Abstract
The case-cohort study involves two-phase sampling: simple random sampling from an infinite super-population at phase one and stratified random sampling from a finite cohort at phase two. Standard analyses of case-cohort data involve solution of inverse probability weighted (IPW) estimating equations, with weights determined by the known phase two sampling fractions. The variance of parameter estimates in (semi)parametric models, including the Cox model, is the sum of two terms: (i) the model based variance of the usual estimates that would be calculated if full data were available for the entire cohort; and (ii) the design based variance from IPW estimation of the unknown cohort total of the efficient influence function (IF) contributions. This second variance component may be reduced by adjusting the sampling weights, either by calibration to known cohort totals of auxiliary variables correlated with the IF contributions or by their estimation using these same auxiliary variables. Both adjustment methods are implemented in the R survey package. We derive the limit laws of coefficients estimated using adjusted weights. The asymptotic results suggest practical methods for construction of auxiliary variables that are evaluated by simulation of case-cohort samples from the National Wilms Tumor Study and by log-linear modeling of case-cohort data from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Although not semiparametric efficient, estimators based on adjusted weights may come close to achieving full efficiency within the class of augmented IPW estimators.
Keywords: Calibration, Case-cohort, Estimation, Log-linear model, Semiparametric
1 Introduction
Two phase stratified sampling designs were proposed by Neyman (1938) for estimation of the finite population mean of a target variable that was difficult to measure. The average amount of money spent on food by each family residing in a given district was mentioned as a possible target of inference. At the first phase, a large sample is drawn from the population. Information on an auxiliary variable, easier to measure but correlated with the target variable, is collected and used to stratify the sample. At phase two, random sub-samples are drawn without replacement from each stratum for measurement of the target variable. The technique is widely used in survey sampling to reduce costs.
Two phase designs have also been proposed for use in epidemiology. They are particularly valuable when a large cohort (the phase one sample) is under surveillance for a disease event of interest and sampling from the cohort is required to obtain information on additional covariates. White (1982) proposed stratifying the second phase of sampling on both disease status and exposure when more information was needed on confounding factors. She argued that, when both disease and exposure were rare, this was more efficient than the standard case-control design that stratified on disease status alone. Borgan et al. (2000) considered exposure stratified versions of the case-cohort study (Prentice, 1986).
In these epidemiologic applications, the target of inference is not a finite population mean but rather parameters in a probability model – an infinite “superpopulation” from which the cohort is regarded as constituting a phase one random sample. For the stratified case-control study the parameters of interest are odds ratios, exponentiated coefficients in a logistic regression model. For the stratified case-cohort study they are hazard ratios, exponentiated coefficients in the Cox (1972) proportional hazards model, and often also the baseline hazard function.
Current standard practice for estimation of regression coefficients in the Cox model is solution of a Horvitz and Thompson (1952) inverse probability weighted (IPW) version of the Cox (1975) partial likelihood equations (Barlow, 1994; Barlow et al., 1999; Borgan et al., 2000). Survey statisticians advocate this approach on grounds that when the model is misspecified, as is generally the case, it consistently estimates the parameters that would be estimated by fitting the “wrong” model to the cohort were complete data available fot it (Binder, 1992). The Horvitz-Thompson approach is known to be inefficient, however, sometimes seriously so (Robins et al., 1994). One reason is that it often ignores much of the information available for the cohort. The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) investigators, for example, conduct numerous stratified case-control and case-cohort studies nested in their cohort of 15,972 subjects sampled from four U.S. communities (The ARIC Investigators 1989). Information on standard risk factors for cardiovascular disease is available for nearly the entire cohort from interviews, bioassays and imaging studies conducted at baseline. Additional information on candidate genes or biomarkers is collected for a phase two cohort random sample (CRS), also known as a sub-cohort, that is stratified on demographic factors and sometimes also on carotid wall thickness. Even when enriched by disease cases that occur outside the CRS, the phase two sample typically contains no more than 10–15% of the cohort. ARIC analyses have ignored information on adjustment factors available for the great majority of potential controls.
Recently improved communication between biostatisticians and survey methodologists has led to a better understanding of the two phase sampling designs used in epidemiology and to improved methods of analysis. Statistical efficiency may be enhanced by adjustment of the standard Horvitz-Thompson sampling weights, either by calibrating the weights to cohort totals of auxiliary variables (Deville and Särndal, 1992) or by using these variables to estimate the weights (Robins et al., 1994). We describe some theory and methods for calibration and estimation of weights when fitting semiparametric models that apply a fortiori to the fitting of parametric models. The resulting improvements in precision are illustrated by fitting a log-linear model to data from an ARIC study of coronary heart disease (Ballantyne et al., 2004). A companion paper for epidemiologists (Breslow et al., 2009) investigates the corresponding gains in efficiency of hazard ratios estimated from the ARIC data. By simulation of case-cohort samples from the National Wilms Tumor Study (NWTS) (D’Angio et al., 1989; Green et al., 1998), we also illustrate the problems that may occur when one attempts to use too many auxiliary variables for calibration or estimation of the weights.
A proposal is made for construction of auxiliary variables with the goal of achieving approximate optimality within the class of augmented IPW estimators (Wang and Chen, 2001). We do not consider semiparametric efficient methods of estimation that make greater use of the assumptions of the fitted model, usually at the price of introducing bias if the model does not hold. Such methods are reasonably well developed for logistic regression analysis of stratified case-control data when the covariates available for the entire cohort are all discrete (Scott and Wild, 1997; Breslow and Holubkov, 1997). Semiparametric efficient methods for estimation of hazard ratios from stratified case-cohort samples, which pose greater computational problems, are currently under development; see, for example, Nan (2004); Scheike and Martinussen (2004); Zeng and Lin (2007).
