Abstract
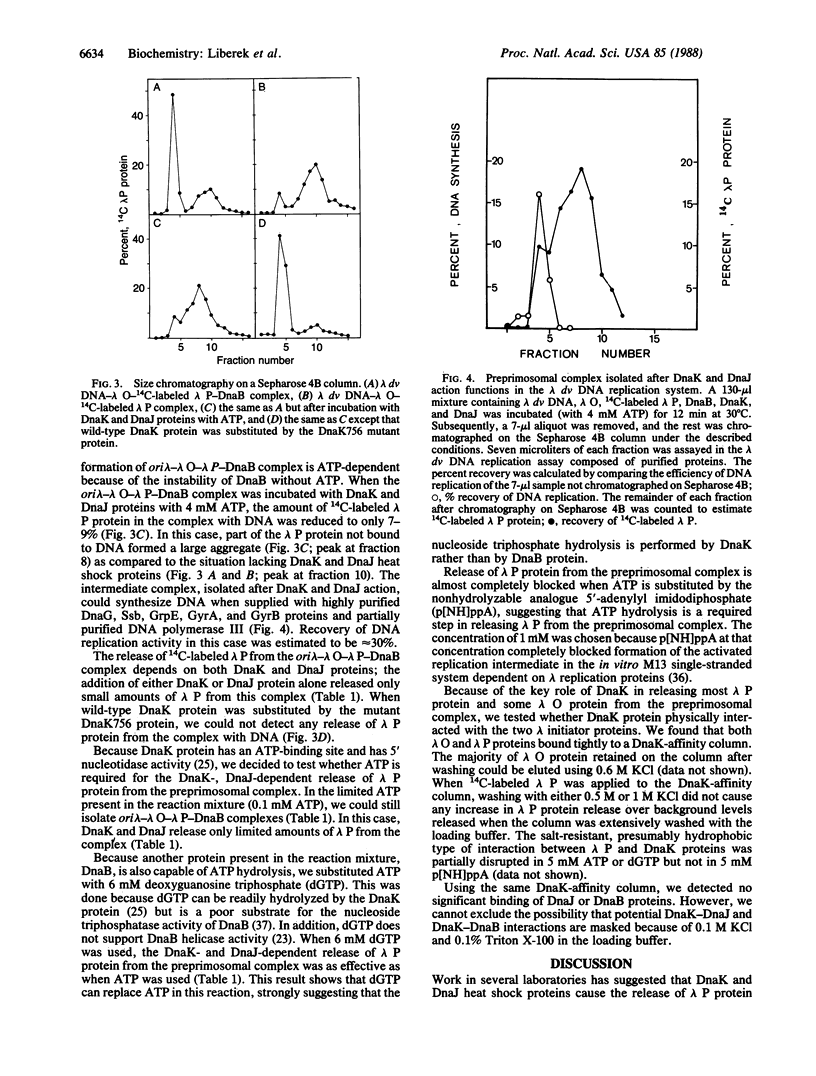
We examined the role of two Escherichia coli heat shock proteins, the dnaK and dnaJ gene products, during the initiation of lambda dv DNA replication in vitro. Using 14C-labeled lambda P protein we showed that the DnaK and DnaJ heat shock proteins function together to release lambda P protein from the preprimosomal complex consisting of lambda origin of replication-lambda O-lambda P-DnaB protein. Hydrolysis of ATP, catalyzed presumably by DnaK, is required during this reaction. Substitution of DnaK protein with that of the mutant DnaK756 protein blocks lambda P release. After DnaK and DnaJ action, the preprimosomal complex, isolated on Sepharose 4B, can support lambda dv DNA replication without any additional prepriming proteins. Using DnaK-affinity chromatography we showed that both lambda O and lambda P proteins bind to DnaK protein. The lambda P protein interacts with DnaK protein in a salt-resistant, hydrophobic manner, and ATP hydrolysis is necessary to elute at least part of lambda P protein from the DnaK-affinity column. The proposed mechanism of action of the prokaryotic DnaK and DnaJ heat shock proteins agrees with the hypothesis that Hsp70, the DnaK analogue of eukaryotes, uses ATP to disrupt hydrophobic aggregates [Pelham, H. R. B. (1986) Cell 46, 959-961].
