Abstract
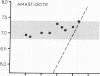
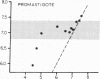
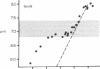
Intracellular pH and pH gradients of Leishmania donovani amastigotes and promastigotes were determined over a broad range of extracellular pH values. Intracellular pH was determined by 31P NMR and by equilibrium distribution studies with 5,5-dimethyloxazolidine-2,4-dione or methylamine. Promastigotes maintain intracellular pH values close to neutral between extracellular pH values of 5.0 and 7.4. Amastigote intracellular pH is maintained close to neutral at external pH values as low as 4.0. Both life stages maintain a positive pH gradient to an extracellular pH of 7.4, which is important for active transport of substrates. Treatment with ionophores, such as nigericin and carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone and the ATPase inhibitor dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, reduced pH gradients in both stages. Maintenance of intracellular pH in the physiologic range is especially relevant for the survival of the amastigote in its acidic in vivo environment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booth I. R. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):359–378. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.359-378.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delhez J., Dufour J. P., Thines D., Goffeau A. Comparison of the properties of plasma membrane-bound and mitochondria-bound ATPases in the yeast Schizosaccharmoyces pombe. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep 15;79(1):319–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11812.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T. Estimation of the cytoplasmic pH of Coxiella burnetii and effect of substrate oxidation on proton motive force. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):591–597. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.591-597.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heytler P. G. Uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:462–442. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfer M., Misra P. C. Evidence for a proton/sugar symport in the yeast Rhodotorula gracilis (glutinis). Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):15–22. doi: 10.1042/bj1720015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade J. C., Glaser T. A., Bonventre P. F., Mukkada A. J. Enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in Leishmania donovani amastigotes. J Protozool. 1984 Feb;31(1):156–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb04307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. B., Richards J. H. Determination of intracellular pH by 31P magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7276–7278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukkada A. J., Meade J. C., Glaser T. A., Bonventre P. F. Enhanced metabolism of Leishmania donovani amastigotes at acid pH: an adaptation for intracellular growth. Science. 1985 Sep 13;229(4718):1099–1101. doi: 10.1126/science.4035350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukkada A. J., Schaefer F. W., 3rd, Simon M. W., Neu C. Delayed in vitro utilization of glucose by Leishmania tropica promastigotes. J Protozool. 1974 May;21(2):393–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon G., Ogawa S., Shulman R. G., Yamane T. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):87–91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon G., Ogawa S., Shulman R. G., Yamane T. High-resolution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of metabolism in aerobic Escherichia coli cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):888–891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S. pH homeostasis in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec;650(2-3):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W. Ionophores. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:435–454. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of membrane potential and deltapH in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:547–569. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salhany J. M., Yamane T., Shulman R. G., Ogawa S. High resolution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of intact yeast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4966–4970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson R., Silver S. Methylammonium uptake by Escherichia coli: evidence for a bacterial NH4+ transport system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 25;75(4):1133–1139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91501-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell W. J., Bates R. G. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1969 Apr;49(2):285–329. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1969.49.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Agmon V., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Escherichia coli intracellular pH, membrane potential, and cell growth. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):246–252. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.246-252.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Dwyer D. M. Protonmotive force-driven active transport of D-glucose and L-proline in the protozoan parasite Leishmania donovani. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1716–1720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]