Abstract
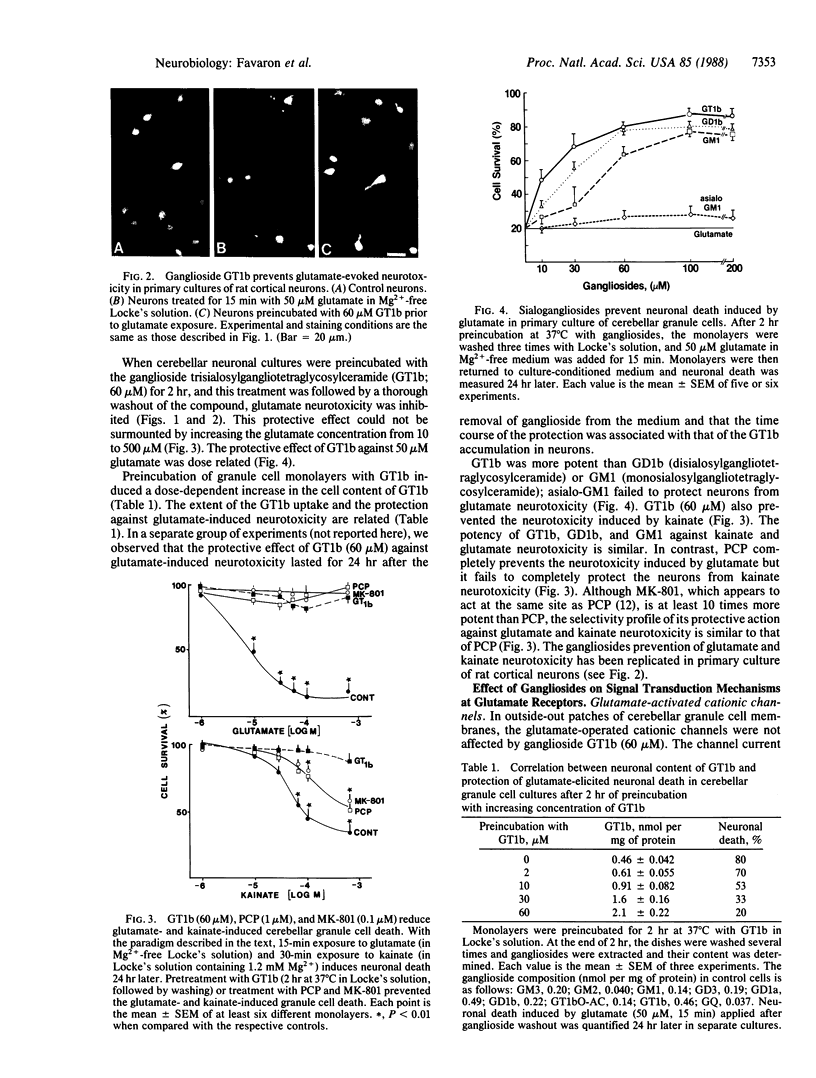
Using a sensitive histofluorescence staining method that allows for a quantitation of neuronal death, we compared the protective effects of gangliosides (a group of naturally occurring glycosphingolipids), phencyclidine (PCP), and MK-801 (dibenzocyclohepteneimine) on glutamate- and kainate-induced neuronal death in primary cultures of cortical and cerebellar neurons prepared from neonatal rats. PCP and MK-801 block neurotoxicity induced by glutamate doses 50 times higher than the LD50 (LD50 in Mg2+-free medium, 10 microM) but only partially block the kainate neurotoxicity (LD50 in presence of Mg2+, 100 microM). In contrast, pretreatment with gangliosides (GT1b greater than GD1b greater than GM1) results in complete and insurmountable protection against the neurotoxicity elicited by glutamate or kainate. In primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells gangliosides, unlike PCP and MK-801, fail to block glutamate-gated cationic currents and the glutamate-evoked increase of (i) inositol phospholipid hydrolysis (ii) c-fos mRNA content, and (iii) nuclear accumulation of c-fos protein. Protection of glutamate neurotoxicity by gangliosides does not require their presence in the incubation medium; however, it is proportional to the amount of glycosphingolipid accumulated in the neuronal membranes. The ganglioside concentration (30-60 microM) that blocks glutamate-elicited neuronal death also prevents glutamate- and kainate-induced protein kinase C translocation from cytosol to neuronal membranes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akers R. F., Lovinger D. M., Colley P. A., Linden D. J., Routtenberg A. Translocation of protein kinase C activity may mediate hippocampal long-term potentiation. Science. 1986 Feb 7;231(4738):587–589. doi: 10.1126/science.3003904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alho H., Ferrarese C., Vicini S., Vaccarino F. Subsets of GABAergic neurons in dissociated cell cultures of neonatal rat cerebral cortex show co-localization with specific modulator peptides. Brain Res. 1988 Apr 1;467(2):193–204. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(88)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anis N. A., Berry S. C., Burton N. R., Lodge D. The dissociative anaesthetics, ketamine and phencyclidine, selectively reduce excitation of central mammalian neurones by N-methyl-aspartate. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolino M., Vicini S., Mazzetta J., Costa E. Phencyclidine and glycine modulate NMDA-activated high conductance cationic channels by acting at different sites. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Feb 3;84(3):351–355. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90534-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Ionic dependence of glutamate neurotoxicity. J Neurosci. 1987 Feb;7(2):369–379. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-02-00369.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W., Koh J. Y., Peters S. Pharmacology of glutamate neurotoxicity in cortical cell culture: attenuation by NMDA antagonists. J Neurosci. 1988 Jan;8(1):185–196. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-01-00185.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W., Maulucci-Gedde M., Kriegstein A. R. Glutamate neurotoxicity in cortical cell culture. J Neurosci. 1987 Feb;7(2):357–368. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-02-00357.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Wadman W. J., Hockberger P. E., Wong R. K. Sustained dendritic gradients of Ca2+ induced by excitatory amino acids in CA1 hippocampal neurons. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):649–653. doi: 10.1126/science.2452481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Bird S. J., Evans R. H., Gulley R. L., Nadler J. V., Nicklas W. J., Olney J. W. Excitatory amino acid neurotoxins: selectivity, specificity, and mechanisms of action. Based on an NRP one-day conference held June 30, 1980. Neurosci Res Program Bull. 1981;19(4):1–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins are complexed with a 39,000-dalton cellular protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Gill R., Kemp J. A., Woodruff G. N. Systemic administration of MK-801 prevents N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neuronal degeneration in rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1987 May 19;76(3):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90420-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R., Foster A. C., Woodruff G. N. Systemic administration of MK-801 protects against ischemia-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration in the gerbil. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3343–3349. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03343.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M. Lysosphingolipids inhibit protein kinase C: implications for the sphingolipidoses. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):670–674. doi: 10.1126/science.3101176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. Glutamate activates multiple single channel conductances in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):522–525. doi: 10.1038/325522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. H., Senft J. A. An improved method to determine cell viability by simultaneous staining with fluorescein diacetate-propidium iodide. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Jan;33(1):77–79. doi: 10.1177/33.1.2578146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutter D., Kim J. Y., Goldenring J. R., Rasmussen H., Ukomadu C., DeLorenzo R. J., Yu R. K. Regulation of protein kinase C activity by gangliosides. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1633–1637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishan A. Rapid flow cytofluorometric analysis of mammalian cell cycle by propidium iodide staining. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jul;66(1):188–193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumakura K., Guidotti A., Costa E. Primary cultures of chromaffin cells: molecular mechanisms for the induction of tyrosine hydroxylase mediated by 8-Br-cyclic AMP. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(3):865–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarewicz J. W., Wroblewski J. T., Palmer M. E., Costa E. Activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate-sensitive glutamate receptors stimulates arachidonic acid release in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells. Neuropharmacology. 1988 Jul;27(7):765–769. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Smith S. J., Barker J. L. NMDA-receptor activation increases cytoplasmic calcium concentration in cultured spinal cord neurones. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):519–522. doi: 10.1038/321519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. N., Thayer S. A., Miller R. J. The effects of excitatory amino acids on intracellular calcium in single mouse striatal neurons in vitro. J Neurosci. 1987 Dec;7(12):4145–4158. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-12-04145.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti F., Wroblewski J. T., Novelli A., Alho H., Guidotti A., Costa E. The activation of inositol phospholipid metabolism as a signal-transducing system for excitatory amino acids in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells. J Neurosci. 1986 Jul;6(7):1905–1911. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-07-01905.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novelli A., Nicoletti F., Wroblewski J. T., Alho H., Costa E., Guidotti A. Excitatory amino acid receptors coupled with guanylate cyclase in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Jan;7(1):40–47. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-01-00040.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotman B., Papermaster B. W. Membrane properties of living mammalian cells as studied by enzymatic hydrolysis of fluorogenic esters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):134–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. Quantitative estimation of sialic acids. II. A colorimetric resorcinol-hydrochloric acid method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):604–611. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar S. M., Sharp F. R., Curran T. Expression of c-fos protein in brain: metabolic mapping at the cellular level. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1328–1331. doi: 10.1126/science.3131879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. P., Swan J. H., Griffiths T., Meldrum B. S. Blockade of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors may protect against ischemic damage in the brain. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):850–852. doi: 10.1126/science.6093256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladeczek F., Pin J. P., Récasens M., Bockaert J., Weiss S. Glutamate stimulates inositol phosphate formation in striatal neurones. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):717–719. doi: 10.1038/317717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekely A. M., Barbaccia M. L., Costa E. Activation of specific glutamate receptor subtypes increases C-fos proto-oncogene expression in primary cultures of neonatal rat cerebellar granule cells. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Dec;26(12):1779–1782. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaccarino F. M., Alho H., Santi M. R., Guidotti A. Coexistence of GABA receptors and GABA-modulin in primary cultures of rat cerebellar granule cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Jan;7(1):65–76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-01-00065.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaccarino F., Guidotti A., Costa E. Ganglioside inhibition of glutamate-mediated protein kinase C translocation in primary cultures of cerebellar neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8707–8711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. H., Kemp J. A., Priestley T., Knight A. R., Woodruff G. N., Iversen L. L. The anticonvulsant MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wroblewski J. T., Nicoletti F., Fadda E., Costa E. Phencyclidine is a negative allosteric modulator of signal transduction at two subclasses of excitatory amino acid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5068–5072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]