Abstract
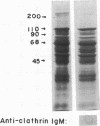
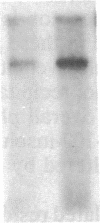
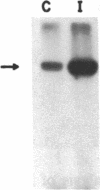
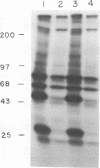
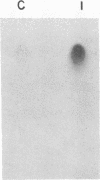
Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II)/mannose 6-phosphate (Man-6-P) receptors immunoprecipitated from purified plasma membranes of 32P-labeled rat adipocytes are markedly heterogenous in their phosphorylation state. Approximately 80% of the plasma membrane receptors are solubilized in 1% (vol/vol) Triton X-100 and are phosphorylated on serine residues at a stoichiometry of approximately 0.1-0.2 mol of phosphate per mol of receptor. In contrast, 15-20% of the receptors are Triton X-100-insoluble and are phosphorylated on serine and threonine residues at approximately 4 or 5 mol of phosphate per mol of receptor. This Triton X-100-insoluble membrane subfraction contains only 5% of the total plasma membrane protein and yet contains all of the clathrin heavy chain associated with plasma membrane, as detected by immunoblotting with a monoclonal antibody. Based on the relative yields of protein in the detergent-insoluble material, IGF-II/Man-6-P receptors are concentrated approximately equal to 3-fold in this clathrin-enriched subfraction. Insulin treatment of intact cells increased the total IGF-II/Man-6-P receptors in the Triton X-100-soluble fraction of the plasma membrane, whereas no change in receptor number in the detergent-insoluble fraction was seen. However, insulin markedly decreased the phosphorylation stoichiometry of the Triton X-100-insoluble receptors. Taken together, these results indicate that insulin decreases the phosphorylation state of a highly phosphorylated subpopulation of IGF-II/Man-6-P receptors on the plasma membrane. In addition, insulin action may prevent the concentration of these receptors in a clathrin-enriched membrane subfraction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar-Zvi D., Branton D. Clathrin-coated vesicles contain two protein kinase activities. Phosphorylation of clathrin beta-light chain by casein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9614–9621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J., Farquhar M. G. The mannose-6-phosphate receptor for lysosomal enzymes is concentrated in cis Golgi cisternae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):295–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90223-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruder G., Wiedenmann B. Identification of a distinct 9S form of soluble clathrin in cultured cells and tissues. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Jun;164(2):449–462. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvera S., Czech M. P. Mechanism of insulin action on membrane protein recycling: a selective decrease in the phosphorylation state of insulin-like growth factor II receptors in the cell surface membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7314–7318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvera S., Roach P. J., DePaoli-Roach A. A., Czech M. P. Insulin action inhibits insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II) receptor phosphorylation in H-35 hepatoma cells. IGF-II receptors isolated from insulin-treated cells exhibit enhanced in vitro phosphorylation by casein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3116–3122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuze H. J., Slot J. W., Strous G. J., Hasilik A., Von Figura K. Ultrastructural localization of the mannose 6-phosphate receptor in rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):2047–2054. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hari J., Pierce S. B., Morgan D. O., Sara V., Smith M. C., Roth R. A. The receptor for insulin-like growth factor II mediates an insulin-like response. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3367–3371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02658.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen J. H., Chestnut M. H., Beck K. A. The clathrin coat assembly polypeptide complex. Autophosphorylation and assembly activities. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3864–3871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. G., Pfeffer S. R., Coussens L., Tepper M. A., Brocklebank C. M., Mole J. E., Anderson J. K., Chen E., Czech M. P., Ullrich A. A single receptor binds both insulin-like growth factor II and mannose-6-phosphate. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1134–1137. doi: 10.1126/science.2964083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Edman J. C., Standring D. N., Fried V. A., Smith M. C., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Insulin-like growth factor II receptor as a multifunctional binding protein. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):301–307. doi: 10.1038/329301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottola C., Czech M. P. The type II insulin-like growth factor receptor does not mediate increased DNA synthesis in H-35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12705–12713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Czech M. P. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin-sensitive hexose transporters in intact rat adipocytes. Direct evidence that latent transporters become exposed to the extracellular space in response to insulin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8125–8133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Rozek L. M., Czech M. P. Direct demonstration of rapid insulin-like growth factor II Receptor internalization and recycling in rat adipocytes. Insulin stimulates 125I-insulin-like growth factor II degradation by modulating the IGF-II receptor recycling process. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9435–9442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer C. L., Pessin J. E., Massague J., Gitomer W., Czech M. P. Insulin action rapidly modulates the apparent affinity of the insulin-like growth factor II receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4824–4830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer C. L., Pessin J. E., Massague J., Gitomer W., Czech M. P. Insulin action rapidly modulates the apparent affinity of the insulin-like growth factor II receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4824–4830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M. Assembly of the mannose-6-phosphate receptor into reconstituted clathrin coats. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2457–2460. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M. Coated vesicles from human placenta carry ferritin, transferrin, and immunoglobulin G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):451–455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahagian G. G., Neufeld E. F. Biosynthesis and turnover of the mannose 6-phosphate receptor in cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7121–7128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usami M., Takahashi A., Kadota K. Protein kinase and its endogenous substrates in coated vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 24;798(3):306–312. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Simpson I. A., Rechler M. M., Cushman S. W. Potential mechanism of the stimulatory action of insulin on insulin-like growth factor II binding to the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent redistribution of receptors cycling between a large intracellular pool and the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8378–8383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Pastan I. H., Sahagian G. G., Jourdian G. W., Neufeld E. F. Morphologic study of the internalization of a lysosomal enzyme by the mannose 6-phosphate receptor in cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6967–6971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Figura K., Hasilik A. Lysosomal enzymes and their receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:167–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]