2 Properties of Horvitz-Thompson Estimators
This section reviews results of Breslow and Wellner (2007). Suppose N subjects are sampled at random from an infinite population and indexed by i = 1, …, N. These subjects constitute the (main) cohort following the first phase of sampling. Denote by V ∈ 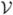 a vector of random variables that is observed for all cohort members. Suppose
a vector of random variables that is observed for all cohort members. Suppose 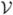 is partitioned
is partitioned 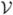 = V1 ∪···∪
= V1 ∪···∪ 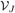 and the cohort is divided correspondingly into J strata, with the ith subject in stratum j if Vi ∈
and the cohort is divided correspondingly into J strata, with the ith subject in stratum j if Vi ∈ 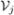 . Let Nj denote the number of subjects in the jth stratum, j = 1, …, J, so N = N1 + … + NJ. For the epidemiologic designs, one stratum typically consists of the disease cases while the remaining strata contain the controls. At the second phase of sampling nj ≤ Nj subjects are sampled at random without replacement from the jth stratum, with sampling for different strata conducted independently. Additional variables are observed for the n = n1 + … + nJ subjects sampled at phase two. Let W ∈
. Let Nj denote the number of subjects in the jth stratum, j = 1, …, J, so N = N1 + … + NJ. For the epidemiologic designs, one stratum typically consists of the disease cases while the remaining strata contain the controls. At the second phase of sampling nj ≤ Nj subjects are sampled at random without replacement from the jth stratum, with sampling for different strata conducted independently. Additional variables are observed for the n = n1 + … + nJ subjects sampled at phase two. Let W ∈ 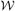 denote the vector of random variables that are potentially available for the cohort, namely, V plus the additional variables known only for the n subjects sampled at phase two. We denote by ΣN = σ[W1, …, WN] the sigma field of information potentially available for everyone. An important aspect of this formulation for the case-cohort study is that it accomodates random sampling of both cases and controls. Often cases (and controls) are absent from the phase two sample because some data are missing by chance rather than by design, for example, because of uninformative biological samples (Mark and Katki, 2006). The methods described herein still apply provided that such absence is random within defined strata.
denote the vector of random variables that are potentially available for the cohort, namely, V plus the additional variables known only for the n subjects sampled at phase two. We denote by ΣN = σ[W1, …, WN] the sigma field of information potentially available for everyone. An important aspect of this formulation for the case-cohort study is that it accomodates random sampling of both cases and controls. Often cases (and controls) are absent from the phase two sample because some data are missing by chance rather than by design, for example, because of uninformative biological samples (Mark and Katki, 2006). The methods described herein still apply provided that such absence is random within defined strata.
Let ξi be a binary indicator of whether (ξi = 1) or not (ξi = 0) the ith subject is sampled at phase two and let πi = Pr(ξi = 1) be the probability of such sampling. Thus, if j(i) denotes the stratum of the ith subject, πi = nj(i)/Nj(i). Furthermore, for any pair i ≠ i′,
| (1) |
The goal of the investigation is to make inferences about parameters in a (superpopulation) model for a random variable X = X(W) ∈ 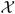 which is completely observed for subjects in the CRS but in general only partially observed for those in the cohort. The model may be parametric or semiparametric. In the latter case it is specified by probability distributions Pθ,η for X that are indexed by a Euclidean parameter θ ∈ Θ ⊂ ℝp and an infinite dimensional parameter η ∈ Ξ. The paradigm is the Cox model, where θ denotes the vector of regression coefficients and η the baseline cumulative hazard function. We denote by P0 = Pθ0,η0 the “true” model and use operator notation Pf = EP f (X) for expectations.
which is completely observed for subjects in the CRS but in general only partially observed for those in the cohort. The model may be parametric or semiparametric. In the latter case it is specified by probability distributions Pθ,η for X that are indexed by a Euclidean parameter θ ∈ Θ ⊂ ℝp and an infinite dimensional parameter η ∈ Ξ. The paradigm is the Cox model, where θ denotes the vector of regression coefficients and η the baseline cumulative hazard function. We denote by P0 = Pθ0,η0 the “true” model and use operator notation Pf = EP f (X) for expectations.
Let ℓ̇θ,η denote the usual parametric likelihood score for θ and Bθ,η denote the score operator (Begun et al., 1983) that maps one dimensional submodels for η, indexed by directions h ∈ ℋ from which η’s in the submodel approach η0, into the corresponding score functions. If X was known for all N cohort subjects, parameters could be estimated by solving likelihood equations (van der Vaart, 1998, Sect. 25.12)
| (2) |
| (3) |
for estimators (θ̃N, η̃N), where ℙN denotes empirical measure based on X1, …, XN. Assumptions are made at least sufficient to guarantee that is asymptotically Gaussian. For two phase data, ℙN in (2) and (3) is replaced by IPW empirical measure defined by
| (4) |
where δXi is Dirac measure that puts unit mass on Xi, and the solution is denoted by (θ̂N, η̂N). When applied with the Cox model this leads to an IPW version of the so called Breslow (1974) estimator of the cumulative hazard function and to the same IPW version of the partial-likelihood equations that has been proposed by Binder (1992) and Lin (2000), among others.
Denote the efficient information by and the efficient influence function by , where is the adjunct of B0. Invertibility of the information operator is implicit in the assumption that η is estimable at a rate. The principal result of Breslow and Wellner (2007, p. 94) is
| (5) |
The first term on the right hand side of (5) represents the usual asymptotic expansion for the unobservable estimator θ̃N. It converges in distribution to 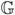 ℓ̃0, where
ℓ̃0, where 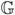 is the P0-Brownian bridge (van der Vaart and Wellner, 1996, Sect. 2.1). Conditionally on ΣN, and hence considered as a random function only of the sampling indicators ξi, the second term converges similarly by virtue of the weak convergence
is the P0-Brownian bridge (van der Vaart and Wellner, 1996, Sect. 2.1). Conditionally on ΣN, and hence considered as a random function only of the sampling indicators ξi, the second term converges similarly by virtue of the weak convergence
| (6) |
Here ℱ is a (Donsker) class of functions that contains the likelihood scores for (θ, η) in a neighborhood of (θ0, η0); νj = lim Nj/N is the fraction of the population in stratum j; pj = lim nj/Nj is the limiting samping fraction; and 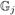 denotes the Brownian bridge process restricted to stratum j, i.e., based on the distribution P0|j(·) = E(·|V ∈
denotes the Brownian bridge process restricted to stratum j, i.e., based on the distribution P0|j(·) = E(·|V ∈ 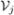 ). Furthermore, the processes {
). Furthermore, the processes {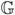 ,
, 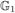 , …,
, …, 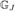 } are mutually independent.
