Abstract
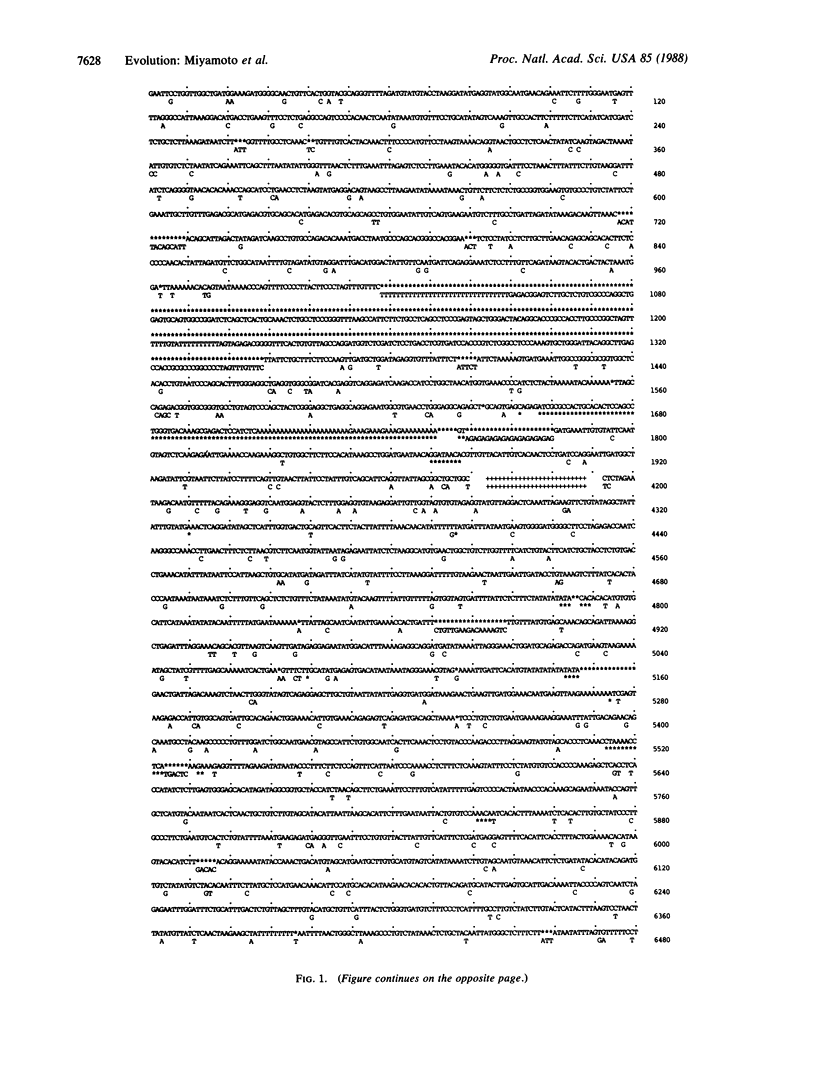
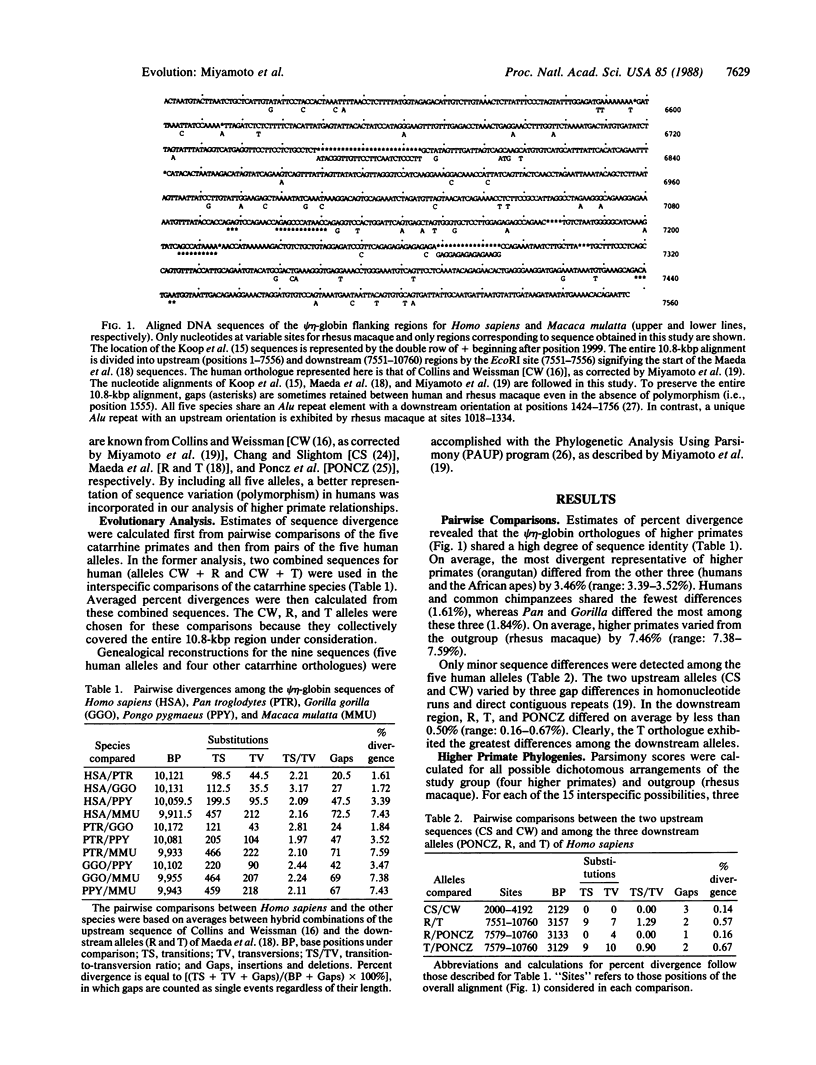
We obtained 5' and 3' flanking sequences (5.4 kilobase pairs) from the psi eta-globin gene region of the rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) and combined them with available nucleotide data. The completed sequence, representing 10.8 kilobase pairs of contiguous noncoding DNA, was compared to the same orthologous regions available for human (Homo sapiens, as represented by five different alleles), common chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes), gorilla (Gorilla gorilla), and orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus). The nucleotide sequence for Macaca mulatta provided the outgroup perspective needed to evaluate better the relationships of humans and great apes. Pairwise comparisons and parsimony analysis of these orthologues clearly demonstrated (i) that humans and great apes share a high degree of genetic similarity and (ii) that humans, chimpanzees, and gorillas form a natural monophyletic group. These conclusions strongly favor a genealogical classification for higher primates consisting of a single family (Hominidae) with two subfamilies (Homininae for Homo, Pan, and Gorilla and Ponginae for Pongo).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P., Cronin J. E. The relationships of Sivapithecus and Ramapithecus and the evolution of the orang-utan. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):541–546. doi: 10.1038/297541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. Y., Slightom J. L. Isolation and nucleotide sequence analysis of the beta-type globin pseudogene from human, gorilla and chimpanzee. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):767–784. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90256-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Weissman S. M. The molecular genetics of human hemoglobin. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1984;31:315–462. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60382-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delson E. Primate and human phylogeny. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):532–533. doi: 10.1038/313532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M., Koop B. F., Czelusniak J., Weiss M. L. The eta-globin gene. Its long evolutionary history in the beta-globin gene family of mammals. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):803–823. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90258-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist R., Miyamoto M. M., Goodman M. Analysis of higher-primate phylogeny from transversion differences in nuclear and mitochondrial DNA by Lake's methods of evolutionary parsimony and operator metrics. Mol Biol Evol. 1988 May;5(3):217–236. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop B. F., Goodman M., Xu P., Chan K., Slightom J. L. Primate eta-globin DNA sequences and man's place among the great apes. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):234–238. doi: 10.1038/319234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop B. F., Miyamoto M. M., Embury J. E., Goodman M., Czelusniak J., Slightom J. L. Nucleotide sequence and evolution of the orangutan epsilon globin gene region and surrounding Alu repeats. J Mol Evol. 1986;24(1-2):94–102. doi: 10.1007/BF02099956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Tanimura M. The molecular clock runs more slowly in man than in apes and monkeys. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):93–96. doi: 10.1038/326093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Wu C. I., Bliska J., Reneke J. Molecular evolution of intergenic DNA in higher primates: pattern of DNA changes, molecular clock, and evolution of repetitive sequences. Mol Biol Evol. 1988 Jan;5(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M. M., Slightom J. L., Goodman M. Phylogenetic relations of humans and African apes from DNA sequences in the psi eta-globin region. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):369–373. doi: 10.1126/science.3116671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Schwartz E., Ballantine M., Surrey S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the delta beta-globin gene region in humans. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11599–11609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarich V. M., Wilson A. C. Immunological time scale for hominid evolution. Science. 1967 Dec 1;158(3805):1200–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3805.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savatier P., Trabuchet G., Chebloune Y., Faure C., Verdier G., Nigon V. M. Nucleotide sequence of the beta-globin genes in gorilla and macaque: the origin of nucleotide polymorphisms in human. J Mol Evol. 1987;24(4):309–318. doi: 10.1007/BF02134129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savatier P., Trabuchet G., Chebloune Y., Faure C., Verdier G., Nigon V. M. Nucleotide sequence of the delta-beta-globin intergenic segment in the macaque: structure and evolutionary rates in higher primates. J Mol Evol. 1987;24(4):297–308. doi: 10.1007/BF02134128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. H. The evolutionary relationships of man and orang-utans. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):501–505. doi: 10.1038/308501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley C. G., Ahlquist J. E. DNA hybridization evidence of hominoid phylogeny: results from an expanded data set. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(1-2):99–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02111285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley C. G., Ahlquist J. E. The phylogeny of the hominoid primates, as indicated by DNA-DNA hybridization. J Mol Evol. 1984;20(1):2–15. doi: 10.1007/BF02101980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Theisen T. W., Koop B. F., Goodman M. Orangutan fetal globin genes. Nucleotide sequence reveal multiple gene conversions during hominid phylogeny. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7472–7483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



