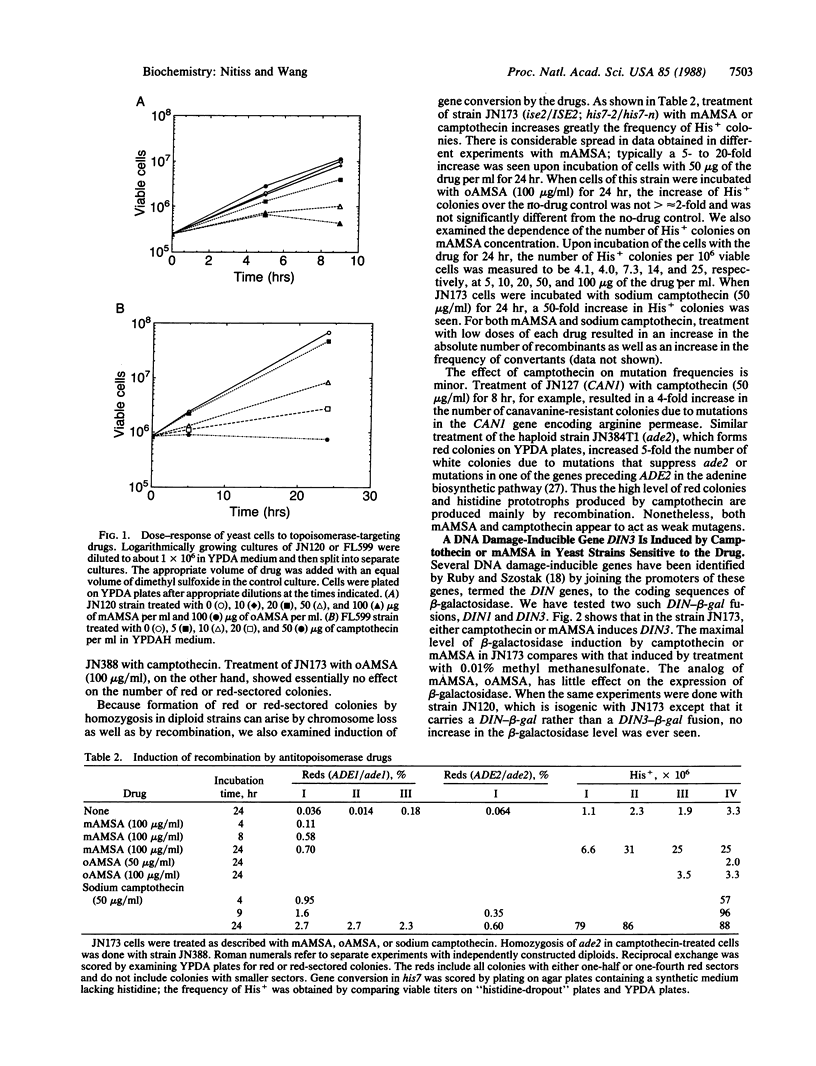
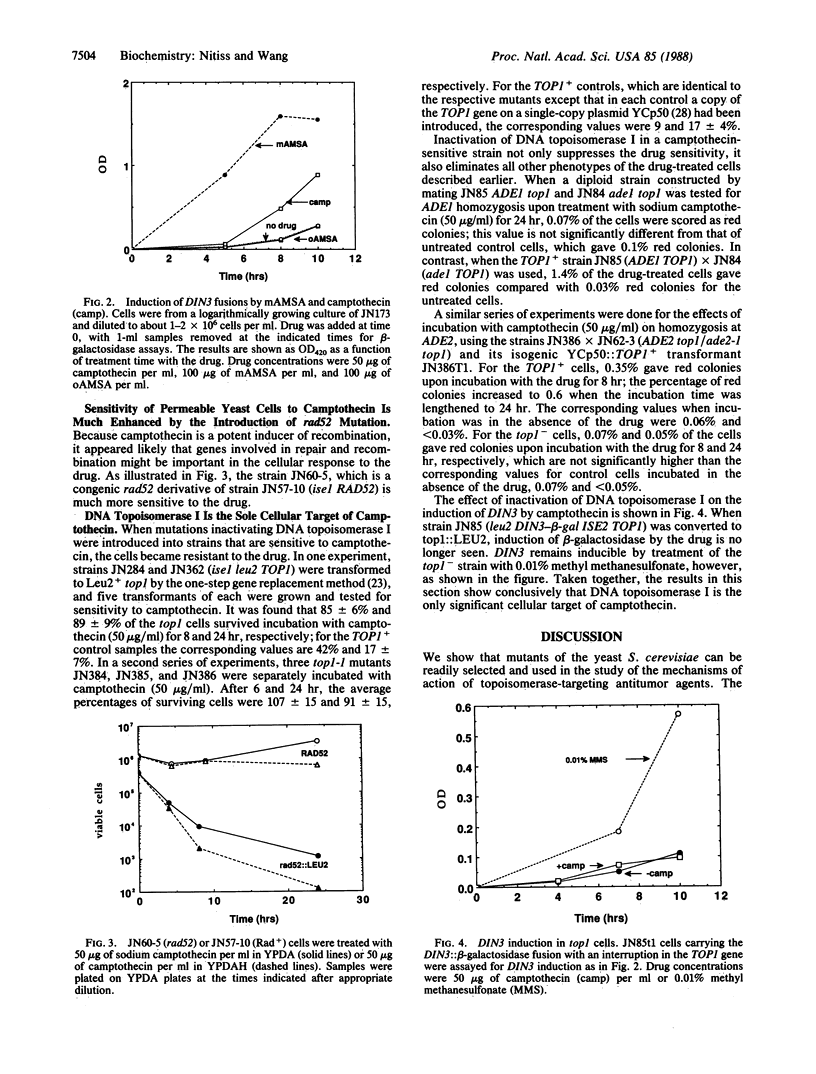
Abstract
The antitumor drugs camptothecin and an anilinoacridine, 4'-(9-acridinylamino)-methanesulfon-m-anisidide (mAMSA), which act on DNA topoisomerase I and II, respectively, are shown to inhibit the growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants selected for their permeability to other inhibitors. In addition to growth inhibition, these drugs induce high levels of homologous recombination and induce the expression of a DNA damage-inducible gene DIN3. Cytotoxicity of the drugs is more pronounced in strains that also carry a rad52 mutation. An analog of mAMSA), which is ineffective as an inhibitor of DNA topoisomerase II in mammalian cells, is also ineffective in eliciting physiological responses in these yeast strains. The physiological effects of camptothecin, but not those of mAMSA, disappear if the TOP1 gene encoding DNA topoisomerase I is disrupted. This shows that DNA topoisomerase I is the sole target of camptothecin cytotoxicity and illustrates that a nonessential enzyme can nevertheless be the target for a cytotoxic drug.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andoh T., Ishii K., Suzuki Y., Ikegami Y., Kusunoki Y., Takemoto Y., Okada K. Characterization of a mammalian mutant with a camptothecin-resistant DNA topoisomerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5565–5569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K. Biology of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid topoisomerases. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):273–289. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.273-289.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Franco R. J. Inhibitors of DNA topoisomerases. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2253–2259. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gause G. F., Laiko A. V., Selesneva T. I. Yeast mutants with distorted cell membranes as tests in the screening for antitumor antibiotics. Cancer Treat Rep. 1976 May;60(5):637–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Hertzberg R., Hecht S., Liu L. F. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14873–14878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Liu L. F. Identification of mammalian DNA topoisomerase I as an intracellular target of the anticancer drug camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1722–1726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen E., Bonven B. J., Andoh T., Ishii K., Okada K., Bolund L., Westergaard O. Characterization of a camptothecin-resistant human DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3912–3916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Escherichia coli mutants thermosensitive for deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase subunit A: effects on deoxyribonucleic acid replication, transcription, and bacteriophage growth. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):424–435. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.424-435.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Yanagihara Y. Osmotic-sensitive mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as screening organisms for promutagens and procarcinogens. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1985 Apr;33(4):1576–1582. doi: 10.1248/cpb.33.1576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A., Nitiss J., Edwards C., Malone R. E. Meiosis can induce recombination in rad52 mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1986 Jul;113(3):531–550. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. E. DNA topoisomerases as targets for cancer therapy. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 15;34(24):4191–4195. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe T. C., Tewey K. M., Liu L. F. Identification of the breakage-reunion subunit of T4 DNA topoisomerase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9177–9181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Szostak J. W., Murray A. W. Cloning regulated yeast genes from a pool of lacZ fusions. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:253–269. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Szostak J. W. Specific Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes are expressed in response to DNA-damaging agents. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):75–84. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrash C., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., Sternglanz R. Cloning, characterization, and sequence of the yeast DNA topoisomerase I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4374–4378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosberg H. P. DNA topoisomerases: enzymes that control DNA conformation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;114:19–102. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70227-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Recent studies of DNA topoisomerases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 6;909(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintersberger U., Karwan A. Retardation of cell cycle progression in yeast cells recovering from DNA damage: a study at the single cell level. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):320–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00331596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwelling L. A., Silberman L., Estey E. Intercalator-induced, topoisomerase II-mediated DNA cleavage and its modification by antineoplastic antimetabolites. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986 Jul;12(7):1041–1047. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(86)90222-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