} are mutually independent.
The asymptotic variance of θ̂N is thus the sum of two components, one corresponding to each phase of sampling. The first component is the usual variability of an estimator based on random sampling from an infinite population (model) assuming no missing data. It is not amenable to modification using methods described here. The second component, which is amenable to improvement, represents the additional variability stemming from the fact that some components of X are observable only at phase two. It is the normalized design based variance of the standard Horvitz-Thompson estimator of an unknown finite population total, namely, the total of the efficient influence function (IF) contributions for all N phase one subjects. Similar results have appeared in the sample survey literature for estimation of Euclidean parameters by solving estimating equations that contain no nuisance functions (Rao et al., 2002; Rubin-Bleuer and Kratina, 2005). Equations (5) and (6) provide the extension to semiparametric models under two-phase stratified sampling, with the semiparametric efficient influence function ℓ̃0 playing the role of the ordinary parametric IF. For phase two subjects the IF contributions ℓ̃0(xi) may be approximated with negligible error from the observed xi by dfbeta’s (Therneau and Grambsch, 2000, p. 155) defined by
| (7) |
Explicit formulae are available for the Cox model (Cain and Lange, 1984; van der Vaart, 1998, Sect. 25.12.1). Values may be obtained from standard statistical packages as a type of residual following a model fit. In R, for example, they are obtained with the command db<-resid(model.fit, type=’dfbeta’).
3 Calibration and Estimation of the Weights
Survey statisticians are adept at improving estimates of finite population (here, cohort or phase one) totals when auxiliary variables, closely correlated with the target variable, are available for the entire population. We consider ℓ̃0(xi) to be the vector of target variables, denote by zi = z(vi) a q-vector of auxiliary variables and set . Some suggestions for choice of the zi are given later. The idea behind calibration is to modify the design weights to new weights wi = gidi such that the wi and di are as close as possible yet the phase one totals ztot of the auxiliary variables are exactly estimated. If G(w, d) denotes a distance measure, the problem is thus to minimize subject to the constraints
| (8) |
known as the calibration equations. Here we consider G(w, d) = (w−d)2/2d and G(w, d) = w log(w/d)−w+d, the Poisson deviance. See Deville and Särndal (1992) for other possibilities.
Let λ be a q-vector of Lagrange multipliers corresponding to the constraints (8). For G(w, d) = (w−d)2/2d, solution of the constrained minimization problem by standard calculus yields gi = 1 − λTzi which, when substituted into (8), leads to an explicit solution for λ:
| (9) |
The estimator obtained with the resulting weights is known as the generalized regression or GREG estimator (Särndal et al., 1989). When used to estimate a finite population total via
the GREG estimator is the finite population sum of the fitted values plus the Horvitz-Thompson estimator of the sum of the residuals.
When G(w, d) is the Poisson deviance, solution of the minimization problem gives gi = exp(−λTzi) and the calibration equations, now solved iteratively for λ, become
Under standard regularity assumptions (Isaki and Fuller, 1982) applicable to design based inference, Deville and Särndal (1992, p. 379) show that the solution generally satisfies
| (10) |
| (11) |
When the calibrated weights are always positive (with GREG they may not be) and the resulting estimator is known as the (generalized) raking estimator. Since under mild regularity conditions (see Sect. 7, Appendix) , the gi converge to 1 and hence the estimated wi converge to the design weights di.
The asymptotic properties of the estimator θ̂N (λ̂N) based on calibrated weights may be derived from results in Breslow and Wellner (2008) by letting the Lagrange multipliers λ play the role of “nuisance” parameters α. Regardless of which distance function is used for calibration (Deville and Särndal, 1992), one finds
| (12) |
Here is the least squares projection of each component of ℓ̃0 onto the linear subspace of L2(P0) spanned by components of Z. Hence the effect of calibration on the (asymptotic) phase two component of variance is to replace ℓ̃0 by the residual after its (population) least squares regression on Z. The Appendix contains a brief derivation of (12).
The asymptotic variance of the calibration estimator could be further reduced if we replaced Q in the jth summand of (12) by
, the projection with respect to the conditional distribution of the data in stratum. This is because, with
, QjZ minimizes Varj (ℓ̃0 − AZ) among all linear functions of Z. Consequently, instead of calibrating to the overall total, one might consider calibrating to the subtotals of z within each stratum. This is accomplished by defining a new q × J vector of calibration variables by
where Zj = 1(V ∈ 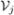 )Z and setting
. Then
and
)Z and setting
. Then
and 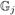 (ℓ̃ − Q̃Z̃) =
(ℓ̃ − Q̃Z̃) = 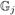 (ℓ̃ − QjZ) as desired. However, since this may greatly increase the number of calibration variables, the increased variability in the weights may result in an estimator with increased rather than reduced finite sample variance in all but the largest samples. See Sect. 5 below.
(ℓ̃ − QjZ) as desired. However, since this may greatly increase the number of calibration variables, the increased variability in the weights may result in an estimator with increased rather than reduced finite sample variance in all but the largest samples. See Sect. 5 below.
