Abstract
The pluripotent rat islet tumor cell line MSL-G2 expresses primarily glucagon or cholecystokinin and not insulin in vitro but changes phenotype completely after prolonged in vivo cultivation to yield small-sized hypoglycemic tumors composed almost entirely of insulin-producing beta cells. When a genomic DNA fragment containing the coding and upstream regulatory regions of the human insulin gene was stably transfected into MSL-G2 cells no measurable amounts of insulin or insulin mRNA were detected in vitro. However, successive transplantation of two transfected clones resulted in hypoglycemic tumors that efficiently coexpressed human and rat insulin as determined by human C-peptide-specific immunoreagents. These results demonstrate that cis-acting tissue-specific insulin gene enhancer elements are conserved between rat and human insulin genes. We propose that the in vivo differentiation of MSL-G2 cells and transfected subclones into insulin-producing cells reflects processes of natural beta-cell ontogeny leading to insulin gene expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Santerre R. F., Mullenbach G. T. Hamster preproglucagon contains the sequence of glucagon and two related peptides. Nature. 1983 Apr 21;302(5910):716–718. doi: 10.1038/302716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boel E., Schwartz T. W., Norris K. E., Fiil N. P. A cDNA encoding a small common precursor for human pancreatic polypeptide and pancreatic icosapeptide. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):909–912. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01904.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucchini D., Ripoche M. A., Stinnakre M. G., Desbois P., Lorès P., Monthioux E., Absil J., Lepesant J. A., Pictet R., Jami J. Pancreatic expression of human insulin gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2511–2515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Keim P., Steiner D. F. Cell-free synthesis of rat preproinsulins: characterization and partial amino acid sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1964–1968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chick W. L., Warren S., Chute R. N., Like A. A., Lauris V., Kitchen K. C. A transplantable insulinoma in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):628–632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. L., Steiner D. F. Insulin biosynthesis in the rat: demonstration of two proinsulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):278–285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell B., Bell G., Tischer E., DeNoto F. M., Ullrich A., Pictet R., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Isolation and characterization of a cloned rat insulin gene. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):533–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
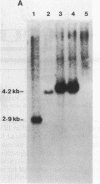
- Cordell B., Diamond D., Smith S., Pünter J., Schöne H. H., Goodman H. M. Disproportionate expression of the two nonallelic rat insulin genes in a pancreatic tumor is due to translational control. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90309-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber O. K., Binder C., Markussen J., Heding L. G., Naithani V. K., Kuzuya H., Blix P., Horwitz D. L., Rubenstein A. H. Characterization of seven C-peptide antisera. Diabetes. 1978;27 (Suppl 1):170–177. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.s170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Rotwein P., Chirgwin J. M., Scharp D., Permutt M. A. Analysis of insulin gene expression in human pancreas. Diabetes. 1983 Aug;32(8):777–780. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.8.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. H., Jacobs J. W., Chin W. W., Lund P. K., Dee P. C., Habener J. F. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned structural gene coding for a precursor of pancreatic somatostatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5869–5873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):115–122. doi: 10.1038/315115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartling S. G., Dinesen B., Kappelgård A. M., Faber O. K., Binder C. ELISA for human proinsulin. Clin Chim Acta. 1986 May 15;156(3):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(86)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Edlund T., Moss J. B., Rutter W. J., Walker M. D. A mutational analysis of the insulin gene transcription control region: expression in beta cells is dependent on two related sequences within the enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8819–8823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P., Rosenthal N., Efstratidadis A., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Tizard R. The structure and evolution of the two nonallelic rat preproinsulin genes. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):545–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen O. D., Cohen R. M., Fitch F. W., Rubenstein A. H., Steiner D. F. The production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for human proinsulin using a sensitive microdot assay procedure. Endocrinology. 1983 Dec;113(6):2135–2144. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-6-2135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen O. D., Larsson L. I., Rehfeld J. F., Schwartz T. W., Lernmark A., Labrecque A. D., Steiner D. F. Cloned cell lines from a transplantable islet cell tumor are heterogeneous and express cholecystokinin in addition to islet hormones. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):2025–2034. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.2025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen O. D., Larsson L. I., Rehfeld J. F., Schwartz T. W., Lernmark A., Labrecque A. D., Steiner D. F. Cloned cell lines from a transplantable islet cell tumor are heterogeneous and express cholecystokinin in addition to islet hormones. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):2025–2034. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.2025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen O. D. Proinsulin-specific monoclonal antibodies. Immunocytochemical application as beta-cell markers and as probes for conversion. Diabetes. 1987 Oct;36(10):1203–1211. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.10.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Walker M. D., Lee F., Kelly R. B. Expressing a human proinsulin cDNA in a mouse ACTH-secreting cell. Intracellular storage, proteolytic processing, and secretion on stimulation. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel R., Khoury G., Reid L. M. Regulation of insulin mRNA abundance and adenylation: dependence on hormones and matrix substrata. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):337–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir U., Walker M. D., Rutter W. J. Regulation of rat insulin 1 gene expression: evidence for negative regulation in nonpancreatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Aagaard L. Analysis of a 1963-bp polymorphic region flanking the human insulin gene. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):475–479. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Hägglöf B., Lernmark A., Holmgren G. Susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes defined by restriction enzyme polymorphism of HLA-D region genomic DNA. Diabetes. 1984 Oct;33(10):958–965. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.10.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe J., Mojsov S., Drucker D. J., Habener J. F. Proglucagon processing in a rat islet cell line resembles phenotype of intestine rather than pancreas. Endocrinology. 1986 Dec;119(6):2833–2839. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-6-2833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P., Chyn R., Chirgwin J., Cordell B., Goodman H. M., Permut M. A. Polymorphism in the 5'-flanking region of the human insulin gene and its possible relation to type 2 diabetes. Science. 1981 Sep 4;213(4512):1117–1120. doi: 10.1126/science.6267694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample C. E., Steiner D. F. Tissue-specific binding of a nuclear factor to the insulin gene promoter. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 5;222(2):332–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80396-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroer J. A., Bender T., Feldmann R. J., Kim K. J. Mapping epitopes on the insulin molecule using monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Sep;13(9):693–700. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R. F., Skośkiewicz M. J., Howie K. B., Russell P. S., Goodman H. M. Regulation of human insulin gene expression in transgenic mice. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):525–528. doi: 10.1038/321525a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Oyer P. E. The biosynthesis of insulin and a probable precursor of insulin by a human islet cell adenoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):473–480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]