Abstract
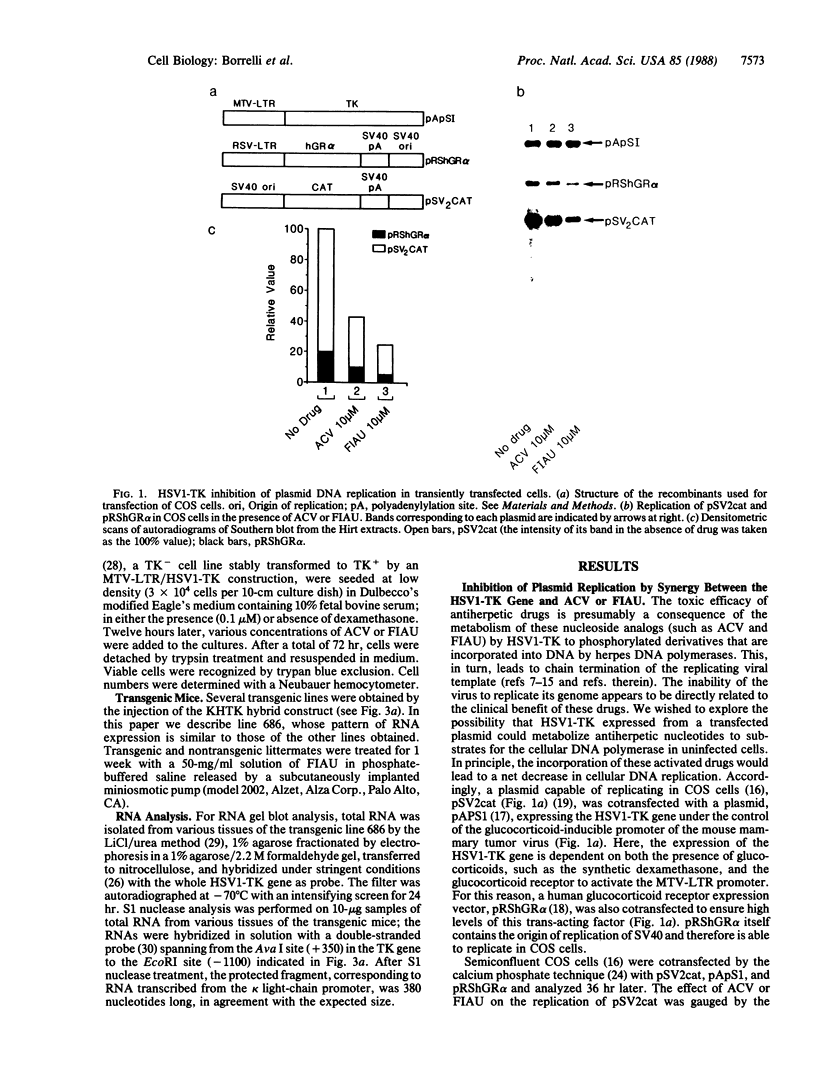
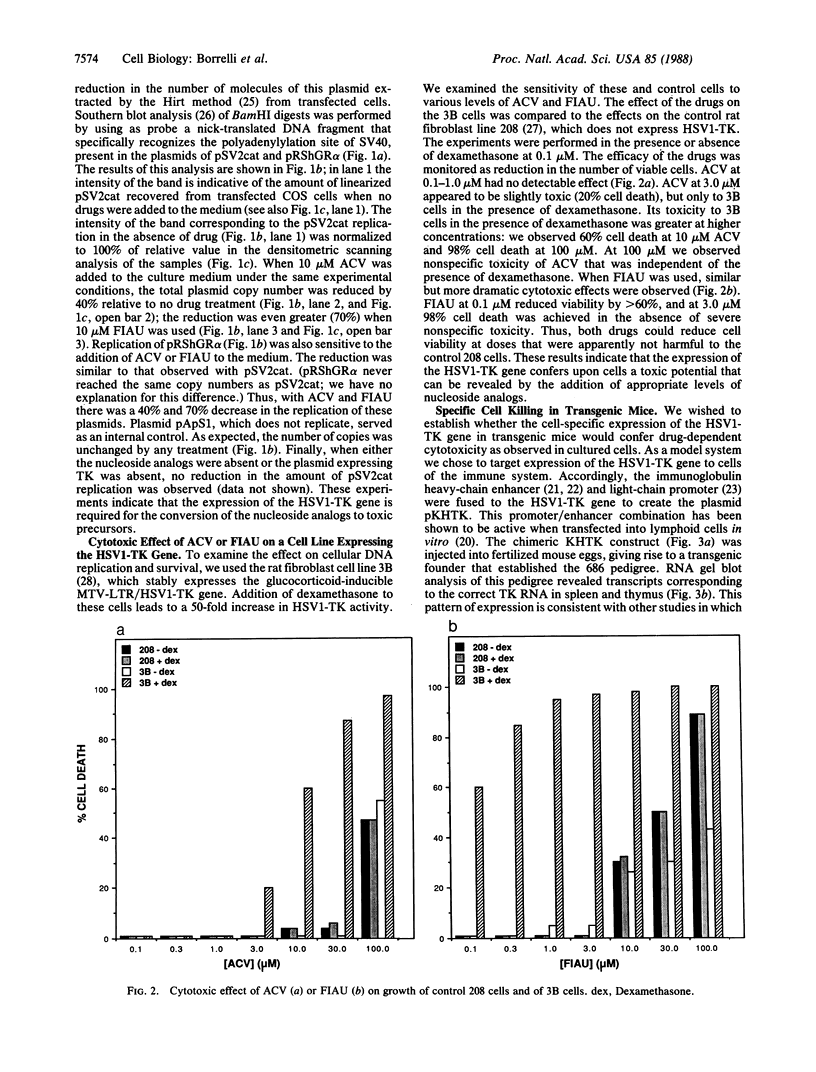
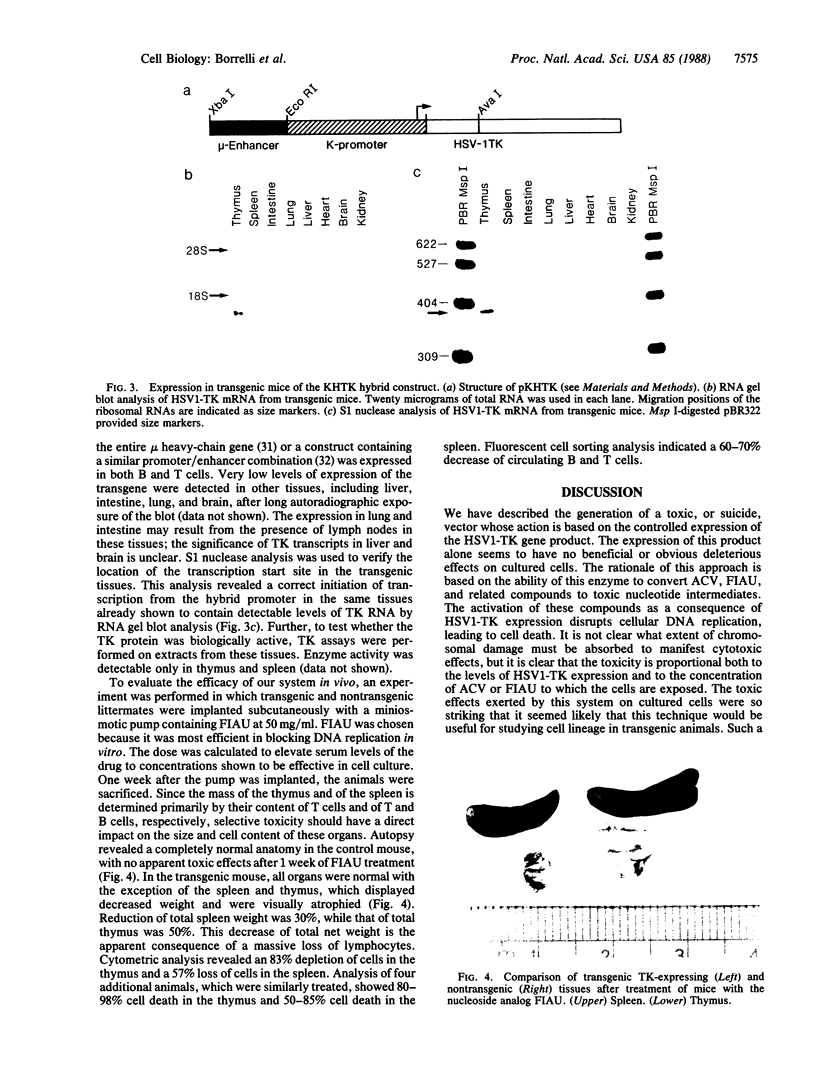
We have developed a toxic, or suicide, vector whose action is based on the targeted expression of the herpes simplex virus 1 thymidine kinase gene product in cultured cells or transgenic animals. This protein is able to convert nucleoside analogs such as acyclovir and 1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-beta-D-arabino-furanosyl)-5-iodouracil (FIAU) to toxic intermediates. The activation of these compounds disrupts cellular DNA replication, leading to rapid cell death. Neither acyclovir, FIAU, nor the herpes thymidine kinase alone is harmful to cells. This approach is simple and should have widespread applicability in studying lineage formation in cultured cells and transgenic animals.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman M. L., Clapoff S., Rossant J., Tsui L. C., Glode L. M., Maxwell I. H., Bernstein A. Genetic ablation: targeted expression of a toxin gene causes microphthalmia in transgenic mice. Science. 1987 Dec 11;238(4833):1563–1565. doi: 10.1126/science.3685993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. S., Amico L. A., Speelman D. J. Kinetics of the interaction of monophosphates of the antiviral nucleosides 2'-fluoro-1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylpyrimidine and (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine with thymidylate kinases from Vero cells and herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Nov;26(5):778–780. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.5.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Dutschman G., Fox J. J., Watanabe K. A., Machida H. Differential activity of potential antiviral nucleoside analogs on herpes simplex virus-induced and human cellular thymidine kinases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Sep;20(3):420–423. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.3.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion G. B. Mechanism of action and selectivity of acyclovir. Am J Med. 1982 Jul 20;73(1A):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe J. A., Keller P. M., Furman P. A., Miller R. L., Elion G. B. Thymidine kinase from herpes simplex virus phosphorylates the new antiviral compound, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8721–8727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Bich-Thuy L. T., Stafford J., Queen C. Synergism between immunoglobulin enhancers and promoters. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):383–385. doi: 10.1038/322383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlinger P., LeMeur M., Irrmann C., Renard P., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. B-lymphocyte targeting of gene expression in transgenic mice with the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6565–6577. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant A. J., Feinberg A., Chou T. C., Watanabe K. A., Fox J. J., Philips F. S. Incorporation of metabolites of 2'-fluoro-5-iodo-1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine into deoxyribonucleic acid of neoplastic and normal mammalian tissues. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Mar 15;31(6):1103–1108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90349-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Weaver D., Baltimore D., Costantini F. Introduction of a mu immunoglobulin gene into the mouse germ line: specific expression in lymphoid cells and synthesis of functional antibody. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):647–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansuri M. M., Ghazzouli I., Chen M. S., Howell H. G., Brodfuehrer P. R., Benigni D. A., Martin J. C. 1-(2-Deoxy-2-fluoro-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-ethyluracil. A highly selective antiherpes simplex agent. J Med Chem. 1987 May;30(5):867–871. doi: 10.1021/jm00388a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. The nucleotide sequence and transcript map of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Behringer R. R., Quaife C. J., Maxwell F., Maxwell I. H., Brinster R. L. Cell lineage ablation in transgenic mice by cell-specific expression of a toxin gene. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90497-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Transgenic mice. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):343–345. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quade K. Transformation of mammalian cells by avian myelocytomatosis virus and avian erythroblastosis virus. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):461–465. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90569-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Lira S. A., Swanson L., Borrelli E., Heyman R., Evans R. M. Transgenic mice: applications to the study of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:353–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Miller W. H., Miller R. L., Lambe C. U., Furman P. A. Inhibition of cellular alpha DNA polymerase and herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerases by the triphosphate of BW759U. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):191–194. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]