Biostatisticians (Robins et al., 1994) have also suggested adjustment of the sampling weights to improve efficiency, namely, by estimating the weights using a correct parametric model π(zi; α) = Pr(ξi = 1|Zi = zi). For two-phase stratified sampling the model is rendered correct by including the J binary stratum indicators among the adjustment variables z. Logistic regression is typically used for π(zi; α), in which case the estimating equations for α become
| (13) |
where wi = p(zi; α̂N)−1 denotes the weight estimated for subject i. Note the parallel with the calibration equations (8): the weights appear on opposite sides. Results of Breslow and Wellner (2008) may again be used to derive the asymptotic distribution of θ̂N (α̂N) under two-phase stratified sampling. See the Appendix for a brief derivation of the weak convergence
| (14) |
Note that R is also a projection matrix, now of components of ℓ̃0 onto the linear span of π0Z with respect to the distribution Pπ defined by .
Previous discussions of Horvitz-Thompson methods with estimated weights have derived their properties for Bernoulli sampling, whereby the N phase one subjects are selected independently for membership in the phase two sample with known sampling probabilities π0(v) (Robins et al., 1994; Mark and Katki, 2006). This facilitates comparison of asymptotic properties in terms of influence functions. Using the asymptotic expansions in the Appendix, which hold for both sampling schemes, the influence function under Bernoulli sampling for the estimator based on calibrated weights is readily shown to equal
| (15) |
where π0(v) = pj for v ∈ 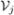 . The asymptotic phase two variance under Bernoulli sampling is therefore
. The limit laws under the two sampling schemes, however, are subtly different. The asymptotic phase two variance implied by (12) for two phase stratified sampling, namely,
, is less than that for Bernoulli sampling.
. The asymptotic phase two variance under Bernoulli sampling is therefore
. The limit laws under the two sampling schemes, however, are subtly different. The asymptotic phase two variance implied by (12) for two phase stratified sampling, namely,
, is less than that for Bernoulli sampling.
Expression (15) shows immediately how to choose z. Selecting zopt = E(ℓ̃0|V = v), we find Qzopt = zopt and conclude that the class of calibrated IPW estimators contains the optimal member of the class of augmented IPW estimators considered by Robins et al. (1994), Wang and Chen (2001) and Mark and Katki (2006). Influence functions for this class take the form (15) with Qz(v) replaced by φ(v), an arbitrary function of v, and the choice φ = zopt minimizes the asymptotic variance. Similarly, the influence function when weights are estimated using auxiliary variables z has the form (15) where Qz is replaced by Rπ0z. To obtain the optimal influence function, therefore, one would include the variables zopt/π0(v) together with the stratum indicators as predictors of the weights.
Calculation of zopt = E(ℓ̃0|V = v) requires knowledge of the conditional distribution [X|V], which is generally unavailable. One approach to approximating zopt is to specify parametric regression models for the components of ℓ̃0 on V (Robins et al., 1994, Sect. 2.7) and to estimate the parameters by IPW regression of the dfbeta on V using the second phase data. Kulich and Lin (2004) proposed an alternative “plug in” method for approximating the conditional expectation that we adopt here. It is likely to be most useful when there are only one or two partially missing variables. The steps are as follows:
Using (linear or logistic) regression models fitted by IPW to the phase two data, develop and fit parametric models to predict each partially missing variable (known only at phase two) given variables v known for all.
Use the models in step 1 to impute values x̂i for everyone in the phase one sample; variables already known for everyone are used in their original form.
Fit the interest model Pθ,η(X) to the phase one sample using the imputed values x̂i.
Construct auxiliary variables z as imputed dfbetas (7) from the model fitted in step 3; these are estimates of zopt.
Estimate θ using weights adjusted to the zi.
Examples of this approach are given in the companion paper (Breslow et al., 2009) and in Sect. 5 below.
An interesting special case arises when V is discrete with K > J levels, say V ∈ {1, …, K}. Define ZT = (1(V = 1), …, 1(V = K)). Then both calibration and estimation lead to the same adjusted weights, namely, the inverse sampling fractions within each of the K strata defined by levels of V. This is a finer stratification than that actually used for sampling. Since , where P0|k is defined analogously to P0|j, it follows that Horwitz-Thompson estimation based on the finer stratification yields the most efficient estimate within the augmented IPW class. Survey statisticians refer to this method as post-stratification.
4 Log-linear Modeling
We first consider log-linear modeling of multinomial outcomes δ corresponding to occupancy of one of L cells (ℓ = 1, …, L) in a multidimensional table, with calibration to marginal totals rather than to IF contributions in a regression model. The outcome for subject i is where δi,ℓ = 1 if the subject occupies cell ℓ, otherwise δi,ℓ = 0. Redefine X to denote a L × p design matrix (p < L), without the intercept to maintain identifiability, and let θ ∈ Θ ⊂ Rp be a parameter vector such that, with xℓ denoting the ℓth row of X,
| (16) |
The fully parametric model Pθ(δ) thus has likelihood
Our results for semiparametric models and two-phase stratified samples apply to this situation with ℓ̃θ denoting the ordinary (parametric) influence function rather than the semiparametric efficient one. Details have been worked out by Kovacevic and Rai (2002) for joint model-design based inference for parameters in log-linear models under more general sampling designs. With p(θ) defined by pT(θ) = (p1(θ), …, pL(θ)) denoting the vector of cell occupancy probabilites under the model, the likelihood score is ℓ̇θ = XT[δ − p(θ)]. With denoting the (unobserved) vector of table frequencies for the phase one sample, the MLE θ̃N would be obtained from (2) as the solution to ℙN ℓ̇θ(δi) = XT[O − p(θ)N] = 0. The equation to be solved for θ̂N is instead where denotes the estimated vector of frequencies and (= N for two-phase stratified sampling) is the estimated phase one total. Thus one simply fits the log-linear model to the estimated table of frequencies.
With denoting the parametric information and the parametric influence function, one can use equations (5) and (6) to determine the asymptotic variance of θ̂N. The phase one component of variance is estimated by (NIθ̂N)−1 or more robustly
by
where p̂ = p(θ̂N) and eℓ denotes the L-vector with one in the ℓth position and zeroes elsewhere. Similarly, if Oj,ℓ denotes the number of phase two subjects in stratum j observed to occupy cell ℓ of the table, then the phase two component of variance is estimated by
and p̂(j) is the observed vector of cell occupancy fractions in stratum j.
