Abstract
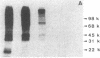
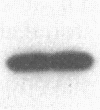
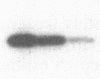
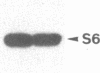
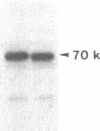
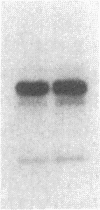
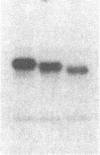
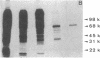
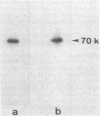
To investigate the role of phosphorylation in the activation of S6 kinase, the enzyme was isolated from 32P-labeled Swiss mouse 3T3 cells before and after stimulation with serum. The kinase activity was followed through several purification steps, and a radioactive protein of Mr 70,000 was obtained from the stimulated cells. This band was not detected in resting cells. The Mr 70,000 protein exhibited the same size upon NaDodSO4/PAGE as the homogeneous kinase, and it comigrated with the in vitro autophosphorylated form of the enzyme. Treatment of the in vivo-labeled material with phosphatase 2A led to a loss of kinase activity concomitant with a release of 32Pi from the Mr 70,000 protein. The partially dephosphorylated protein migrated faster during PAGE, displaying distinct species of Mr 69,000 and 68,000. Most importantly, phospho amino acid analysis of the labeled S6 kinase showed only phosphoserine and phosphothreonine. These results argue that the S6 kinase is phosphorylated at multiple sites in vivo and that it is activated by serine/threonine phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballou L. M., Jenö P., Thomas G. Protein phosphatase 2A inactivates the mitogen-stimulated S6 kinase from Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1188–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Regulation of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity by the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, serum, or phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7621–7625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Regulation of protein kinase activities in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3441–3447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04667.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Stimulation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity by pp60v-src or by serum: dissociation from phorbol ester-stimulated activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1733–1737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Kuo C. J., Erikson R. L. Identification of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase regulated by transformation and growth-promoting stimuli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14373–14376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H. An insulin-stimulated ribosomal protein S6 kinase in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):12994–12999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham D. D., Pardee A. B. Transport changes rapidly initiated by serum addition to "contact inhibited" 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1049–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in avian sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4112–4115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. A protein kinase from Xenopus eggs specific for ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Purification and characterization of a protein kinase from Xenopus eggs highly specific for ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A., Yellowlees D., Kernohan J. C., Cohen P. Purification of glycogen synthase kinase 3 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Copurification with the activating factor (FA) of the (Mg-ATP) dependent protein phosphatase. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(3):443–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenö P., Ballou L. M., Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. Identification and characterization of a mitogen-activated S6 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):406–410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg J., Hofsteenge J., Thomas G. Identification of the 40 S ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation sites induced by cycloheximide. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11473–11477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Thomas G. EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin induce the phosphorylation of identical S6 peptides in swiss mouse 3T3 cells: effect of cAMP on early sites of phosphorylation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Pérez J., Thomas G. Ordered phosphorylation of 40S ribosomal protein S6 after serum stimulation of quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):926–930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Guroff G. Purification and mechanism of activation of a nerve growth factor-sensitive S6 kinase from PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2832–2844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Gunsalus J. R., Avruch J. An insulin-stimulated (ribosomal S6) protein kinase from soluble extracts of H4 hepatoma cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 15;245(1):196–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90205-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. An activated S6 kinase in extracts from serum- and epidermal growth factor-stimulated Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5995–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. Epidermal growth factor-mediated activation of an S6 kinase in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10314–10319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier A. R., Ballou L. M., Thomas G. Differential regulation of S6 phosphorylation by insulin and epidermal growth factor in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells: insulin activation of type 1 phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4720–4724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palen E., Traugh J. A. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and mitogen-stimulated S6 kinase differentially alters translation of globin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3518–3523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Krebs E. G. Mitogen-activated S6 kinase is stimulated via protein kinase C-dependent and independent pathways in Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11598–11606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Olwin B. B., Krebs E. G. Fibroblast growth factor treatment of Swiss 3T3 cells activates a subunit S6 kinase that phosphorylates a synthetic peptide substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5968–5972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryshyn R., Levin D. H., London I. M. Double-stranded RNA-dependent eIF-2alpha protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:346–362. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resink T. J., Hemmings B. A., Tung H. Y., Cohen P. Characterisation of a reconstituted Mg-ATP-dependent protein phosphatase. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):455–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudland P. S., Weil S., Hunter A. R. Changes in RNA metabolism and accumulation of presumptive messenger RNA during transition from the growing to the quiescent state of cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 25;96(4):745–766. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanovic D., Erikson E., Pike L. J., Maller J. L. Activation of a ribosomal protein S6 protein kinase in Xenopus oocytes by insulin and insulin-receptor kinase. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):157–160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04190.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Cohen S., Garbers D. L. Inhibition of membrane phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity by vanadate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1104–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Activation of S6 kinase activity in 3T3-L1 cells by insulin and phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Otto A. M. The effect of serum, EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin on S6 phosphorylation and the initiation of protein and DNA synthesis. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Siegmann M., Gordon J. Multiple phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during transition of quiescent 3T3 cells into early G1, and cellular compartmentalization of the phosphate donor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Hunter T. Isolation and characterization of two distinct forms of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4836–4843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Khalaf N., Czech M. P. Insulin stimulates a membrane-bound serine kinase that may be phosphorylated on tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):3972–3976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.3972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]