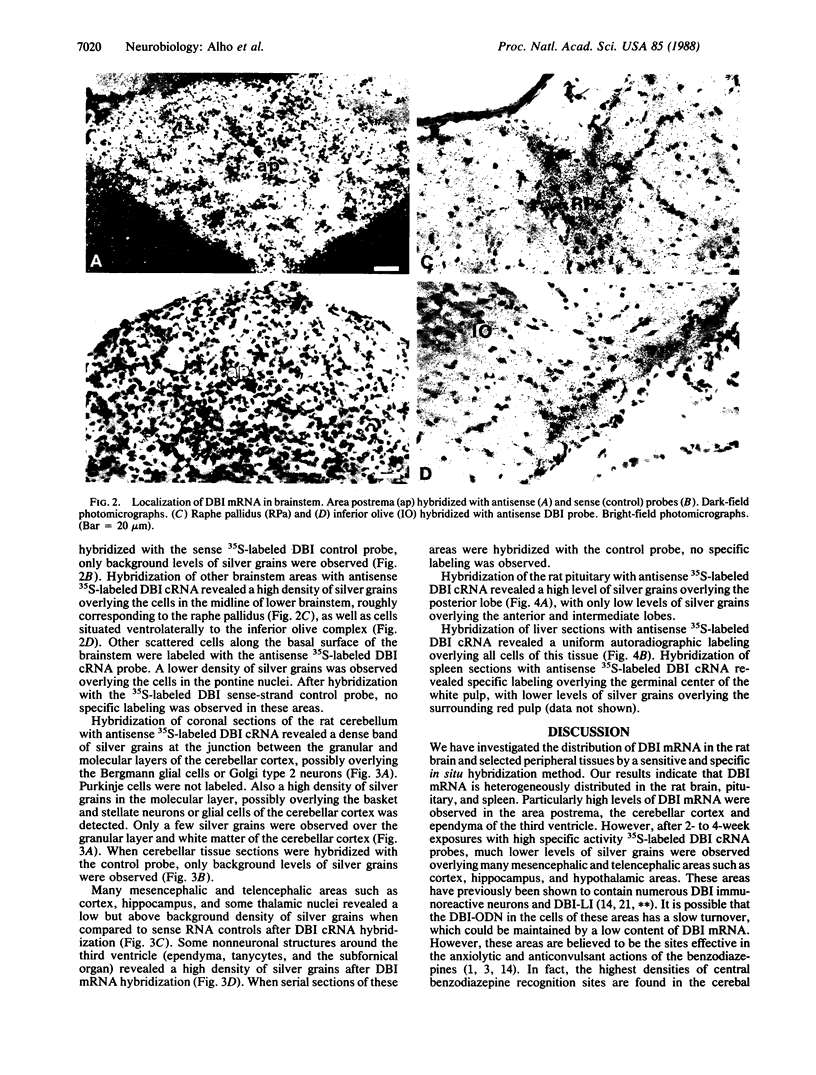
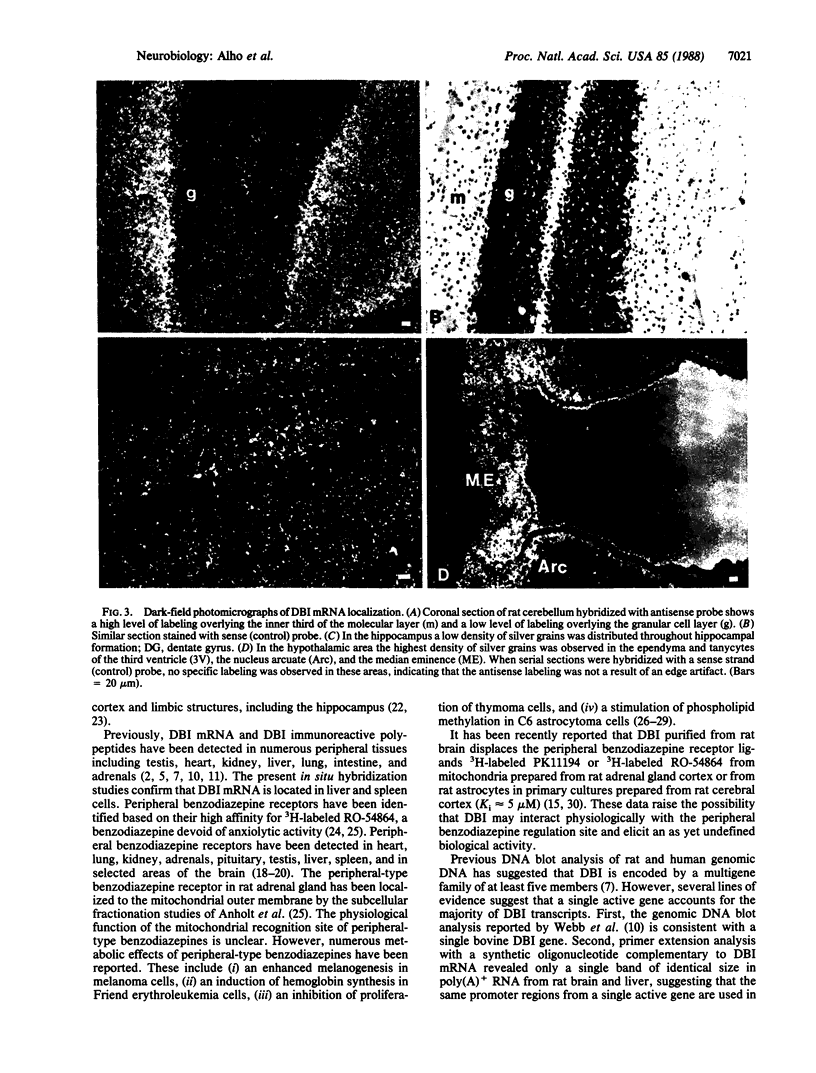
Abstract
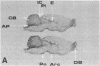
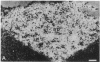
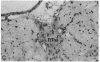
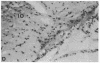
Diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI), an endogenous 10-kDa polypeptide was isolated from rat and human brain by monitoring displacement of radioactive diazepam bound to specific recognition sites in brain synaptic and mitochondrial membranes. The cellular location of DBI mRNA was studied in rat brain and selected peripheral tissues by in situ hybridization histochemistry with a 35S-labeled single-stranded complementary RNA probe. DBI mRNA was heterogeneously distributed in rat brain, with particularly high levels in the area postrema, the cerebellar cortex, and ependyma of the third ventricle. Intermediate levels were found in the olfactory bulb, pontine nuclei, inferior colliculi, arcuate nucleus, and pineal gland. Relatively low but significant levels of silver grains were observed overlying many mesencephalic and telencephalic areas that have previously been shown to contain numerous DBI-immunoreactive neurons and a high density of central benzodiazepine receptors. In situ hybridizations also revealed high levels of DBI mRNA in the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland, liver, and germinal center of the white pulp of spleen, all tissues that are rich in peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites. The tissue-specific pattern of DBI gene expression described here could be exploited to further understand the physiological function of DBI in the brain and periphery.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alho H., Costa E., Ferrero P., Fujimoto M., Cosenza-Murphy D., Guidotti A. Diazepam-binding inhibitor: a neuropeptide located in selected neuronal populations of rat brain. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):179–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3892688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anholt R. R., De Souza E. B., Oster-Granite M. L., Snyder S. H. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors: autoradiographic localization in whole-body sections of neonatal rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 May;233(2):517–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anholt R. R., Pedersen P. L., De Souza E. B., Snyder S. H. The peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor. Localization to the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):576–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J. Electrophysiology of GABAA and GABAB receptor subtypes. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Mar;11(3):112–116. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J., Ferrero P., Guidotti A., Costa E. Neuropeptide modulation of GABA receptor C1- channels. Regul Pept Suppl. 1985;4:33–38. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(85)90215-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. W., Agerberth B., Gell K., Andersson M., Mutt V., Ostenson C. G., Efendić S., Barros-Söderling J., Persson B., Jörnvall H. Isolation and characterization of porcine diazepam-binding inhibitor, a polypeptide not only of cerebral occurrence but also common in intestinal tissues and with effects on regulation of insulin release. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jun 1;174(2):239–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Souza E. B., Anholt R. R., Murphy K. M., Snyder S. H., Kuhar M. J. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors in endocrine organs: autoradiographic localization in rat pituitary, adrenal, and testis. Endocrinology. 1985 Feb;116(2):567–573. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-2-567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarese C., Vaccarino F., Alho H., Mellstrom B., Costa E., Guidotti A. Subcellular location and neuronal release of diazepam binding inhibitor. J Neurochem. 1987 Apr;48(4):1093–1102. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero P., Costa E., Conti-Tronconi B., Guidotti A. A diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI)-like neuropeptide is detected in human brain. Brain Res. 1986 Dec 3;399(1):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90607-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero P., Santi M. R., Conti-Tronconi B., Costa E., Guidotti A. Study of an octadecaneuropeptide derived from diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI): biological activity and presence in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):827–831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehlert D. R., Yamamura H. I., Wamsley J. K. Autoradiographic localization of "peripheral-type" benzodiazepine binding sites in the rat brain, heart and kidney. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;328(4):454–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00692915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Glaister D., Seeburg P. H., Guidotti A., Costa E. Cloning and expression of cDNA for human diazepam binding inhibitor, a natural ligand of an allosteric regulatory site of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7547–7551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Forchetti C. M., Corda M. G., Konkel D., Bennett C. D., Costa E. Isolation, characterization, and purification to homogeneity of an endogenous polypeptide with agonistic action on benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3531–3535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., De Souza E. B., Unnerstall J. R. Neurotransmitter receptor mapping by autoradiography and other methods. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:27–59. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Todaro G. J., Shoyab M. Complete amino acid sequences of bovine and human endozepines. Homology with rat diazepam binding inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9727–9731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata M., Mocchetti I., Ferrarese C., Guidotti A., Costa E. Protracted treatment with diazepam increases the turnover of putative endogenous ligands for the benzodiazepine/beta-carboline recognition site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1444–1448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocchetti I., Einstein R., Brosius J. Putative diazepam binding inhibitor peptide: cDNA clones from rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7221–7225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. G., Schoch P., Häring P., Takacs B., Möhler H. Resolving GABAA/benzodiazepine receptors: cellular and subcellular localization in the CNS with monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci. 1987 Jun;7(6):1866–1886. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-06-01866.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., Gentry L. E., Marquardt H., Todaro G. J. Isolation and characterization of a putative endogenous benzodiazepineoid (endozepine) from bovine and human brain. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11968–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Hirata F., Axelrod J., Mallorga P., Tallman J. F., Henneberry R. C. Benzodiazepine and beta-adrenergic receptor ligands independently stimulate phospholipid methylation. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):857–859. doi: 10.1038/282857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. K., Morgan J. I., Spector S. Benzodiazepines that bind at peripheral sites inhibit cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):753–756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. K., Morgan J. I., Spector S. Differentiation of Friend erythroleukemia cells induced by benzodiazepines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3770–3772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb N. R., Rose T. M., Malik N., Marquardt H., Shoyab M., Todaro G. J., Lee D. C. Bovine and human cDNA sequences encoding a putative benzodiazepine receptor ligand. DNA. 1987 Feb;6(1):71–79. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Gehlert D. R., Gee K. W., Wamsley J. K., Horst W. D., Roeske W. R. Specific high-affinity [3H]Ro5-4864 Ro5-4864 benzodiazepine binding sites in the brain and periphery. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;192:187–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]