As an illustration, we studied the association between high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) and lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) using data from the ARIC case-cohort study of Ballantyne et al. (2004). Measurements on HDL-C were available for the entire cohort of 12,345 participants who had plasma collected at their second follow-up visit and were free of coronary heart disease (CHD) at that time. Levels of Lp-PLA2 were determined by assay of the stored plasma samples for the 604 who developed CHD during the 6–8 years of additional follow-up and for 732 controls who had been sampled for the cohort random sample after stratification on gender, age and ethnicity (two levels each). The ARIC investigators were interested in whether their data would support the finding by Persson et al. (2007) of a negative association between Lp-PLA2, a new biomarker of inflammation, and the well known risk factor HDL-C. Sampling weights for the nine sampling strata ranged from 1.2 for the stratum consisting of the CHD cases to 32 for white female controls under age 55. (The CHD cases were effectively sampled at less than 100% since some plasma samples were uninformative.)
All statistical analyses were carried out using the R survey package (Lumley, 2004) available from http://cran.r-project.org/. Table 1A shows the frequencies for the cross-classification of the two risk factors, estimated together with their standard errors using standard sampling weights. They were obtained using IPW estimates of population means that are implemented in the svytotal function. Note that the marginal HDL-C totals of the frequencies estimated using standard weights do not agree with the actual (integral) HDL-C totals for the cohort.
Table 1.
Association between HDL-C and Lp-PLA2: Standard vs Calibrated Weights
| A. Standard weights | B. Calibrated weights | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDL-C (mg/L) | Lp-PLA2 (μG/L) |
Lp-PLA2 (μG/L) |
||||||
| 0–0.309 | 0.31–0.42 | 0.421–1 | Total | 0–0.309 | 0.31–0.42 | 0.421–1 | Total | |
| Estimated frequencies | Estimated frequencies | |||||||
| <40 | 701.4 | 938.6 | 1,561.3 | 3,201.3 | 739.0 | 988.9 | 1,645.0 | 3,373 |
| 40–59.0 | 1,764.4 | 2,310.2 | 2,175.3 | 6,249.9 | 1,665.0 | 2,180.1 | 2,052.9 | 5,898 |
| ≥60.0 | 1,569.6 | 909.4 | 414.8 | 2,893.8 | 1,667.4 | 966.0 | 440.6 | 3,074 |
| Total | 4,035.4 | 4,158.2 | 4,154.4 | 12,345 | 4,071.4 | 4,135.1 | 4,138.5 | 12,345 |
| Standard errors | Standard errors | |||||||
| <40 | 105.7 | 111.3 | 138.9 | 185.4 | 99.7 | 105.0 | 117.7 | 49.5 |
| 40–59.0 | 166.9 | 187.5 | 170.0 | 234.1 | 144.4 | 155.9 | 146.7 | 55.5 |
| ≥60.0 | 164.2 | 124.1 | 81.9 | 197.7 | 128.0 | 117.0 | 83.1 | 48.0 |
| Total | 217.3 | 222.2 | 206.1 | 212.9 | 220.3 | 201.8 | ||
To formally assess the statistical significance of the clearly negative association, we fit a log-linear model with a term for a linear×linear interaction. The design matrix was specified as
The first four columns of X (rows of XT) describe the standard independence model, a log-linear model with main effects for rows (HDL-C) and columns (Lp-PLA2). The interaction term in the last column corresponds to the single degree of freedom linear by linear association test for dependence in a two-way table. Fitting the model using svyloglin, the interaction coefficient was −0.5323 with standard error 0.0734 yielding a test statistic Z2 = 52.6, p = 4 × 10−13. Expanding the model to saturation and testing for dependence using a Wald statistic yielded χ2 = 60.1, DF = 4, p = 3 × 10−12. Most of the association was explained by the linear interaction.
Table 1B shows the tabular frequencies estimated after calibration of the weights to the marginal totals of HDL-C using the generalized raking procedure described in Sect. 3. These are the classical raking estimates that are proportionally adjusted to the known marginal totals (Deming and Stephan, 1940) so that the estimated and actual marginal (HDL-C) totals do now agree. The standard errors of the estimated marginal totals reflect only the binomial sampling variability at phase one; the phase two component is zero. With one minor exception where the estimated frequency also increased, the standard errors of frequencies in the cross-classification decreased markedly. There was no meaningful change in the precision of estimation of the marginal totals of Lp-PLA2, reflecting the fact that no phase one information about this margin was utilized. Fitting the interaction model with calibrated weights led to a slightly more significant linear by linear association test, Z2 = 54.0, p = 2 × 10−13, but there was virtually no change in the 4 DF test (χ2 = 60.2).
Results of estimating the table frequencies using estimated weights (not shown) were similar to those obtainned with calibrated weights in terms of precision. The estimated marginal HDL-C totals were 3412.9, 6014.9 and 2915.2, however, and hence differed from the actual totals shown in the margin of Table 2B. Nonetheless, the phase two contributions to the SEs of the marginal totals were still neglible if not absolutely zero. For the three levels of HDL-C, the SEs reported by svytotal were 49.693, 55.534 and 47.190, whereas the SEs based only on phase one variability were 49.687, 55.527 and 47.184.
Table 2.
