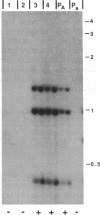
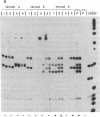
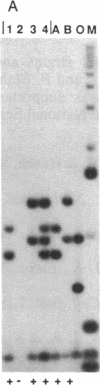
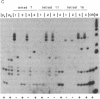
Abstract
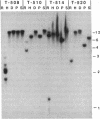
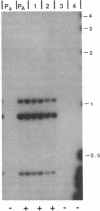
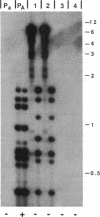
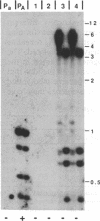
Transforming sequences are faithfully replicated in vegetative cells of Neurospora but are typically subject at high frequency to sequence alterations and methylation in the period between fertilization and nuclear fusion. Previous work showed a correlation between the occurrence of these radical changes, referred to by the acronym RIP, and the presence of sequence duplications resulting from the introduced DNA. Various possible causes for the RIP process were investigated. Introduction of a single copy of a DNA fragment containing the Neurospora am gene into a strain having a deletion of this DNA did not lead to RIP, whereas introduction of two or more copies of the same fragment did. A conventional cross of strains having single copies of am at unlinked chromosomal locations was used to build a strain duplicated for am. Both copies of the duplicated gene were subject to the RIP process in crosses of this strain. We conclude that sequence duplications, per se, trigger RIP.
Full text
PDF
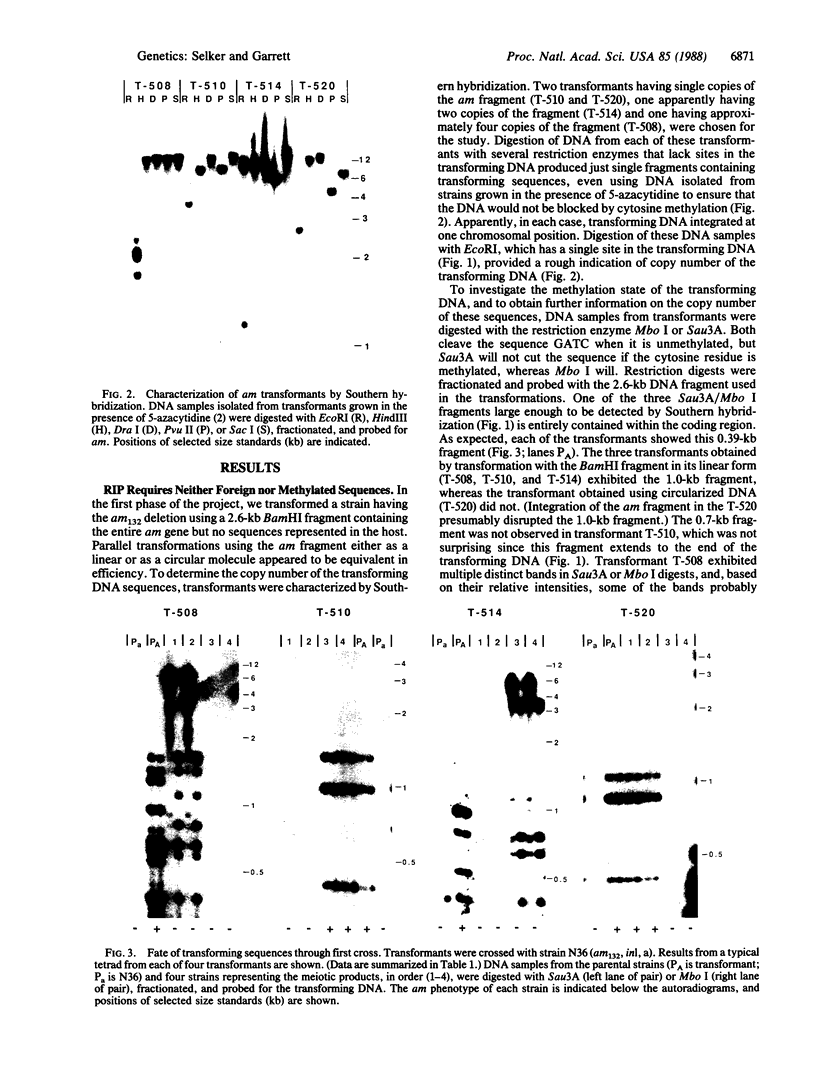

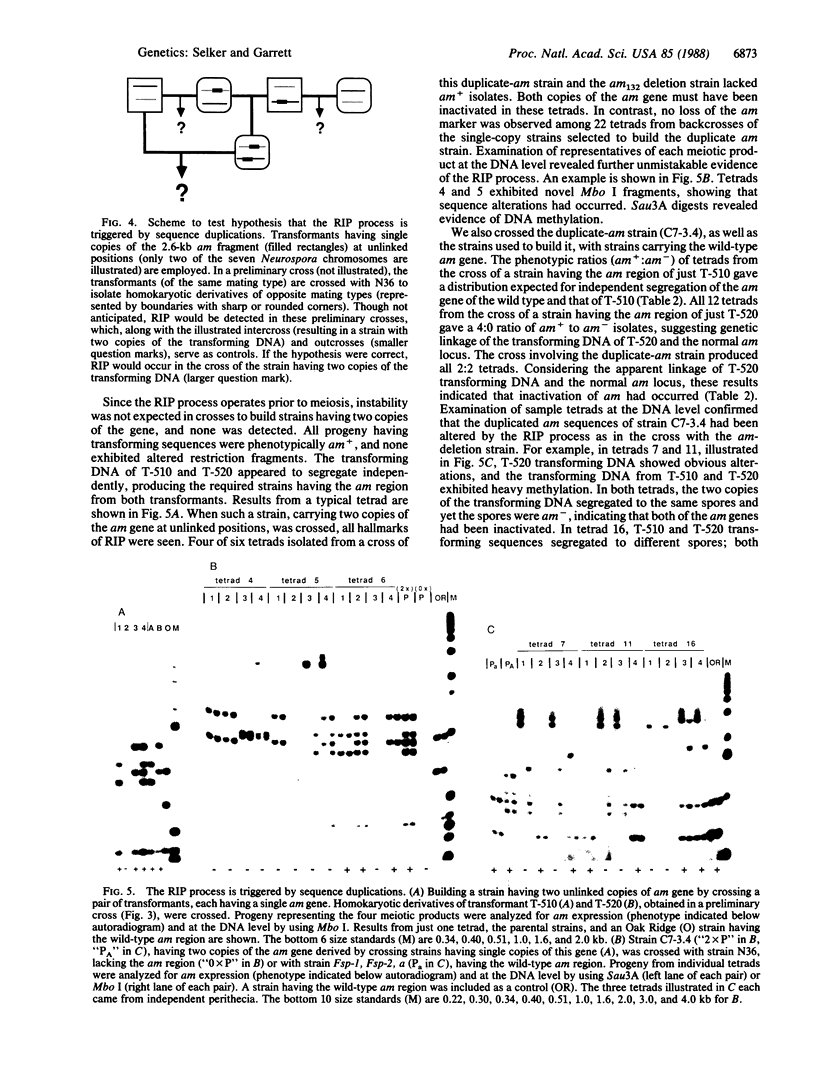

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Case M. E. Genetical and molecular analyses of qa-2 transformants in Neurospora crassa. Genetics. 1986 Jul;113(3):569–587. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case M. E., Schweizer M., Kushner S. R., Giles N. H. Efficient transformation of Neurospora crassa by utilizing hybrid plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5259–5263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D. M., Lambowitz A. M., Rambosek J. A., Kinsey J. A. Transformation of Neurospora crassa with recombinant plasmids containing the cloned glutamate dehydrogenase (am) gene: evidence for autonomous replication of the transforming plasmid. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2041–2051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnaird J. H., Fincham J. R. The complete nucleotide sequence of the Neurospora crassa am (NADP-specific glutamate dehydrogenase) gene. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnaird J. H., Keighren M. A., Kinsey J. A., Eaton M., Fincham J. R. Cloning of the am (glutamate dehydrogenase) gene of Neurospora crassa through the use of a synthetic DNA probe. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90207-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins D. D., Barry E. G. The cytogenetics of Neurospora. Adv Genet. 1977;19:133–285. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60246-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Cambareri E. B., Jensen B. C., Haack K. R. Rearrangement of duplicated DNA in specialized cells of Neurospora. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Jensen B. C., Richardson G. A. A portable signal causing faithful DNA methylation de novo in Neurospora crassa. Science. 1987 Oct 2;238(4823):48–53. doi: 10.1126/science.2958937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Stevens J. N. DNA methylation at asymmetric sites is associated with numerous transition mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8114–8118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Stevens J. N. Signal for DNA methylation associated with tandem duplication in Neurospora crassa. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1032–1038. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]