Abstract
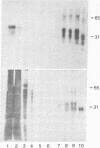
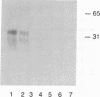
Prions are unusual infectious pathogens causing scrapie of sheep and goats as well as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease of humans. Biochemical and genetic studies contend that the scrapie isoform of the prion protein (PrPSc) is a major component of the prion. Limited proteinase K digestion of PrPSc produced a protein of 27-30 kDa. After dispersion of brain microsomes isolated from scrapie-infected hamsters into detergent-lipid-protein complexes, copurification of PrPSc and scrapie infectivity was obtained with scrapie prion protein of 27-30 kDa monoclonal antibody-affinity columns. PrPSc was enriched approximately equal to 5700-fold with respect to total brain protein, whereas scrapie prion infectivity was enriched approximately equal to 4000-fold. The ratio of prion titer to PrPSc remained constant throughout purification. Heterologous monoclonal antibody columns failed to bind either PrPSc or scrapie infectivity. Polyclonal rabbit prion protein antiserum raised against NaDodSO4/PAGE-purified scrapie prion protein of 27-30 kDa reduced scrapie infectivity dispersed into detergent-lipid-protein complexes by a factor of 100. These results represent direct immunologic and chromatographic demonstrations of a relationship between PrPSc and prion infectivity as well as providing additional support for the contention that PrPSc is a major component of the infectious scrapie particle. That PrPSc is a host-encoded protein is an important feature distinguishing prions from viruses.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E. Monoclonal antibodies to the glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. Identification of the transporter as a Mr = 55,000 protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8668–8675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry R. A., Prusiner S. B. Monoclonal antibodies to the cellular and scrapie prion proteins. J Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;154(3):518–521. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barzilai A., Spanier R., Rahamimoff H. Immunological identification of the synaptic plasma membrane Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10315–10320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Oesch B., Scott M., Westaway D., Wälchli M., Groth D. F., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B., Weissmann C. Scrapie and cellular PrP isoforms are encoded by the same chromosomal gene. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90662-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman J. M., Kingsbury D. T., McKinley M. P., Bendheim P. E., Prusiner S. B. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease prion proteins in human brains. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 10;312(2):73–78. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501103120202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman J. M., Prusiner S. B., Tateishi J., Kingsbury D. T. Immunoblotting of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease prion proteins: host species-specific epitopes. Ann Neurol. 1987 Jun;21(6):589–595. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Identification of a protein that purifies with the scrapie prion. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1309–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.6815801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Molecular characteristics of the major scrapie prion protein. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):5898–5906. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braig H. R., Diringer H. Scrapie: concept of a virus-induced amyloidosis of the brain. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2309–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03931.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P., Coker-Vann M., Pomeroy K., Franko M., Asher D. M., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease by Western blot identification of marker protein in human brain tissue. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 27;314(9):547–551. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602273140904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler D. A., Scott M. R., Bockman J. M., Borchelt D. R., Taraboulos A., Hsiao K. K., Kingsbury D. T., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie-infected murine neuroblastoma cells produce protease-resistant prion proteins. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1558–1564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1558-1564.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson G. A., Kingsbury D. T., Goodman P. A., Coleman S., Marshall S. T., DeArmond S., Westaway D., Prusiner S. B. Linkage of prion protein and scrapie incubation time genes. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90875-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Race R., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Bloom M., Lechner D., Bergstrom S., Robbins K., Mayer L., Keith J. M. Identification of scrapie prion protein-specific mRNA in scrapie-infected and uninfected brain. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):331–333. doi: 10.1038/315331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Gelderblom H., Hilmert H., Ozel M., Edelbluth C., Kimberlin R. H. Scrapie infectivity, fibrils and low molecular weight protein. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):476–478. doi: 10.1038/306476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabizon R., McKinley M. P., Groth D. F., Kenaga L., Prusiner S. B. Properties of scrapie prion protein liposomes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4950–4955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabizon R., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Purified prion proteins and scrapie infectivity copartition into liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4017–4021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Sklaviadis T., Manuelidis E. E. Evidence suggesting that PrP is not the infectious agent in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):341–347. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh R. F., Kimberlin R. H. Comparison of scrapie and transmissible mink encephalopathy in hamsters. II. Clinical signs, pathology, and pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):104–110. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. P., Bolton D. C., Prusiner S. B. A protease-resistant protein is a structural component of the scrapie prion. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Bolton D. C., Groth D. F., Bowman K. A., Cochran S. P., McKinley M. P. Further purification and characterization of scrapie prions. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6942–6950. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Cochran S. P., Groth D. F., Downey D. E., Bowman K. A., Martinez H. M. Measurement of the scrapie agent using an incubation time interval assay. Ann Neurol. 1982 Apr;11(4):353–358. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D. F., Cochran S. P., Masiarz F. R., McKinley M. P., Martinez H. M. Molecular properties, partial purification, and assay by incubation period measurements of the hamster scrapie agent. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4883–4891. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D. F., McKinley M. P., Cochran S. P., Bowman K. A., Kasper K. C. Thiocyanate and hydroxyl ions inactivate the scrapie agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4606–4610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Hadlow W. J., Garfin D. E., Cochran S. P., Baringer J. R., Race R. E., Eklund C. M. Partial purification and evidence for multiple molecular forms of the scrapie agent. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):4993–4999. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Groth D. F., Glenner G. G. Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rods. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):136–144. doi: 10.1126/science.6801762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Prions and neurodegenerative diseases. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 17;317(25):1571–1581. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712173172505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. W., Lofthouse R., Brown R., Crow T. J., Barry R. A., Prusiner S. B. Prion-protein immunoreactivity in human transmissible dementias. N Engl J Med. 1986 Nov 6;315(19):1231–1233. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198611063151919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., Newman R. A., Sutherland D. R., Asser U., Greaves M. F. A one-step purification of membrane proteins using a high efficiency immunomatrix. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10766–10769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siakotos A. N., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Traub R. D., Bucana C. Partial purification of the scrapie agent from mouse brain by pressure disruption and zonal centrifugation in sucrose-sodium chloride gradients. Virology. 1976 Mar;70(1):230–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targoff I. N., Reichlin M. Measurement of antibody to Jo-1 by ELISA and comparison to enzyme inhibitory activity. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2874–2882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., Goodman P. A., Mirenda C. A., McKinley M. P., Carlson G. A., Prusiner S. B. Distinct prion proteins in short and long scrapie incubation period mice. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):651–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]