Average Total Standard Error (SE) and Empirical Phase Two Standard Error (RMSE). Adjustment to Within Stratum Totals of Estimated Influence Function Contributions
| Cox | Standard weights | Calibrated weights* | Estimated weights | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model term | SE | SE | RMSE | SE | RMSE | SE | RMSE |
| UH | .503 | .537 | .188 | .572 | .157 | .517 | .146 |
| Age0 (yr) | .321 | .360 | .158 | .429 | .228 | .323 | .085 |
| Age1 (yr) | .015 | .026 | .021 | .024 | .030 | .016 | .016 |
| Stage (III, IV vs I, II) | .259 | .346 | .231 | .365 | .265 | .271 | .116 |
| Diameter (cm) | .015 | .021 | .015 | .021 | .018 | .015 | .008 |
| Stage × Diameter | .020 | .029 | .020 | .028 | .020 | .021 | .010 |
| UH×Age0 | .552 | .612 | .287 | .668 | .321 | .587 | .258 |
| UH×Age1 | .033 | .051 | .048 | .053 | .060 | .046 | .050 |
Based on 998 replications for which coefficients were obtained
See the companion paper for Cox regression analyses of the ARIC data.
5 Simulation Study of Cox Regression Modeling
To study the effect of different methods of adjustment of sampling weights on the performance of Cox regression coefficients estimated with the svycoxph function, we used data on N = 3, 915 NWTS patients that were also considered in the the companion paper. The data and sample R code are available from the website http://faculty.washington.edu/norm/software.html. These data were also used by Kulich and Lin (2004), whom we follow in choice of models, to illustrate their “combined, doubly weighted” estimator. The goal was to estimate hazards associated with prognostic variables in a failure time analysis, with event-free survival (time from diagnosis to disease progression or death) as the endpoint. The most important prognostic factor was histologic subtype, classified as favorable (FH) or unfavorable histology (UH). Information on histology was available both from the central pathology reference laboratory and from the institution where the patient was treated. This made possible the simulation of exposure stratified case-cohort studies (Borgan et al., 2000), treating the central pathology measurement as known only for the phase two sample and the institutional pathology measurement as one of the variables used for stratification of the sample and adjustment of the weights. The Cox model was first fit to the entire cohort, yielding the normally unobservable θ̃N for comparison with the two-phase estimates θ̂N. Mean squared differences (θ̃N − θ̂N)2 averaged over 10,000 phase two samples provided an empirical estimate of the phase two variance component.
Phase two sampling was stratified on the basis of institutional histology, stage of disease (low=I, II vs high=III, IV), age at diagnosis (babies vs 1+ year olds) and whether (cases) or not (controls) the patient had relapsed or died before the end of follow-up. All cases and all but the three largest control strata were included in their entirety in the phase two sample: 120 of 452 FH control babies with low stage disease; 160 of 1,620 1+ year old controls with low stage disease; and 120 of 914 1+ year old controls with high stage disease were sampled at random for phase two. This provided 660 phase two controls for comparison with the 669 cases and a phase two sample size of n = 1, 329. The Cox model contained terms for histology (UH), age as a linear spline with separate slopes for babies (Age0) and older children (Age1), a binary indicator of high vs low stage, tumor diameter (cm) and interactions between stage and diameter and between histology and the two age terms.
Auxiliary variables for calibration and estimation of the weights were constructed using the procedure described at the end of Sect. 3. For each of the 10,000 simulated phase two samples we first used the svyglm function with standard sampling weights to predict histology (central pathology) based on a logistic regression model containing terms for institutional (local) histology (the main predictor), stage, age greater or less than 10 years, study (NWTS-3 vs NWTS-4) and an interaction between local UH and stage. The logistic regression coefficients were then used in conjunction with phase one data to yield a predicted probability of having UH for each of the 3,915 phase one subjects. The Cox model was fit using the ordinary coxph procedure with this predicted probability in place of the binary UH covariate. Estimated IF contributions (dfbetas) were extracted, augmented by 1 to ensure that they were positive, and used as the auxiliary variables z for calibration. For estimation the dfbetas were divided by the known sampling probabilities before adding 1, and combined with the stratum indicators in the prediction equation.
Here is a brief summary of results of the initial simulation study as reported in the companion paper (Breslow et al., 2009). Calibration again used the raking procedure. Mean values of the regression coefficients were nearly identical for the three case-cohort estimation methods (standard, calibrated and estimated weights) and close to those estimated for the entire cohort. Both calibration and estimation reduced the phase two variance components, sometimes to negligible levels. For example, the phase two standard error of the Age0 coefficient was reduced from 0.162 with standard weights to 0.037 with calibrated and to 0.061 with estimated weights. The phase two SE for the UH main effect was reduced by 29% with calibration and to 28% with estimation. There were lesser reductions for the interaction with Age0.
Additional simulations based on only 1,000 replications were carried out to determine whether the modification of the auxiliary variables suggested in the paragraph following equation (12) in Sect. 3, intended to reduce the asymptotic phase two variance further under two phase stratified sampling, would actually improve estimates in finite samples. This increased the number of adjustment variables from 8, the number of terms in the Cox model, to 32 in view of the four sampling strata. Substantial numerical difficulties were experienced with the larger number of adjustment variables, particularly for calibration. The survey option to force convergence of the iterative solution of the calibration equations, by returning the weights after 200 iterations, was required to prevent otherwise frequent failure of the algorithm but led to outliers in the estimated regression coefficients and the failure of the svycoxph procedure in 2 samples. This increased the phase two variability in comparison with calibration based on a smaller number of variables.
Results are shown in Table 2. The column labeled Cox SE shows the robust (Lin and Wei, 1989) standard errors for the Cox model fit to the entire cohort. These were noticeably larger than the model based standard errors, reflecting a lack of proportionality for several covariates. The phase one variance components estimated by svycoxph also are the robust versions, emphasizing the sample survey view that the goal is to approximate the results of fitting a possibly misspecified model to the entire cohort. The columns labeled SE for the various two-phase case-cohort methods are averages of the total estimated standard errors, incorporating both phase one and phase two variability. The columns labeled RMSE contain the empirical phase two standard errors. For most coefficients, in stark contrast to results obtained with just 8 adjustment variables, the RMSE using calibrated weights were larger even than with standard sampling weights. The svycoxph procedure returned regression coefficients for all 1,000 replicates when weights were determined by estimation, but they too had slightly larger RMSE than those obtained with fewer adjustment variables. On the other hand, they were more accurate than estimates obtained using standard weights. Qualitatively similar results were obtained when the adjustment variables were limited to the 24 corresponding to the three strata sampled at less than 100%.
