Abstract
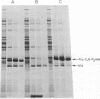
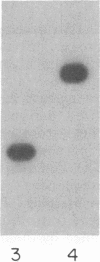
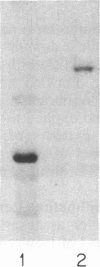
The fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase domain of rat liver 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (EC 2.7.105/EC 3.1.3.46) was expressed in Escherichia coli by using an expression system based on bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. The protein was efficiently expressed (i) as a fusion protein that starts at the T7 major capsid protein initiation site in a pET expression vector and (ii) as a protein that starts within the bisphosphatase sequence by translation reinitiation. Both proteins have similar properties. The protein was purified to homogeneity by anion-exchange chromatography and gel filtration. The purified fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase domain was active and no 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase activity was found associated with it. In contrast to the dimeric bifunctional enzyme, the fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase domain behaved as a monomer of 30 kDa. The turnover number and kinetic properties of the separate bisphosphatase domain were similar to those of the bisphosphatase of the bifunctional enzyme, including the ability to form a phosphoenzyme intermediate. These results support the hypothesis that the rat liver enzyme consists of two independent domains and is a member of a class of enzymes formed by gene fusion.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Colosia A. D., Lively M., el-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis S. J. Isolation of a cDNA clone for rat liver 6-phosphofructo 2-kinase/fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 30;143(3):1092–1098. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone K. C., Steege D. A. Functional analysis of lac repressor restart sites in translational initiation and reinitiation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):733–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90393-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Maghrabi M. R., Claus T. H., Pilkis J., Fox E., Pilkis S. J. Regulation of rat liver fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7603–7607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Maghrabi M. R., Fox E., Pilkis J., Pilkis S. J. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of rat liver 6-phosphofructo 2-kinase, fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 15;106(3):794–802. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91780-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Maghrabi M. R., Pate T. M., Murray K. J., Pilkis S. J. Differential effects of proteolysis and protein modification on the activities of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13096–13103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hass L. F., Kappel W. K., Miller K. B., Engle R. L. Evidence for structural homology between human red cell phosphoglycerate mutase and 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers H. G., Van Schaftingen E. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate 2 years after its discovery. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):1–12. doi: 10.1042/bj2060001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Analysis of phenylthiohydantoins by ultrasensitive gradient high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:486–493. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G. L., Boulanger Y., Hartley B. S. Repeating sequences in aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Nature. 1974 May 24;249(455):316–320. doi: 10.1038/249316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lively M. O., el-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis J., D'Angelo G., Colosia A. D., Ciavola J. A., Fraser B. A., Pilkis S. J. Complete amino acid sequence of rat liver 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):839–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K. J., El-Maghrabi M. R., Kountz P. D., Lukas T. J., Soderling T. R., Pilkis S. J. Amino acid sequence of the phosphorylation site of rat liver 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7673–7681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napoli C., Gold L., Singer B. S. Translational reinitiation in the rIIB cistron of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 5;149(3):433–449. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., Chrisman T., Burgress B., McGrane M., Colosia A., Pilkis J., Claus T. H., el-Maghrabi M. R. Rat hepatic 6-phosphofructo 2-kinase/fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase: a unique bifunctional enzyme. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1983;21:147–173. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(83)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., El-Maghrabi M. R., McGrane M., Pilkis J., Fox E., Claus T. H. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate: a mediator of hormone action at the fructose 6-phosphate/fructose 1,6-bisphosphate substrate cycle. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Mar;25(3):245–266. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., Lively M. O., el-Maghrabi M. R. Active site sequence of hepatic fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Homology in primary structure with phosphoglycerate mutase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12672–12675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinel J. P., Chorover S. L. Inhibition by arousal of epilepsy induced by chlorambucil in rats. Nature. 1972 Mar 31;236(5344):232–234. doi: 10.1038/236232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose Z. B. Evidence for a phosphohistidine protein intermediate in the phosphoglycerate mutase reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Oct;140(2):508–513. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose Z. B., Whalen R. G. The phosphorylation of diphosphoglycerate mutase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 10;248(5):1513–1519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Studier F. W. T7 RNA polymerase can direct expression of influenza virus cap-binding protein (PB2) in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;59(2-3):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart H. B., el-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis S. J. Evidence for a phosphoenzyme intermediate in the reaction pathway of rat hepatic fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):12935–12941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauler A., el-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis S. J. Functional homology of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase, phosphoglycerate mutase, and 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate mutase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16808–16815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K., Furuya E., Richards C. S., Yokoyama M. Fructose-2,6-P2, chemistry and biological function. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Oct 18;48(2):97–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00227610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yourno J., Kohno T., Roth J. R. Enzyme evolution: generation of a bifunctional enzyme by fusion of adjacent genes. Nature. 1970 Nov 28;228(5274):820–824. doi: 10.1038/228820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Maghrabi M. R., Correia J. J., Heil P. J., Pate T. M., Cobb C. E., Pilkis S. J. Tissue distribution, immunoreactivity, and physical properties of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5005–5009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Schaftingen E., Davies D. R., Hers H. G. Fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase from rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):143–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]