Abstract
Crosslinked IgM molecules expressed on the surface of immature B cells mediate responses that inhibit further development, in contrast to the activational and proliferative events that follow crosslinking of the mu heavy chain in mature B cells. Concomitant with this change in IgM signaling capacity is the appearance of surface IgD, which has been proposed to modulate the response elicited by the mu heavy chain. In an attempt to gain insight into the mechanism(s) by which surface IgM is able to generate such disparate responses, delta heavy chain gene transfectants of the murine B-cell lymphoma line WEHI-231 were established. WEHI-231 cells resemble phenotypically immature B cells, in addition to being highly susceptible to the growth-inhibitory effect of surface IgM cross-linking. Endogenous mu and exogenous delta heavy chains expressed on the surface of the transfectants were compared for their role in cell proliferation and on gene expression. Our results indicate that the growth-inhibitory response is associated only with the mu heavy chain and that surface IgD does not mediate such a response. Furthermore, in contrast to IgM, IgD molecules appear to have an inductive effect on the expression of Myc and the endogenous mu and exogenous delta Ig heavy chain genes but not on the expression of the housekeeping gene encoding beta 2-microglobulin. These findings suggest that IgM and IgD are functionally distinct when expressed on the surface of an immature B cell.
Full text
PDF
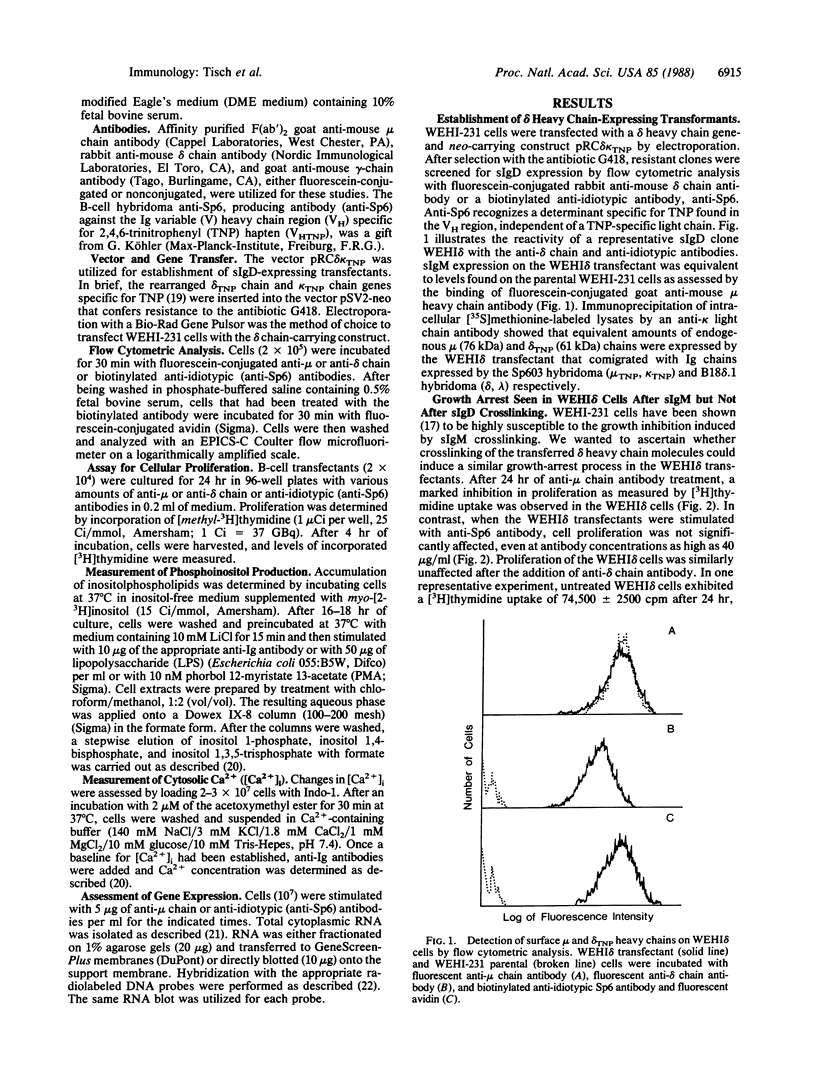



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alés-Martínez J. E., Warner G. L., Scott D. W. Immunoglobulins D and M mediate signals that are qualitatively different in B cells with an immature phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6919–6923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Meade C. J., Turner G. A., Klaus G. G. B lymphocyte receptors and polyphosphoinositide degradation. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Tucker P. W. The molecular biology of immunoglobulin D. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):417–422. doi: 10.1038/307417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. W., Schrader J. W. The regulation of growth and differentiation of a murine B cell lymphoma. II. The inhibition of WEHI 231 by anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2466–2469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Justement L. B., Newell M. K., Chen Z. Z., Harris L. K., Sandoval V. M., Klemsz M. J., Ransom J. T. Transmembrane signals and intracellular "second messengers" in the regulation of quiescent B-lymphocyte activation. Immunol Rev. 1987 Feb;95:37–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Monroe J. G. B cell activation. V. Differentiation signaling of B cell membrane depolarization, increased I-A expression, G0 to G1 transition, and thymidine uptake by anti-IgM and anti-IgD antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):576–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Newell M. K., Justement L. B., McGuire J. C., Leach K. L., Chen Z. Z. Ia binding ligands and cAMP stimulate nuclear translocation of PKC in B lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):629–632. doi: 10.1038/327629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey K. A., DeFranco A. L. Cross-linking membrane IgM induces production of inositol trisphosphate and inositol tetrakisphosphate in WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3935–3942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi T., Chesnut R. W., Grey H. M. B cells as antigen-presenting cells: the requirement for B cell activation. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):109–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. E., Pepe V. H., Kent R. B., Dean M., Marshak-Rothstein A., Sonenshein G. E. Specific regulation of c-myc oncogene expression in a murine B-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5546–5550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuguchi J., Tsang W., Morrison S. L., Beaven M. A., Paul W. E. Membrane IgM, IgD, and IgG act as signal transmission molecules in a series of B lymphomas. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2162–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Seghal E., Kung J., Finkelman F. D. Increased expression of I-region-associated antigen (Ia) on B cells after cross-linking of surface immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):881–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. G., Cambier J. C. B cell activation. I. Anti-immunoglobulin-induced receptor cross-linking results in a decrease in the plasma membrane potential of murine B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):2073–2086. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.2073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. G., Cambier J. C. B cell activation. II. Receptor cross-linking by thymus-independent and thymus-dependent antigens induces a rapid decrease in the plasma membrane potential of antigen-binding B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2641–2644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. G., Cambier J. C. B cell activation. III. B cell plasma membrane depolarization and hyper-Ia antigen expression induced by receptor immunoglobulin cross-linking are coupled. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1589–1599. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi K., Cohen D. I., Blackman M., Nielsen E., Ohara J., Hamaoka T., Koshland M. E., Paul W. E. Ig RNA expression in normal B cells stimulated with anti-IgM antibody and T cell-derived growth and differentiation factors. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1736–1751. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Cellular mechanisms of immunologic tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:33–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Pike B. L., Battye F. L. Mechanisms of clonal abortion tolerogenesis. II. Clonal behaviour of immature B cells following exposure to anti-mu chain antibody. Immunology. 1979 May;37(1):203–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike B. L., Boyd A. W., Nossal G. J. Clonal anergy: the universally anergic B lymphocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2013–2017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzan T., Arslan P., Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J. Anti-immunoglobulin, cytoplasmic free calcium, and capping in B lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):335–340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P. Functional subsets of murine and human B lymphocyte cell lines. Immunol Rev. 1979;48:107–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roifman C. M., Mills G. B., Stewart D., Cheung R. K., Grinstein S., Gelfand E. W. Response of human B cells to different anti-immunoglobulin isotypes: absence of a correlation between early activation events and cell proliferation. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1737–1742. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Marcu K. B., Perry R. P. The synthesis and processing of the messenger RNAs specifying heavy and light chain immunoglobulins in MPC-11 cells. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1495–1509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. W., Layton J. E., Nossal G. J. Role of IgD in the immune response and tolerance. I. Anti-delta pretreatment facilitates tolerance induction in adult B cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1473–1483. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. W., Livnat D., Pennell C. A., Keng P. Lymphoma models for B cell activation and tolerance. III. Cell cycle dependence for negative signalling of WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells by anti-mu. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):156–164. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisch R., Watanabe M., Letarte M., Hozumi N. Assessment of antigen-specific receptor function of surface immunoglobulin M and D with identical hapten specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3831–3835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Cambier J. C., Ligler F. S., Kettman J. R., Uhr J. W. B-cell tolerance. IV. Differential role of surface IgM and IgD in determining tolerance susceptibility of murine B cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1804–1808. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