6 Discussion and Conclusions
This paper has reviewed statistical properties of Horvitz-Thompson estimators of Euclidean parameters in semiparametric models with two-phase stratified samples, derived the corresponding properties for modified estimators where the sampling weights are adjusted by calibration or estimation, and illustrated the methods by log-linear and Cox regression modeling of stratified case-cohort data. A limitation of the results of van der Vaart (1998) for the Cox model, which were used by Breslow and Wellner (2007) and apply therefore to those reported here, is that time-dependent covariates were excluded from consideration. This is currently also a limitation of the svycoxph function in the survey package, at least so far as correct estimation of the variance in concerned. Work is in progress to modify svycoxph so that it will calculate the variances correctly when multiple time slice records are included in the survival analysis for each phase two subject. This will provide the extension needed to deal with time-dependent covariates. We think it likely that the asymptotic results hold for this situation and in fact much more generally. We are hopeful that a general theory for estimation of parameters in semiparametric models can be developed for sample survey designs along the lines of what Lin (2000) has provided for the Cox model.
The asymptotic properties of estimators with weights adjusted using calibration and estimation are very similar. Finite sample performance of the two methods of adjustment was also very similar in the initial simulation results for the NWTS cohort as reported in the companion paper. An advantage of calibration for the survey statistician is that information on the auxiliary variables is not needed for everyone in the cohort (phase one sample). Only the totals over the cohort are required. The more detailed information is required for estimation of the sampling probabilities.
Our asymptotic results suggested the possibility of improvement by using stratum specific versions of the imputed IF contributions for calibration of the weights. Robins et al. (1994) likewise noted that, so far as asymptotic variances are concerned, increasing the number of auxiliary variables used to estimate the weights can only reduce (or at least never increase) the asymptotic variance of the estimators. As the simulations reported here illustrate, however, actual performance in finite samples may be quite different. Adjustment based on calibration was particularly susceptible to numerical problems caused by a large number of auxiliary variables. In practical work, standard or estimated sampling weights should be used when the calibration algorithm fails to converge. Options for calibration that bound the discrepancy between design and calibrated weights have been implemented in the R survey package and further work exploring the finite sample properties of estimators using such weights would be desirable. It would also be of interest to compare our “plug in” method of approximating the optimal auxiliary variables zopt to other methods of estimating the conditional mean.
Methods for improving the analysis of data from two phase stratified samples have now been implemented in the flexible survey package of the freely available R statistical system. There is no longer any excuse for epidemiologists and statisticians to waste valuable information by inefficient analysis of data from stratified case-control and case-cohort studies.
Acknowledgments
The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study is carried out as a collaborative study supported by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute contracts N01-HC-55-15, N01-NC-55016, N01-HC-55019, N01-HC-55020, N01-HC-55021 and N01-HC-55022. The National Wilms Tumor Study and Norman Breslow received financial support from grants R01-CA-054498, R01-CA-40644 and earlier grants from the National Cancer institute. Michal Kulich received financial support from Research Project MSM 0021620839 from Ministry of Education, Czech Republic. The authors thank the staff and participants of the ARIC and NWTS studies for their important contributions.
7 Appendix
Here we provide a brief outline of the derivation of (12) for the calibration estimator. For in a neighborhood of the limiting value λ0 = 0 denote modified weights by , where are known sampling weights depending on v. Define classes of functions
for θ ∈ Θ, η ∈ Ξ, and h ∈ ℋ, and let Ψ1;θ,η,λ = P0 ψ1; θ,η,λ (W, ξ) and Ψ2; θ,η,λ,h = P0 ψ2; θ,η,λ,h(W, ξ) denote their expectation. Then
Substituting these expressions for the analogous quantities Ψ̇1,α and Ψ̇2;αh in Breslow and Wellner (2008, Sect. 3) and reworking the calculations there shows that
From (6), (9) and (11), assuming n ↑ ∞ faster than as N ↑ ∞, we find
Combining the last three equations yields the desired result (12).
The limit law for θ̂N based on estimated weights is derived similarly. From Breslow and Wellner (2008, eq. 18) one concludes for either Bernoulli or two-phase stratified sampling
A Taylor expansion with remainder of α̂N about α0 in (13) leads to
Combining these two equations with (5) we find
and the conclusion (14) follows from the arguments in Breslow and Wellner (2007, Sect. 4).
Contributor Information
Norman E. Breslow, Email: norm@u.washington.edu, Department of Biostatistics, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA, Tel.: +1-206-543-2035, Fax: +1-206-616-2724
Thomas Lumley, Email: tlumley@u.washington.edu, Department of Biostatistics, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA.
Christie M Ballantyne, Email: cmb@bcm.edu, Department of Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX, USA.
Lloyd E. Chambless, Email: Lloyd.Chambless@mail.cscc.unc.edu, Department of Biostatistics, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC, USA
Michal Kulich, Email: kulich@karlin.m3.cuni.cz, Department of Probability and Mathematical Statistics, Charles University, Prague, CZ.
