Abstract
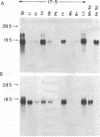
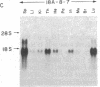
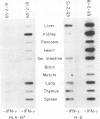
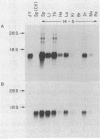
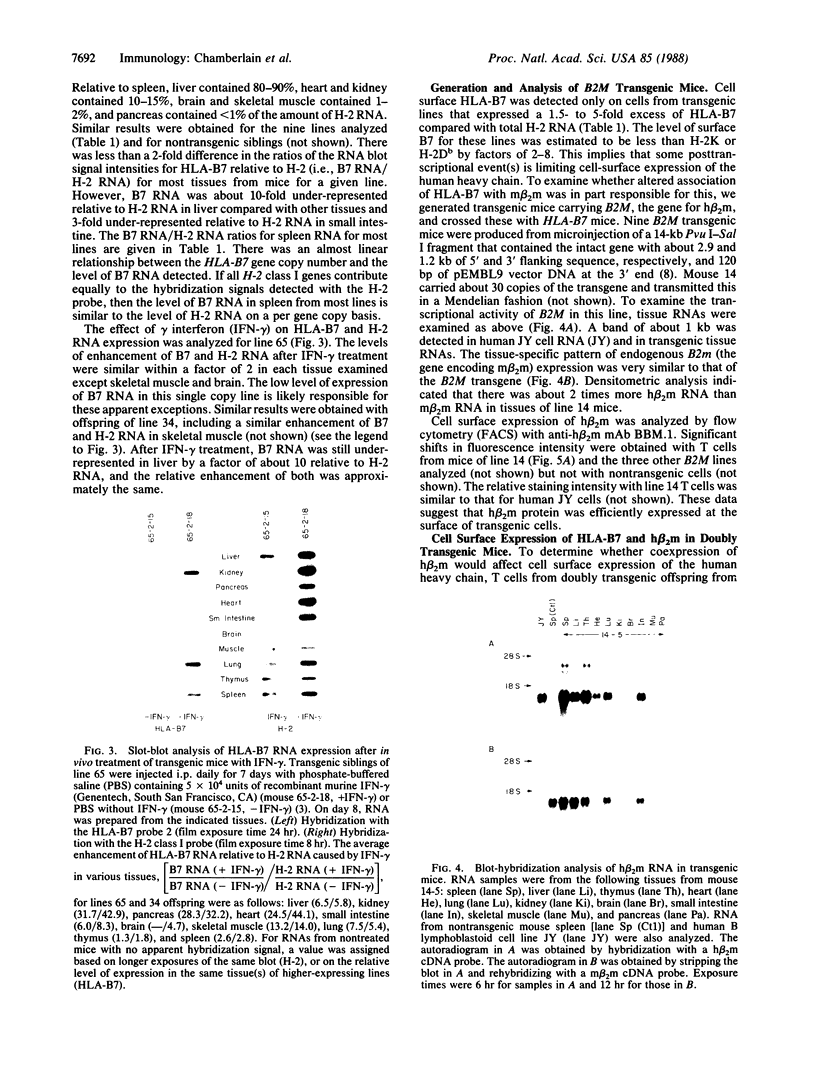
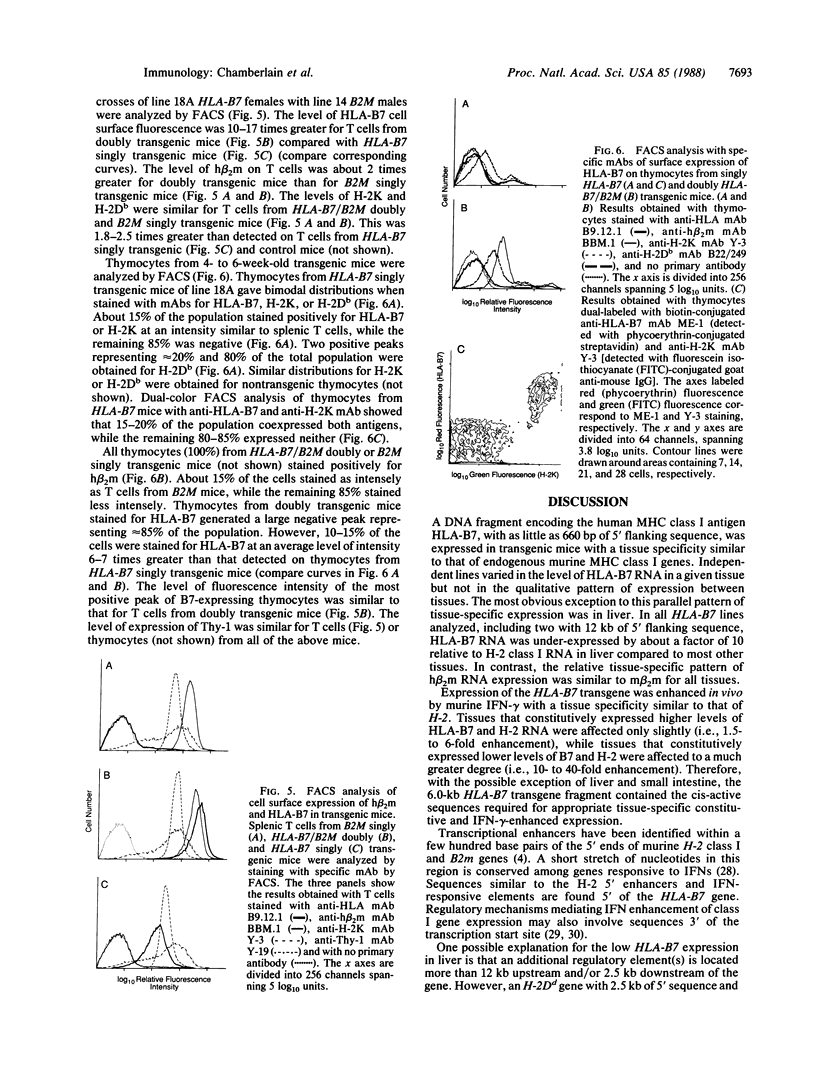
We introduced the human genes HLA-B7 and B2M encoding the heavy (HLA-B7) and light [beta 2-microglobulin (beta 2m)] chains of a human major histocompatibility complex class I antigen into separate lines of transgenic mice. The tissue-specific pattern of HLA-B7 RNA expression was similar to that of endogenous class I H-2 genes, although the HLA-B7 gene was about 10-fold underexpressed in liver. Identical patterns of RNA expression were detected whether the HLA-B7 gene contained 12 or 0.66 kilobase(s) (kb) of 5' flanking sequence. The level of expression was copy number dependent and as efficient as that of H-2 genes; gamma interferon enhanced HLA-B7 RNA expression in parallel to that of H-2. In addition to the mechanism(s) responsible for gamma interferon-enhanced expression, there must be at least one other tissue-specific mechanism controlling the constitutive levels of class I RNA. Tissue-specific human beta 2m RNA expression was similar to that of mouse beta 2m, including high-level expression in liver. Cell surface HLA-B7 increased 10- to 17-fold on T cells and on a subset of thymocytes from HLA-B7/B2M doubly transgenic mice compared to HLA-B7 singly transgenic mice. The pattern of expression of HLA-B7 on thymocytes resembled that of H-2K as opposed to H-2D. These results confirm that coexpression of both human chains is required for efficient surface expression and that HLA-B7 may share a regulatory mechanism with H-2K, which distinguishes it from H-2D.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold B., Burgert H. G., Archibald A. L., Kvist S. Complete nucleotide sequence of the murine H-2Kk gene. Comparison of three H-2K locus alleles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9473–9487. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Two transcription factors, NF-kappa B and H2TF1, interact with a single regulatory sequence in the class I major histocompatibility complex promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieberich C., Scangos G., Tanaka K., Jay G. Regulated expression of a murine class I gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1339–1342. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Bodmer W. F., Parham P. Characterization of a monoclonal anti-beta 2-microglobulin antibody and its use in the genetic and biochemical analysis of major histocompatibility antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jul;9(7):536–545. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceredig R., Lynch F., Newman P. Phenotypic properties, interleukin 2 production, and developmental origin of a "mature" subpopulation of Lyt-2- L3T4- mouse thymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8578–8582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. W., Nolan J. A., Gromkowski S. H., Kelley K. A., Eisenstadt J. M., Herrup K., Janeway C. A., Jr, Weissman S. M. Cell surface expression and alloantigenic function of a human class I MHC heavy chain gene (HLA-B7) in transgenic mice. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1285–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S. A., Taylor C., McMichael A. Recognition of HLA-B27 and related antigen by a monoclonal antibody. Hum Immunol. 1982 Aug;5(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(82)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier P., Fontecilla-Camps J. C., Bucchini D., Caillol D. H., Jordan B. R., Lemonnier F. A. Altered structure of HLA class I heavy chains associated with mouse beta-2 microglobulin. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(4):321–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00430798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Stark G. R. alpha-Interferon-induced transcription of HLA and metallothionein genes containing homologous upstream sequences. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):637–639. doi: 10.1038/314637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. W., Gill T. J., 3rd Expression of class I transplantation antigens. Transplantation. 1986 Aug;42(2):109–117. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198608000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. Evidence that the Thy-1 molecule is the target for T cell mitogenic antibody against brain-associated antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Aug;13(8):678–684. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B., Janeway C. A., Jr Cooperative interaction of B lymphocytes with antigen-specific helper T lymphocytes is MHC restricted. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):547–549. doi: 10.1038/292547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Israël A., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. Detailed analysis of the mouse H-2Kb promoter: enhancer-like sequences and their role in the regulation of class I gene expression. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90760-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korber B., Hood L., Stroynowski I. Regulation of murine class I genes by interferons is controlled by regions located both 5' and 3' to the transcription initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3380–3384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krimpenfort P., Rudenko G., Hochstenbach F., Guessow D., Berns A., Ploegh H. Crosses of two independently derived transgenic mice demonstrate functional complementation of the genes encoding heavy (HLA-B27) and light (beta 2-microglobulin) chains of HLA class I antigens. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1673–1676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02416.