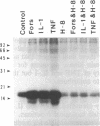
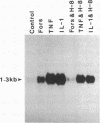
Abstract
Although tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin 1 (IL-1) affect many cell functions, the molecular mechanisms of TNF and IL-1 action are not understood. Our present study shows that exposure of human FS-4 fibroblasts to TNF or IL-1 caused a rapid accumulation of intracellular cAMP and an increase in protein kinase activity. Intracellular cAMP levels peaked 3-5 min after the addition of TNF or IL-1 and returned to basal level by 15 min. Increased phosphorylation of histone HII-B protein was demonstrated with extracts prepared from TNF- or IL-1-treated cells, suggesting an increase in cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity. No evidence was obtained for protein kinase C activation in TNF-treated FS-4 cells. TNF, IL-1, and forskolin all stimulated interleukin 6 (IL-6) mRNA levels in FS-4 cells. The protein kinase inhibitor H-8, inhibiting preferentially cAMP-dependent kinase activity, reduced forskolin-stimulated IL-6 mRNA induction more strongly than TNF- or IL-1-driven IL-6 mRNA induction. These results suggest that activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase by TNF and IL-1 is important in some actions of these cytokines. In addition, our data on IL-6 induction by TNF and IL-1 suggest that other, yet unidentified, signal transduction mechanisms contribute to TNF and IL-1 actions on gene expression in human fibroblasts.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby C. D., Walsh D. A. Characterization of the interaction of a protein inhibitor with adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. I. Interaction with the catalytic subunit of the protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6637–6642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B. A., Cerami A. Recombinant interleukin 1 suppresses lipoprotein lipase activity in 3T3-L1 cells. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3969–3971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J., De Wit L., Pierard D., Derynck R., De Clercq E., Fiers W. Secretory proteins induced in human fibroblasts under conditions used for the production of interferon beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2768–2772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J., De Wit L., Poupart P., Opdenakker G., Van Damme J., Billiau A. Induction of a 26-kDa-protein mRNA in human cells treated with an interleukin-1-related, leukocyte-derived factor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):253–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Biology of interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988 Feb;2(2):108–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Gershon R. K., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. I. The responding cell. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):128–142. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Walton G. M. Assay of cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:93–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Yasukawa K., Harada H., Taga T., Watanabe Y., Matsuda T., Kashiwamura S., Nakajima K., Koyama K., Iwamatsu A. Complementary DNA for a novel human interleukin (BSF-2) that induces B lymphocytes to produce immunoglobulin. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):73–76. doi: 10.1038/324073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and its nuclear substrate proteins. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977;8:267–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Calabretta B., Kao H. T., Heintz N., Nevins J., Baserga R. Control of hsp70 RNA levels in human lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):183–187. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohase M., Henriksen-DeStefano D., May L. T., Vilcek J., Sehgal P. B. Induction of beta 2-interferon by tumor necrosis factor: a homeostatic mechanism in the control of cell proliferation. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90780-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B. Phorbol esters increase the amount of Ca2+, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase associated with plasma membrane. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):621–623. doi: 10.1038/301621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. X., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 cause a rapid and transient stimulation of c-fos and c-myc mRNA levels in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):11908–11911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Akahoshi T., Yamada M., Furutani Y., Oppenheim J. J. Properties of a specific interleukin 1 (IL 1) receptor on human Epstein Barr virus-transformed B lymphocytes: identity of the receptor for IL 1-alpha and IL 1-beta. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4496–4502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May L. T., Helfgott D. C., Sehgal P. B. Anti-beta-interferon antibodies inhibit the increased expression of HLA-B7 mRNA in tumor necrosis factor-treated human fibroblasts: structural studies of the beta 2 interferon involved. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8957–8961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Bank I., Handley D., Cassimeris J., Chess L., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin interacts with endothelial cell receptors to induce release of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1363–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Walther Z., Tamm I. Rapid enhancement of beta 2-interferon/B-cell differentiation factor BSF-2 gene expression in human fibroblasts by diacylglycerols and the calcium ionophore A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3663–3667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther Z., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Transcriptional regulation of the interferon-beta 2/B cell differentiation factor BSF-2/hepatocyte-stimulating factor gene in human fibroblasts by other cytokines. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):974–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Chernajovsky Y., Zeevi M., Shulman L., Soreq H., Nir U., Wallach D., Perricaudet M., Tiollais P., Revel M. Two interferon mRNAs in human fibroblasts: in vitro translation and Escherichia coli cloning studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7152–7156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita T., Tsuda T., Hamamori Y., Takai Y. Possible involvement of cyclic AMP and calcium ion in prostaglandin E1-induced elevation of c-myc mRNA levels in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16878–16882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Lin J. X., Vilcek J. Synthesis of interleukin 6 (interferon-beta 2/B cell stimulatory factor 2) in human fibroblasts is triggered by an increase in intracellular cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6177–6182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]