References
- Ballantyne CM, Hoogeveen RC, Bang H, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and risk for incident coronary heart disease in middle-aged men and women in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Circulation. 2004;109:837–842. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000116763.91992.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow WE. Robust variance estimation for the case-cohort design. Biometrics. 1994;50:1064–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow WE, Ichikawa L, Rosner D, Izumi S. Analysis of case-cohort designs. J Clin Epidemiol. 1999;52:1165–1172. doi: 10.1016/s0895-4356(99)00102-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begun JM, Hall WJ, Huang W-M, Wellner JA. Information and asymptotic efficiency in parametric-nonparametric models. Ann Stat. 1983;11:432–452. [Google Scholar]
- Binder DA. Fitting Cox’s proportional hazards model from survey data. Biometrika. 1992;79:139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Borgan O, Langholz B, Samuelsen SO, et al. Exposure stratified case-cohort designs. Lifetime Data Anal. 2000;6:39–58. doi: 10.1023/a:1009661900674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow N. Covariance analysis of censored survival data. Biometrics. 1974;30:89–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow NE, Holubkov R. Maximum likelihood estimation of logistic regression parameters under two-phase, outcome-dependent sampling. J Roy Stat Soc B. 1997;59:447–461. [Google Scholar]
- Breslow NE, Lumley T, Ballantyne CM, et al. Using the whole cohort in the analysis of case-cohort data. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;192 doi: 10.1093/aje/kwp055. (in press) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow NE, Wellner JA. Weighted likelihood for semiparametric models and two-phase stratified samples, with application to Cox regression. Scand J Stat. 2007;34:86–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9469.2007.00574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow NE, Wellner JA. A Z-theorem with estimated nuisance parameters and correction note for ’Weighted Likelihood for Semiparametric Models and Two-phase Stratified Samples, with Application to Cox Regression’. Scand J Stat. 2008;35:186–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9469.2007.00574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain KC, Lange NT. Approximate case influence for the proportional hazards regression model with censored data. Biometrics. 1984;40:493–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox DR. Regression models and life-tables (with discussion) J Roy Stat Soc B. 1972;34:187–220. [Google Scholar]
- Cox DR. Partial likelihood. Biometrika. 1975;62:269–276. [Google Scholar]
- D’Angio GJ, Breslow N, Beckwith JB, et al. Treatment of Wilms’ tumor: Results of the third National Wilms’ Tumor Study. Cancer. 1989;64:349–360. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890715)64:2<349::aid-cncr2820640202>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deming WE, Stephan FF. On a least squares adjustment of a sampled frequency table when the expected marginal totals are known. Ann Math Stat. 1940;11:427–444. [Google Scholar]
- Deville JC, Särndal C-E. Calibration estimators in survey sampling. J Am Stat Assoc. 1992;87:376–382. [Google Scholar]
- Green DM, Breslow NE, Beckwith JB, et al. Comparison between single-dose and divided-dose administration of dactinomycin and doxorubicin for patients with Wilms’ tumor: A report from the National Wilms’ Tumor Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:237–245. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1998.16.1.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvitz DG, Thompson DJ. A generalization of sampling without replacement from a finite universe. J Am Stat Assoc. 1952;47:663–685. [Google Scholar]
- The ARIC Investigators. The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study: design and objectives. Am J Epidemiol. 1989;129:687–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaki CT, Fuller WA. Survey design under the regression superpopulation model. J Am Stat Assoc. 1982;77:89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacevic MS, Rai SN. Log-linear modelling of change using longitudinal survey data. Commun Stat Theory Methods. 2002;31:1815–1835. [Google Scholar]
- Kulich M, Lin DY. Improving the efficiency of relative-risk estimation in case-cohort studies. J Am Stat Assoc. 2004;99:832–844. [Google Scholar]
- Lin DY. On fitting Cox’s proportional hazards models to survey data. Biometrika. 2000;87:37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Lin DY, Wei LJ. The robust inference for the Cox proportional hazards model. J Am Stat Assoc. 1989;84:1074–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Lumley T. Analysis of complex survey samples. J Stat Software. 2004;9:1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Mark SD, Katki HA. Specifying and implementing nonparametric and semiparametric survival estimators in two-stage (nested) cohort studies with missing case data. J Am Stat Assoc. 2006;101:460–471. [Google Scholar]
- Nan B. E3cient estimation for case-cohort studies. Can J Stat. 2004;32:403–419. [Google Scholar]
- Neyman J. Contribution to the theory of sampling human populations. J Am Stat Assoc. 1938;33:101–116. [Google Scholar]
- Persson M, Nilsson JA, Nelson JJ, et al. The epidemiology of Lp-PLA(2): Distribution and correlation with cardiovascular risk factors in a population-based cohort. Atherosclerosis. 2007;190:388–396. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.02.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice RL. A case-cohort design for epidemiologic cohort studies and disease prevention trials. Biometrika. 1986;73:1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Rao JNK, Yung W, Hidiroglou M. Estimating equations for the analysis of survey data using poststratification information. Sankhya. 2002;64:364–378. [Google Scholar]
- Robins JM, Rotnitzky A, Zhao LP. Estimation of regression coefficients when some regressors are not always observed. J Am Stat Assoc. 1994;89:846–866. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin-Bleuer S, Kratina IS. On the two-phase framework for joint model and design-based inference. Ann Stat. 2005;33:2789–2810. [Google Scholar]
- Särndal C-E, Swensson B, Wretman JH. The weighted residual technique for estimating the variance of the general regression estimator of the finite population total. Biometrika. 1989;76:527–537. [Google Scholar]
- Scheike TH, Martinussen T. Maximum likelihood estimation for Cox’s regression model under case-cohort sampling. Scand J Stat. 2004;31:283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Scott AJ, Wild CJ. Fitting regression models to case-control data by maximum likelihood. Biometrika. 1997;84:57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Therneau TM, Grambsch PM. Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model. Springer-Verlag; New York: 2000. [Google Scholar]
- van der Vaart AW. Asymptotic Statistics. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 1998. [Google Scholar]
- van der Vaart AW, Wellner JA. Weak Convergence and Empirical Processes with Applications in Statistics. Springer; New York: 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang CY, Chen HY. Augmented inverse probability weighted estimator for Cox missing covariate regression. Biometrics. 2001;57:414–419. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341x.2001.00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White JE. A two stage design for the study of the relationship between a rare exposure and a rare disease. Am J Epidemiol. 1982;115:119–128. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng D, Lin DY. Maximum likelihood estimation in semiparametric regression models with censored data. J Roy Stat Soc B. 2007;69:507–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