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalanne J. L., Transy C., Guerin S., Darche S., Meulien P., Kourilsky P. Expression of class I genes in the major histocompatibility complex: identification of eight distinct mRNAs in DBA/2 mouse liver. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke H., Hämmerling G. J., Hämmerling U. Fine specificity analysis with monoclonal antibodies of antigens controlled by the major histocompatibility complex and by the Qa/TL region in mice. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:175–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew A. M., Lillehoj E. P., Cowan E. P., Maloy W. L., van Schravendijk M. R., Coligan J. E. Class I genes and molecules: an update. Immunology. 1986 Jan;57(1):3–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen B., Rebai N., Liabeuf A., Mawas C. Human cytotoxic T cell structures associated with expression of cytolysis. I. Analysis at the clonal cell level of the cytolysis-inhibiting effect of 7 monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Sep;12(9):739–747. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morello D., Moore G., Salmon A. M., Yaniv M., Babinet C. Studies on the expression of an H-2K/human growth hormone fusion gene in giant transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1877–1883. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04439.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Velan B., Felsenfeld A., Ramanathan L., Ferrini U., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Mouse beta 2-microglobulin cDNA clones: a screening procedure for cDNA clones corresponding to rare mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scollay R., Shortman K. Thymocyte subpopulations: an experimental review, including flow cytometric cross-correlations between the major murine thymocyte markers. Thymus. 1983 Sep;5(5-6):245–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoskiewicz M. J., Colvin R. B., Schneeberger E. E., Russell P. S. Widespread and selective induction of major histocompatibility complex-determined antigens in vivo by gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1645–1664. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava R., Duceman B. W., Biro P. A., Sood A. K., Weissman S. M. Molecular organization of the class I genes of human major histocompatibility complex. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;84:93–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs S. V., Wallace R. B., Hirose T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. Use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes: isolation of cloned cDNA sequences for human beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6613–6617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshie O., Schmidt H., Lengyel P., Reddy E. S., Morgan W. R., Weissman S. M. Transcripts of human HLA gene fragments lacking the 5'-terminal region in transfected mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):649–653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]