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderl A., Klein A. Replication of lambda dv DNA in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1733–1740. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ang D., Chandrasekhar G. N., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. Escherichia coli grpE gene codes for heat shock protein B25.3, essential for both lambda DNA replication at all temperatures and host growth at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):25–29. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.25-29.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Kornberg A. Mechanism of dnaB protein action. II. ATP hydrolysis by dnaB protein dependent on single- or double-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5253–5259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):848–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Tilly K., Craig E., King J., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. The nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli K12 dnaJ+ gene. A gene that encodes a heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1782–1785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas S. B., Biswas E. E. Regulation of dnaB function in DNA replication in Escherichia coli by dnaC and lambda P gene products. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7831–7838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. Escherichia coli DnaK protein possesses a 5'-nucleotidase activity that is inhibited by AppppA. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):931–935. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.931-935.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappell T. G., Welch W. J., Schlossman D. M., Palter K. B., Schlesinger M. J., Rothman J. E. Uncoating ATPase is a member of the 70 kilodalton family of stress proteins. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):3–13. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90532-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M., Echols H., Wickner S., Alfano C., Mensa-Wilmot K., Gomes B., LeBowitz J., Roberts J. D., McMacken R. Specialized nucleoprotein structures at the origin of replication of bacteriophage lambda: localized unwinding of duplex DNA by a six-protein reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7638–7642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M., Roberts J., McMacken R., Echols H. Specialized nucleoprotein structures at the origin of replication of bacteriophage lambda: complexes with lambda O protein and with lambda O, lambda P, and Escherichia coli DnaB proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4678–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Multiple DNA-protein interactions governing high-precision DNA transactions. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1050–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.2943018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., McLeester C., Dove W. F. Specificity determinants for bacteriophage lambda DNA replication. I. A chain of interactions that controls the initiation of replication. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 5;126(2):195–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C., Tilly K., Drahos D., Hendrix R. The B66.0 protein of Escherichia coli is the product of the dnaK+ gene. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):1175–1177. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.1175-1177.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein A., Lanka E., Schuster H. Isolation of a complex between the P protein of phage lambda and the dnaB protein of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., McMacken R. The Escherichia coli dnaB replication protein is a DNA helicase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4738–4748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C., McMacken R. Initiation of DNA replication on single-stranded DNA templates catalyzed by purified replication proteins of bacteriophage lambda and Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3988–3992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. Use of peptide tagging to detect proteins expressed from cloned genes: deletion mapping functional domains of Drosophila hsp 70. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3087–3093. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02263.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Speculations on the functions of the major heat shock and glucose-regulated proteins. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):959–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D., McMacken R. The bacteriophage lambda O replication protein: isolation and characterization of the amplified initiator. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7435–7452. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Hase T., Matsubara H., Matsubara K. Bacteriophage lambda initiators: preparation from a strain that overproduces the O and P proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(1):79–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00384387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Matsubara K. Purified bacteriophage lambda O protein binds to four repeating sequences at the lambda replication origin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1789–1799. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Matsubara K. Replication of lambda dv plasmid in vitro promoted by purified lambda O and P proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7639–7643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J., Feramisco J. R. Rapid purification of mammalian 70,000-dalton stress proteins: affinity of the proteins for nucleotides. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1229–1237. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner S. H. DNA replication proteins of Escherichia coli and phage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):303–310. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner S. H., Zahn K. Characterization of the DNA binding domain of bacteriophage lambda O protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7537–7543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Mallory J. B., Roberts J. D., LeBowitz J. H., McMacken R. Initiation of bacteriophage lambda DNA replication in vitro with purified lambda replication proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6176–6180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., McIntyre J., Sell S. M., Georgopoulos C., Skowyra D., Zylicz M. Enzymology of the pre-priming steps in lambda dv DNA replication in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):7996–7999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn K., Blattner F. R. Direct evidence for DNA bending at the lambda replication origin. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):416–422. doi: 10.1126/science.2951850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., Ang D., Georgopoulos C. The grpE protein of Escherichia coli. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17437–17442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. Purification and properties of the Escherichia coli dnaK replication protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8820–8825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., Gorska I., Taylor K., Georgopoulos C. Bacteriophage lambda replication proteins: formation of a mixed oligomer and binding to the origin of lambda DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):401–406. doi: 10.1007/BF00436186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., LeBowitz J. H., McMacken R., Georgopoulos C. The dnaK protein of Escherichia coli possesses an ATPase and autophosphorylating activity and is essential in an in vitro DNA replication system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6431–6435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., Yamamoto T., McKittrick N., Sell S., Georgopoulos C. Purification and properties of the dnaJ replication protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7591–7598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]