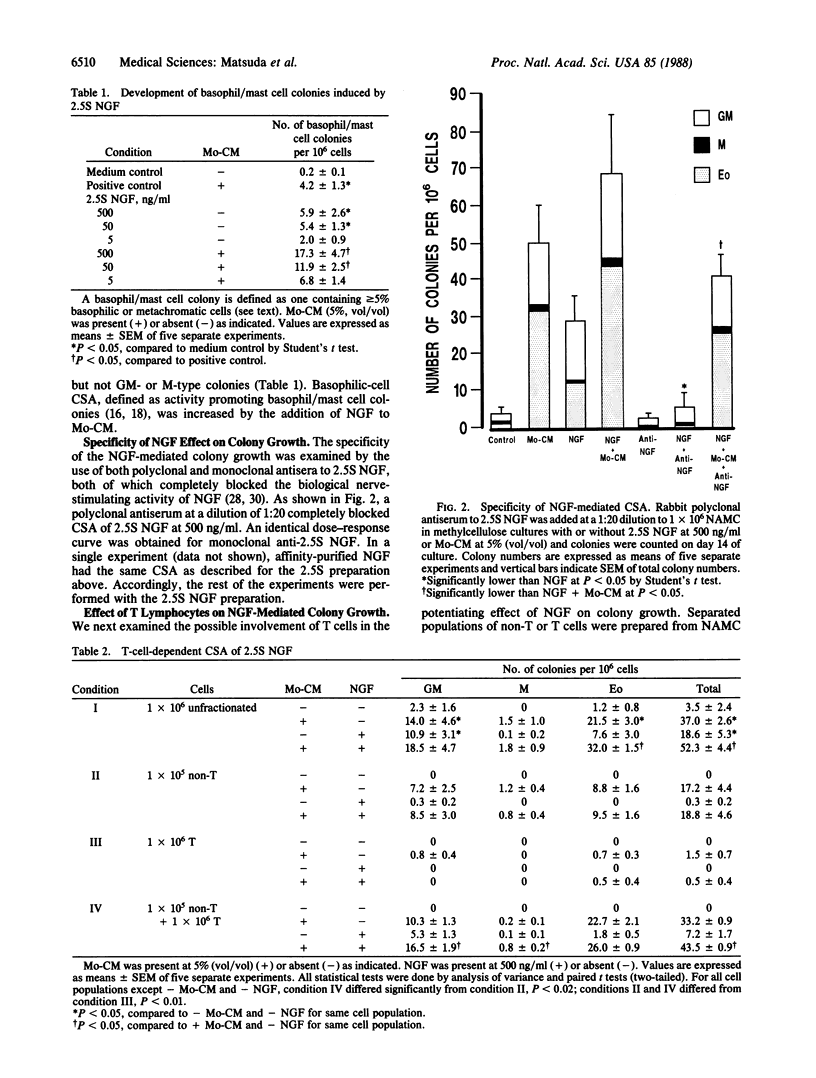
Abstract
Nerve growth factor (NGF) is a neurotropic polypeptide necessary for the survival and growth of some central neurons, as well as sensory afferent and sympathetic neurons. Much is now known of the structural and functional characteristics of NGF, whose gene has recently been cloned. Since it is synthesized in largest amounts by the male mouse submandibular gland, its role exclusively in nerve growth is questionable. NGF also causes histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells in vitro, and we have shown elsewhere that it causes significant, dose-dependent, generalized mast cell proliferation in the rat in vivo when administered neonatally. Our experiments now indicate that NGF causes a significant stimulation of granulocyte colonies grown from human peripheral blood in standard hemopoietic methylcellulose assays. Further, NGF appears to act in a relatively selective fashion to induce the differentiation of eosinophils and basophils/mast cells. Depletion experiments show that the NGF effect may be T-cell dependent and that NGF augments the colony-stimulating effect of supernatants from the leukemic T-cell (Mo) line. The hemopoietic activity of NGF is blocked by polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies to NGF. We conclude that NGF may indirectly act as a local growth factor in tissues other than those of the nervous system by causing T cells to synthesize or secrete molecules with colony-stimulating activity. In view of the synthesis of NGF in tissue injury, the involvement of basophils/mast cells and eosinophils in allergic and other inflammatory processes, and the association of mast cells with fibrosis and tissue repair, we postulate that NGF plays an important biological role in a variety of repair processes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloe L., Levi-Montalcini R. Mast cells increase in tissues of neonatal rats injected with the nerve growth factor. Brain Res. 1977 Sep 16;133(2):358–366. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90772-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby G. C., Jr, Dinarello C. A., Wallace P., Wagner C., Hefeneider S., McCall E. Interleukin 1 stimulates granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating activity release by vascular endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1316–1323. doi: 10.1172/JCI112717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby G. C., Jr, McCall E., Bergstrom K. A., Burger D. A monokine regulates colony-stimulating activity production by vascular endothelial cells. Blood. 1983 Sep;62(3):663–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby G. C., Jr, McCall E., Layman D. L. Regulation of colony-stimulating activity production. Interactions of fibroblasts, mononuclear phagocytes, and lactoferrin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):340–344. doi: 10.1172/JCI110774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks B. E. Nerve growth factor--an enigma still? Biochem Soc Trans. 1984 Apr;12(2):173–176. doi: 10.1042/bst0120173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienenstock J., Tomioka M., Matsuda H., Stead R. H., Quinonez G., Simon G. T., Coughlin M. D., Denburg J. A. The role of mast cells in inflammatory processes: evidence for nerve/mast cell interactions. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;82(3-4):238–243. doi: 10.1159/000234197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claman H. N., Jaffee B. D., Huff J. C., Clark R. A. Chronic graft-versus-host disease as a model for scleroderma. II. Mast cell depletion with deposition of immunoglobulins in the skin and fibrosis. Cell Immunol. 1985 Aug;94(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin M. D., Collins M. B. Nerve growth factor-independent development of embryonic mouse sympathetic neurons in dissociated cell culture. Dev Biol. 1985 Aug;110(2):392–401. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90098-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin M. D., Kessler J. A. Antiserum to a new neuronal growth factor: effects on neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci Res. 1982;8(2-3):289–302. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490080219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denburg J. A., Davison M., Bienenstock J. Basophil production. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):390–399. doi: 10.1172/JCI109682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denburg J. A., Otsuka H., Ohnisi M., Ruhno J., Bienenstock J., Dolovich J. Contribution of basophil/mast cell and eosinophil growth and differentiation to the allergic tissue inflammatory response. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;82(3-4):321–326. doi: 10.1159/000234217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denburg J. A., Richardson M., Telizyn S., Bienenstock J. Basophil/mast cell precursors in human peripheral blood. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):775–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denburg J. A., Telizyn S., Belda A., Dolovich J., Bienenstock J. Increased numbers of circulating basophil progenitors in atopic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985 Sep;76(3):466–472. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(85)90728-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denburg J. A., Telizyn S., Messner H., Lim B., Jamal N., Ackerman S. J., Gleich G. J., Bienenstock J. Heterogeneity of human peripheral blood eosinophil-type colonies: evidence for a common basophil-eosinophil progenitor. Blood. 1985 Aug;66(2):312–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C., Weisbart R. H., Kaufman S. E., Clark S. C., Hewick R. M., Wong G. G., Golde D. W. Purified human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: direct action on neutrophils. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1339–1342. doi: 10.1126/science.6390681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto T., Befus D., Low R., Bienenstock J. Mast cell heterogeneity and hyperplasia in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis of rats. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Nov;130(5):797–802. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.5.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudat F., Laubscher A., Otten U., Pletscher A. Shape changes induced by biologically active peptides and nerve growth factor in blood platelets of rabbits. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;74(3):533–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Oroszlan S., Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Fitch F., Prystowsky M. B., Goldwasser E., Schrader J. W., Palaszynski E. Biologic properties of homogeneous interleukin 3. I. Demonstration of WEHI-3 growth factor activity, mast cell growth factor activity, p cell-stimulating factor activity, colony-stimulating factor activity, and histamine-producing cell-stimulating factor activity. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Guilbert L. J., Weyman C. Complete replacement of serum in primary cultures of erythropoietin-dependent red cell precursors (CFU-E) by albumin, transferrin, iron, unsaturated fatty acid, lecithin and cholesterol. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Mar;126(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90476-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. E., Clark C. An improved rosetting assay for detection of human T lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Jul;5(2):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushansky K., Lin N., Adamson J. W. Interleukin 1 stimulates fibroblasts to synthesize granulocyte-macrophage and granulocyte colony-stimulating factors. Mechanism for the hematopoietic response to inflammation. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):92–97. doi: 10.1172/JCI113316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiernan J. A. A study of chemically induced acute inflammation in the skin of the rat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1977 Apr;62(2):151–161. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1977.sp002385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Gasson J., Ranyard J., Souza L., Shepard M., Munker R. Recombinant human TNF alpha stimulates production of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Holzer P. Substance P as neurogenic mediator of antidromic vasodilation and neurogenic plasma extravasation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;310(2):175–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00500282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor: thirty-five years later. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1145–1154. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02347.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li A. K., Koroly M. J., Schattenkerk M. E., Malt R. A., Young M. Nerve growth factor: acceleration of the rate of wound healing in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4379–4381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd G., Green F. H., Fox H., Mani V., Turnberg L. A. Mast cells and immunoglobulin E in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1975 Nov;16(11):861–865. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.11.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murase T., Hotta T., Saito H., Ohno R. Effect of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor on the colony growth of human leukemia progenitor cells and normal hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):467–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F., Cantor H. Inducer T lymphocytes synthesize a factor that stimulates proliferation of cloned mast cells. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):332–334. doi: 10.1038/291332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. G., Chess L., Hillman D. G., Clarke B., Breard J., Merler E., Housman D. E. Human erythroid burst-forming unit: T-cell requirement for proliferation in vitro. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):324–339. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi M., Ruhno J., Dolovich J., Denburg J. A. Allergic rhinitis nasal mucosal conditioned medium stimulates growth and differentiation of basophil/mast cell and eosinophil progenitors from atopic blood. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988 Jun;81(6):1149–1154. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(88)90883-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oster W., Lindemann A., Horn S., Mertelsmann R., Herrmann F. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha but not TNF-beta induces secretion of colony stimulating factor for macrophages (CSF-1) by human monocytes. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1700–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka H., Dolovich J., Richardson M., Bienenstock J., Denburg J. A. Metachromatic cell progenitors and specific growth and differentiation factors in human nasal mucosa and polyps. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Sep;136(3):710–717. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.3.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. F., Jr, Rothenberg M. E., Silberstein D. S., Gasson J. C., Stevens R. L., Austen K. F., Soberman R. J. Regulation of human eosinophil viability, density, and function by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor in the presence of 3T3 fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):129–141. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L., Thompson H. L. Some characteristics of histamine secretion from rat peritoneal mast cells stimulated with nerve growth factor. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:379–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S., Dierich M. P., Reisfeld R. A. Enhancement of sheep red blood cell human lymphocyte rosette formation by the sulfhydryl compound 2-amino ethylisothiouronium bromide. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Jan;3(3):324–333. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg M. E., Owen W. F., Jr, Silberstein D. S., Soberman R. J., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Eosinophils cocultured with endothelial cells have increased survival and functional properties. Science. 1987 Aug 7;237(4815):645–647. doi: 10.1126/science.3110954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Warren D. J., Strath M. Identification of a lymphokine that stimulates eosinophil differentiation in vitro. Its relationship to interleukin 3, and functional properties of eosinophils produced in cultures. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):60–74. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W. In in vitro production and cloning of the P cell, a bone marrow-derived null cell that expresses H-2 and Ia-antigens, has mast cell-like granules, and is regulated by a factor released by activated T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):452–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson A. R. Mast cells in areas of experimental bone resorption and remodelling. Br J Exp Pathol. 1969 Feb;50(1):17–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Peptide growth factors and inflammation, tissue repair, and cancer. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):329–332. doi: 10.1172/JCI112580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stach R. W., Wagner B. J., Stach B. M. A more rapid method for the isolation of the 7S nerve growth factor complex. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90505-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisz A., Scicchitano R., Stead R., Matsuda H., Tomioka M., Denburg J., Bienenstock J. Neuropeptides and immunity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Dec;136(6 Pt 2):S48–S51. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.6_Pt_2.S48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead R. H., Bienenstock J., Stanisz A. M. Neuropeptide regulation of mucosal immunity. Immunol Rev. 1987 Dec;100:333–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead R. H., Tomioka M., Quinonez G., Simon G. T., Felten S. Y., Bienenstock J. Intestinal mucosal mast cells in normal and nematode-infected rat intestines are in intimate contact with peptidergic nerves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2975–2979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadokoro K., Stadler B. M., De Weck A. L. Factor-dependent in vitro growth of human normal bone marrow-derived basophil-like cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):857–871. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanno Y., Bienenstock J., Richardson M., Lee T. D., Befus A. D., Denburg J. A. Reciprocal regulation of human basophil and eosinophil differentiation by separate T-cell-derived factors. Exp Hematol. 1987 Jan;15(1):24–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Edgar D. Neurotrophic factors. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):238–242. doi: 10.1126/science.2409599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe L. W., Stach R. W., Hashim G. A., Marchetti D., Perez-Polo J. R. Receptors for nerve growth factor on rat spleen mononuclear cells. J Neurosci Res. 1987;17(2):128–134. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490170206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon S., Nomura J., Shooter E. M. The isolation of the mouse nerve growth factor protein in a high molecular weight form. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):2202–2209. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M., Oger J., Blanchard M. H., Asdourian H., Amos H., Arnason B. G. Secretion of a nerve growth factor by primary chick fibroblast cultures. Science. 1975 Jan 31;187(4174):361–362. doi: 10.1126/science.1167427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



