Abstract
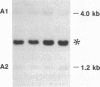
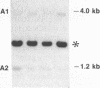
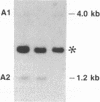
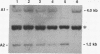
The human ETS2 gene, a member of the ETS gene family, with sequence homology with the retroviral ets sequence of the avian erythroblastosis retrovirus E26 is located on chromosome 21. Molecular genetic analysis of Down syndrome (DS) patients with partial trisomy 21 allowed us to reinforce the supposition that ETS2 may be a gene of the minimal DS genetic region. It was originally proposed that a duplication of a portion of the DS region represents the genetic basis of Alzheimer disease, a condition associated also with DS. No evidence of either rearrangements or duplications of ETS2 could be detected in DNA from fibroblasts and brain tissue of Alzheimer disease patients with either the sporadic or the familiar form of the disease. Thus, an altered ETS2 gene dosage does not seem to be a genetic cause or component of Alzheimer disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borgaonkar D. S., Greene A. E., Coriell L. L. A (6;21) translocation, unbalanced, 46 chromosomes. Repository identification no. GM-144. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1974;13(4):403–405. doi: 10.1159/000130290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Q., Kan N. C., Pribyl L., Lautenberger J. A., Moudrianakis E., Papas T. S. Molecular cloning of the ets proto-oncogene of the sea urchin and analysis of its developmental expression. Dev Biol. 1988 Feb;125(2):432–440. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. V., Nadeau J. H., Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Jagadesh J., Taylor B. A., Haines J. L., Sacchi N., Gusella J. F. Comparative mapping of DNA markers from the familial Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome regions of human chromosome 21 to mouse chromosomes 16 and 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6032–6036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Epstein L. B., Epstein C. J. Genes coding for sensitivity to interferon (IfRec) and soluble superoxide dismutase (SOD-1) are linked in mouse and man and map to mouse chromosome 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2168–2172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Smith S. A., Epstein L. B., Epstein C. J. Mouse trisomy 16 as an animal model of human trisomy 21 (Down syndrome): production of viable trisomy 16 diploid mouse chimeras. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):416–424. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90156-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. G., Jenkins E. C., Klinger H. P., Weed R. G. A child with presumptive monosomy 21 (45,XY,-21) in a family in which some members are Gq-. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;17(2):65–77. doi: 10.1159/000130691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabar J. M., Goldgaber D., Lamour Y., Nicole A., Huret J. L., de Grouchy J., Brown P., Gajdusek D. C., Sinet P. M. Beta amyloid gene duplication in Alzheimer's disease and karyotypically normal Down syndrome. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1390–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2950593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabar J. M., Lamour Y., Gegonne A., Davous P., Roudier M., Nicole A., Ceballos I., Amouyel P., Stehelin D., Sinet P. M. Rearrangement of chromosome 21 in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Genet. 1986;29(4):226–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabar J. M., Sinet P. M., Chadefaux B., Nicole A., Gegonne A., Stehelin D., Fridlansky F., Créau-Goldberg N., Turleau C., de Grouchy J. Submicroscopic duplication of chromosome 21 and trisomy 21 phenotype (Down syndrome). Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;76(3):225–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00283612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein C. J., Avraham K. B., Lovett M., Smith S., Elroy-Stein O., Rotman G., Bry C., Groner Y. Transgenic mice with increased Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase activity: animal model of dosage effects in Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8044–8048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein C. J., Cox D. R., Epstein L. B. Mouse trisomy 16: an animal model of human trisomy 21 (Down syndrome). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;450:157–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb21490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong C. T., Brodeur G. M. Down's syndrome and leukemia: epidemiology, genetics, cytogenetics and mechanisms of leukemogenesis. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1987 Sep;28(1):55–76. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(87)90354-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Fisher R. J., Seth A., Bhat N. K., Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Papas T. S. Characterization and localization of the products of the human homologs of the v-ets oncogene. Oncogene. 1988 Feb;2(2):99–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halloran K. H., Breg W. R., Mahoney M. J. 21 monosomy in a retarded female infant. J Med Genet. 1974 Dec;11(4):386–389. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.4.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huret J. L., Delabar J. M., Marlhens F., Aurias A., Nicole A., Berthier M., Tanzer J., Sinet P. M. Down syndrome with duplication of a region of chromosome 21 containing the CuZn superoxide dismutase gene without detectable karyotypic abnormality. Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;75(3):251–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00281069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlinsky H. Alzheimer's disease in Down's syndrome. A review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1986 Oct;34(10):728–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1986.tb04304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman R. Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 1986 Apr 10;314(15):964–973. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198604103141506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkilionis A. J., Sergovich F. R. Down syndrome with apparently normal chromosomes: an update. J Pediatr. 1986 May;108(5 Pt 1):793–794. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)81077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEJEUNE J., GAUTIER M., TURPIN R. Etude des chromosomes somatiques de neuf enfants mongoliens. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1959 Mar 16;248(11):1721–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niebuhr E. Down's syndrome. The possibility of a pathogenetic segment on chromosome no. 21. Humangenetik. 1974 Jan 22;21(1):99–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00278575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver C., Holland A. J. Down's syndrome and Alzheimer's disease: a review. Psychol Med. 1986 May;16(2):307–322. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700009120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson T. A., Yochem J., Byers B., Nunn M. F., Duesberg P. H., Doolittle R. F., Reed S. I. A relationship between the yeast cell cycle genes CDC4 and CDC36 and the ets sequence of oncogenic virus E26. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):556–558. doi: 10.1038/309556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podlisny M. B., Lee G., Selkoe D. J. Gene dosage of the amyloid beta precursor protein in Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):669–671. doi: 10.1126/science.2960019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poissonnier M., Saint-Paul B., Dutrillaux B., Chassaigne M., Gruyer P., de Blignières-Strouk G. Trisomie 21 partielle (21q21 leads to 21q22.2) Ann Genet. 1976 Mar;19(1):69–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock N. J., Mirra S. S., Binder L. I., Hansen L. A., Wood J. G. Filamentous aggregates in Pick's disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, and Alzheimer's disease share antigenic determinants with microtubule-associated protein, tau. Lancet. 1986 Nov 22;2(8517):1211–1211. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92212-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribyl L. J., Watson D. K., McWilliams M. J., Ascione R., Papas T. S. The Drosophila ets-2 gene: molecular structure, chromosomal localization, and developmental expression. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S. I. Brain evolution and Alzheimer's disease. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1988;144(2):79–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. S., Rao V. N., Papas T. S. The erg gene: a human gene related to the ets oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6131–6135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERGOVICH F. R., VALENTINE G. H., CARR D. H., SOLTAN H. C. MONGOLISM (DOWN'S SYNDROME) WITH ATYPICAL CLINICAL AND CYTOGENETIC FEATURES. J Pediatr. 1964 Aug;65:197–207. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80520-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
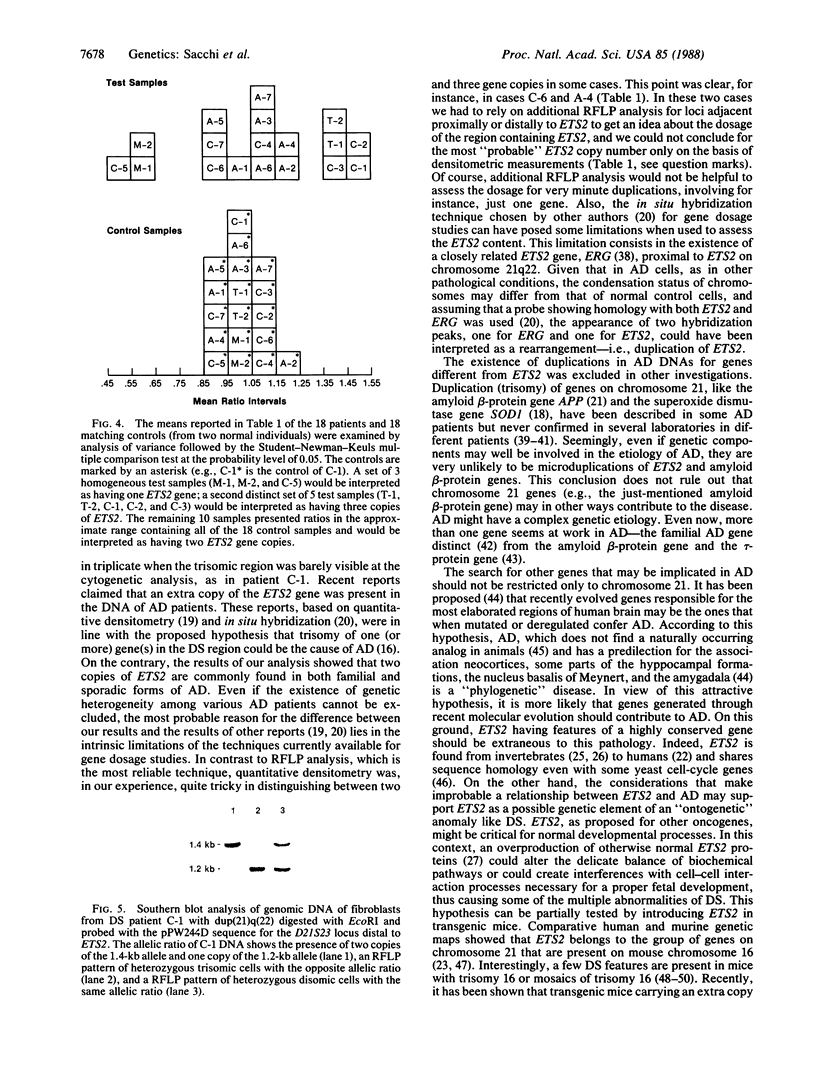
- Sacchi N., Cheng S. V., Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Drabkin H. A., Patterson D., Haines J. H., Papas T. S. The ETS genes on chromosome 21 are distal to the breakpoint of the acute myelogenous leukemia translocation (8;21). Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):110–116. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90140-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi N., Gusella J. F., Perroni L., Bricarelli F. D., Papas T. S. Lack of evidence for association of meiotic nondisjunction with particular DNA haplotypes on chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4794–4798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R., Mundel G., Rosenblatt M., Katznelson M. B. Apparent G-monosomy, G-deletion, and incomplete Down's syndrome in a single family. J Med Genet. 1972 Dec;9(4):457–461. doi: 10.1136/jmg.9.4.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweber M. A possible unitary genetic hypothesis for Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;450:223–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb21495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Bell D. S., Podlisny M. B., Price D. L., Cork L. C. Conservation of brain amyloid proteins in aged mammals and humans with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):873–877. doi: 10.1126/science.3544219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Bird E. D., Latt S. A., Neve R. L. The amyloid beta protein gene is not duplicated in brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):666–669. doi: 10.1126/science.2890207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Haines J. L., Watkins P. C., Stewart G. D., Wallace M. R., Hallewell R., Wong C., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. Genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., St George-Hyslop P. H., Haines J. L., Polinsky R. J., Nee L., Foncin J. F., Neve R. L., McClatchey A. I., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. The genetic defect in familial Alzheimer's disease is not tightly linked to the amyloid beta-protein gene. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):156–157. doi: 10.1038/329156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams-Smith M. J., Kozak C., Reeves R., Gearhart J., Nunn M. F., Nash W., Fowle J. R., 3rd, Duesberg P., Papas T. S. Conserved chromosomal positions of dual domains of the ets protooncogene in cats, mice, and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1792–1796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams-Smith M. J., Nunn M. F., Duesberg P. H., O'Brien S. J., Papas T. S. The ets sequence from the transforming gene of avian erythroblastosis virus, E26, has unique domains on human chromosomes 11 and 21: both loci are transcriptionally active. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7294–7298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. D., Summitt R. L., Martens P. R., Kimbrell R. A. Familial Down syndrome due to t(10;21) translocation: evidence that the Down phenotype is related to trisomy of a specific segment of chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Jul;27(4):478–485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]