Abstract
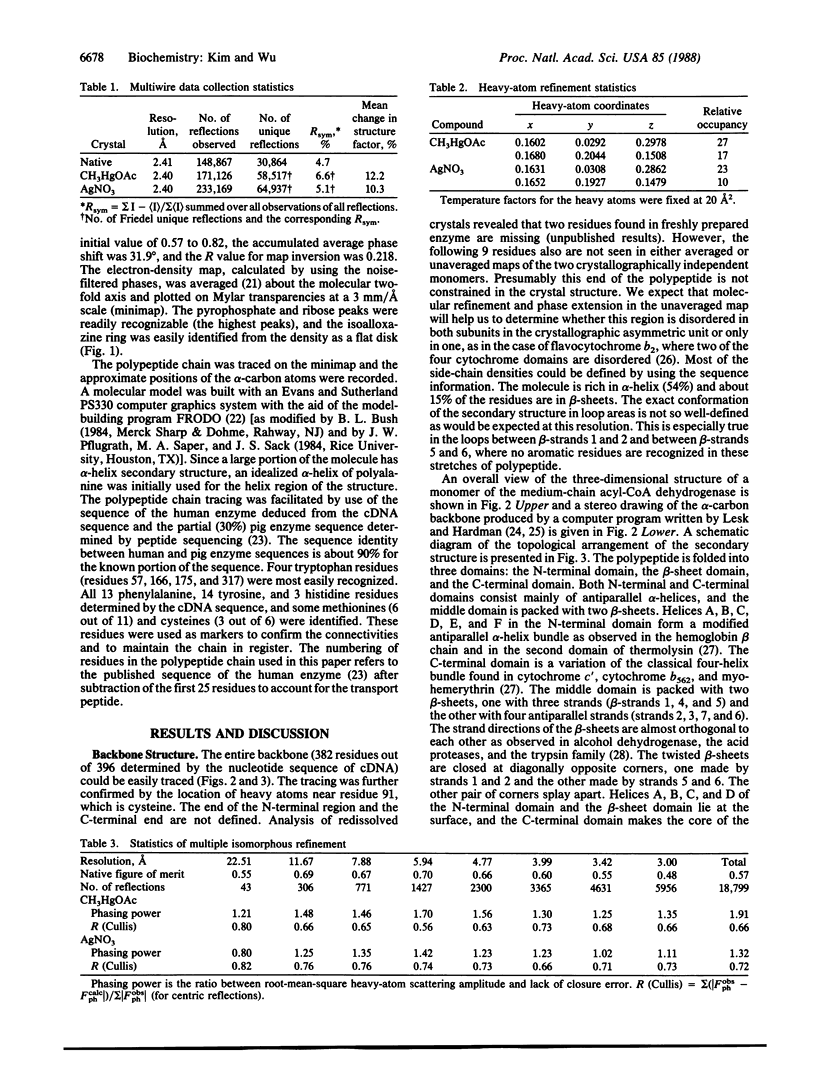
The three-dimensional structure of the medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.99.3) from pig liver mitochondria has been determined to 3.0-A resolution by the x-ray diffraction method. The enzyme is a tetramer of four identical 43-kDa subunits and contains one equivalent of flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) per subunit. The polypeptide is folded into three domains. The N-terminal and the C-terminal domains are composed mainly of alpha-helices, and the middle domain is packed with orthogonal beta-sheets. The FAD has an extended conformation: the flavin ring lies between the N-terminal and the beta-sheet domains, and the adenine moiety is found at the junction between the C-terminal and the beta-sheet domains of one subunit and the C-terminal domain of a neighboring subunit. The polypeptide chain folding near the FAD binding site is different from those observed in other flavoproteins, such as glutathione reductase and glycolate oxidase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auer H. E., Frerman F. E. Circular dichroism studies of acyl-CoA dehydrogenase and electron transfer flavoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8157–8163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benecky M., Li T. Y., Schmidt J., Frerman F., Watters K. L., McFarland J. Resonance Raman study of flavins and the flavoprotein fatty acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 7;18(16):3471–3476. doi: 10.1021/bi00583a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE F. L., BEINERT H. On the mechanism of dehydrogenation of fatty acyl derivatives of coenzyme A. II. The electron-transferring flavoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):717–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Janin J. Orthogonal packing of beta-pleated sheets in proteins. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):3955–3965. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerman F. E., Kim J. J., Huhta K., McKean M. C. Properties of the general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase from pig liver. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2195–2198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerman F. E., Miziorko H. M., Beckmann J. D. Enzyme-activated inhibitors, alternate substrates, and a dead end inhibitor of the general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11192–11198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund K., Mizzer J., Dick W., Thorpe C. Inactivation of general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase from pig kidney by 2-alkynoyl coenzyme A derivatives: initial aspects. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 8;24(21):5996–6002. doi: 10.1021/bi00342a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN D. E., MII S., MAHLER H. R., BOCK R. M. Studies on the fatty acid oxidizing system of animal tissues. III. Butyryl coenzyme A dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jan;206(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUGE J. G., CRANE F. L., BEINERT H. On the mechanism of dehydrogenation of fatty acyl derivatives of coenzyme A. III. Palmityl coA dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):727–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. L., Kamin H. The purification and some properties of electron transfer flavoprotein and general fatty acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase from pig liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3476–3486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda Y., Okamura-Ikeda K., Tanaka K. Spectroscopic analysis of the interaction of rat liver short-chain, medium-chain, and long-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenases with acyl coenzyme A substrates. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7192–7199. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. P., Kim J. J., Billadello J. J., Hainline B. E., Chu T. W., Strauss A. W. Nucleotide sequence of medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase mRNA and its expression in enzyme-deficient human tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4068–4072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. J., Vollmer S. H., Frerman F. E. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray data for the general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3318–3319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesk A. M., Hardman K. D. Computer-generated pictures of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:381–390. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesk A. M., Hardman K. D. Computer-generated schematic diagrams of protein structures. Science. 1982 Apr 30;216(4545):539–540. doi: 10.1126/science.7071602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L. W., Shamala N., Mathews F. S., Steenkamp D. J., Hamlin R., Xuong N. H. Three-dimensional structure of the iron-sulfur flavoprotein trimethylamine dehydrogenase at 2.4-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15140–15146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist Y., Brändén C. I. Structure of glycolate oxidase from spinach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6855–6859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manstein D. J., Pai E. F., Schopfer L. M., Massey V. Absolute stereochemistry of flavins in enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6807–6816. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara Y., Kraus J. P., Ozasa H., Glassberg R., Finocchiaro G., Ikeda Y., Mole J., Rosenberg L. E., Tanaka K. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA encoding the entire precursor of rat liver medium chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10104–10108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizzer J. P., Thorpe C. An essential methionine in pig kidney general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 25;19(24):5500–5504. doi: 10.1021/bi00565a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura-Ikeda K., Ikeda Y., Tanaka K. An essential cysteine residue located in the vicinity of the FAD-binding site in short-chain, medium-chain, and long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenases from rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1338–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. C., Sternberg M. J., Thornton J. M., Wilson I. A. An analysis of the structure of triose phosphate isomerase and its comparison with lactate dehydrogenase. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):329–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90440-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter T. D., Kasper C. B. NADPH-cytochrome P-450 oxidoreductase: flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide domains evolved from different flavoproteins. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1682–1687. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington S., Wiegand G., Huber R. Crystallographic refinement and atomic models of two different forms of citrate synthase at 2.7 and 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 15;158(1):111–152. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90452-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:167–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruzicka F. J., Beinert H. A new iron-sulfur flavoprotein of the respiratory chain. A component of the fatty acid beta oxidation pathway. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8440–8445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz G. E., Schirmer R. H., Sachsenheimer W., Pai E. F. The structure of the flavoenzyme glutathione reductase. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):120–124. doi: 10.1038/273120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:90–112. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenz A., Ghisla S., Thorpe C. Studies with general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase from pig kidney. Inactivation by a novel type of "suicide" inhibitor, 3,4-pentadienoyl-CoA. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 15;147(3):553–560. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-2956.1985.00553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Drenth J., Schulz G. E. Comparison of the three-dimensional protein and nucleotide structure of the FAD-binding domain of p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase with the FAD- as well as NADPH-binding domains of glutathione reductase. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):725–739. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., de Jong R. J., Kalk K. H., Hol W. G., Drenth J. Crystal structure of p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 15;131(1):55–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90301-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Z. X., Shamala N., Bethge P. H., Lim L. W., Bellamy H. D., Xuong N. H., Lederer F., Mathews F. S. Three-dimensional structure of flavocytochrome b2 from baker's yeast at 3.0-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2629–2633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



