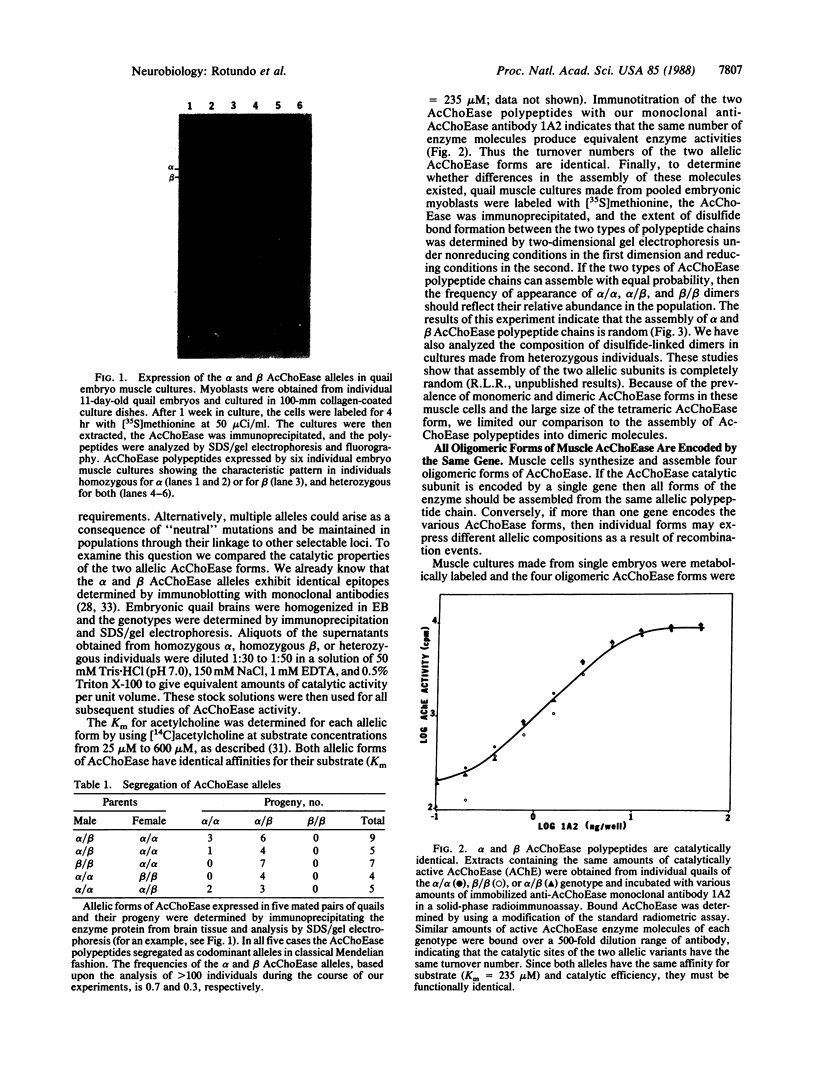
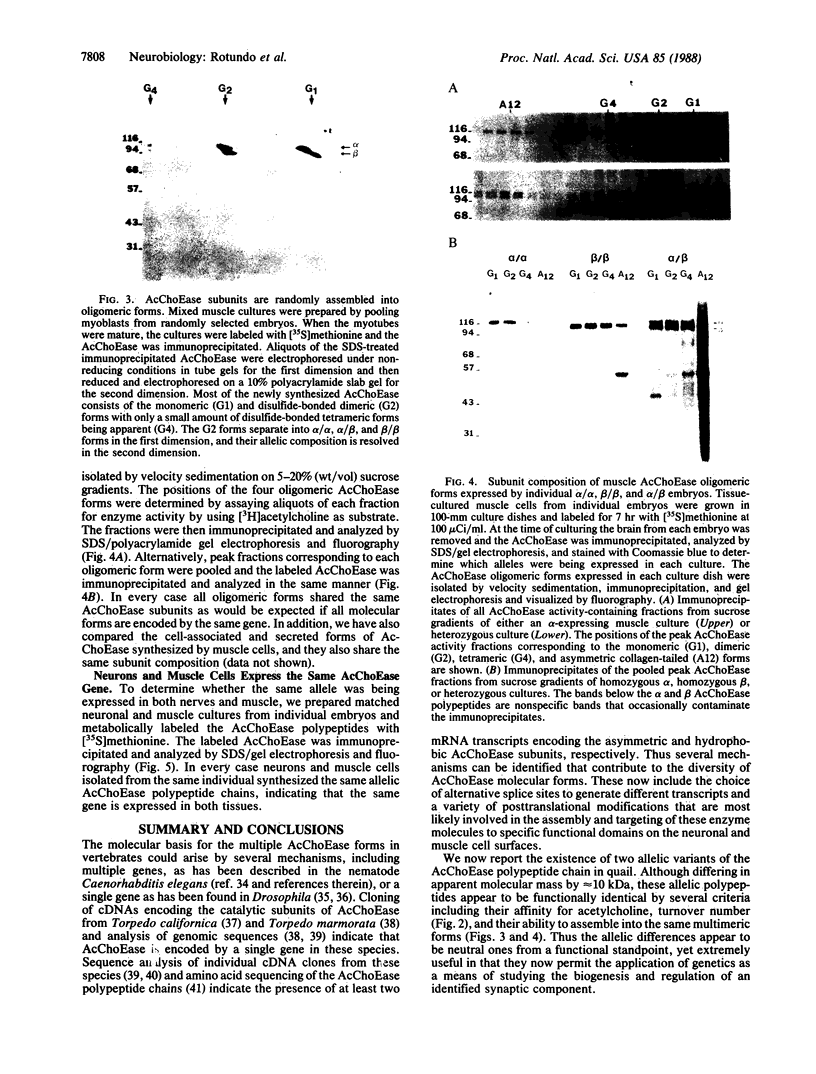
Abstract
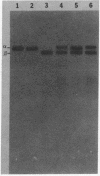
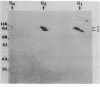
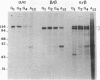
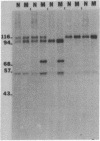
Two acetylcholinesterase (AcChoEase) polypeptide chains, alpha and beta, are expressed in avian nerves and muscles with apparent molecular masses of 110 and 100 kDa, respectively. We now show that individual quails express alpha, beta, or both AcChoEase polypeptide chains. By mating studies we show that the two AcChoEase polypeptides are autosomal and segregate as codominant alleles in classical Mendelian fashion. Biochemical studies of the two allelic AcChoEase polypeptides indicate that they have the same turnover number, have the same Km for acetylcholine, are immunoprecipitated to the same extent with a monoclonal anti-AcChoEase antibody, and can assemble with equal efficiency into multimeric forms. Thus there are no obvious functional differences between the two alleles. In heterozygotes, the rates of synthesis of the two polypeptides are identical, suggesting that there are no differences in expression of these two genes. Within an individual, nerves and muscles always express the same AcChoEase forms isolated from muscle indicates that all AcChoEase forms are comprised of the same allelic polypeptide chains. In contrast to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors that appear to be encoded by complex multigene families, our studies on AcChoEase show that all forms of this important synaptic component in electrically excitable cells are encoded by a single gene. Thus differences in assembly and localization of the multiple synaptic forms of AcChoEase must arise through posttranscriptional events, posttranslational modifications of a similar AcChoEase polypeptide chain or both.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betz W., Sakmann B. Effects of proteolytic enzymes on function and structure of frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):673–688. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimijoin S. Axonal transport and subcellular distribution of molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase in rabbit sciatic nerve. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 May;15(3):641–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimijoin S. Molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase in brain, nerve and muscle: nature, localization and dynamics. Prog Neurobiol. 1983;21(4):291–322. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(83)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockman S. K., Przybylski R. J., Younkin S. G. Cellular localization of the molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase in cultured embryonic rat myotubes. J Neurosci. 1982 Dec;2(12):1775–1785. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-12-01775.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R., Koelle G. B. Electron microscope localization of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in the superior cervical ganglion of the cat. I. Normal ganglion. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):785–809. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Giamberardino L., Couraud J. Y. Rapid accumulation of high molecular weight acetylcholinesterase in transected sciatic nerve. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):170–172. doi: 10.1038/271170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoso J. A., Fernandez H. L. Cellular localization of cytochemically stained acetylcholinesterase activity in adult rat skeletal muscle. J Neurocytol. 1985 Oct;14(5):795–808. doi: 10.1007/BF01170829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibney G., MacPhee-Quigley K., Thompson B., Vedvick T., Low M. G., Taylor S. S., Taylor P. Divergence in primary structure between the molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1140–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. C., Kankel D. R. Genetics of acetylcholinesterase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1976 Jul;83(3 PT2):517–535. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Spierer P. The Ace locus of Drosophila melanogaster: structural gene for acetylcholinesterase with an unusual 5' leader. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2949–2954. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W., Kelly R. B. Enzymatic detachment of endplate acetylcholinesterase from muscle. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 14;232(28):62–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio232062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inestrosa N. C., Roberts W. L., Marshall T. L., Rosenberry T. L. Acetylcholinesterase from bovine caudate nucleus is attached to membranes by a novel subunit distinct from those of acetylcholinesterases in other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4441–4444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jedrzejczyk J., Silman I., Lai J., Barnard E. A. Molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase in synaptic and extrasynaptic regions of avian tonic muscle. Neurosci Lett. 1984 May 18;46(3):283–289. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. D., Rand J. B., Herman R. K., Stern B. D., Russell R. L. The acetylcholinesterase genes of C. elegans: identification of a third gene (ace-3) and mosaic mapping of a synthetic lethal phenotype. Neuron. 1988 Apr;1(2):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. D., Russell R. L. A rapid, simple radiometric assay for cholinesterase, suitable for multiple determinations. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelle G. B., Massoulié J., Eugène D., Melone M. A., Boulla G. Distributions of molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in nervous tissue of the cat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7749–7752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig J., Rieger F. Biochemical stability of the AChE molecular forms after cytochemical staining: postnatal focalization of the 16S AChE in rat muscle. Dev Neurosci. 1981;4(4):249–257. doi: 10.1159/000112764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. Y., Bon C. Presence of a membrane-bound acetylcholinesterase form in a preparation of nerve endings from Torpedo marmorata electric organ. J Neurochem. 1983 Feb;40(2):338–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb11288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Finean J. B. Release of alkaline phosphatase from membranes by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj1670281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lwebuga-Mukasa J. S., Lappi S., Taylor P. Molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo californica: their relationship to synaptic membranes. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 6;15(7):1425–1434. doi: 10.1021/bi00652a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Bon S. The molecular forms of cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1982;5:57–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.05.030182.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McISAAC R. J., KOELLE G. B. Comparison of the effects of inhibition of external, internal and total acetylcholinesterase upon ganglionic transmission. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 May;126(1):9–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan U. J., Sanes J. R., Marshall L. M. Cholinesterase is associated with the basal lamina at the neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):172–174. doi: 10.1038/271172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall W. R., Tsim K. W., Lai J., Barnard E. A. Monoclonal antibodies against chicken brain acetylcholinesterase. Their use in immunopurification and immunochemistry to demonstrate allelic variants of the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Apr 1;164(1):95–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Rosenberry T. L. Selective radiolabeling and isolation of the hydrophobic membrane-binding domain of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3091–3098. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L. Acetylcholinesterase biosynthesis and transport in tissue culture. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:353–367. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L. Asymmetric acetylcholinesterase is assembled in the Golgi apparatus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):479–483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L., Carbonetto S. T. Neurons segregate clusters of membrane-bound acetylcholinesterase along their neurites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2063–2067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L., Fambrough D. M. Molecular forms of chicken embryo acetylcholinesterase in vitro and in vivo. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4790–4799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L. Purification and properties of the membrane-bound form of acetylcholinesterase from chicken brain. Evidence for two distinct polypeptide chains. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13186–13194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M., Camp S., Maulet Y., Newton M., MacPhee-Quigley K., Taylor S. S., Friedmann T., Taylor P. Primary structure of Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase deduced from its cDNA sequence. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):407–409. doi: 10.1038/319407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorav J. L., Krejci E., Massoulié J. cDNA sequences of Torpedo marmorata acetylcholinesterase: primary structure of the precursor of a catalytic subunit; existence of multiple 5'-untranslated regions. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1865–1873. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silman I., Futerman A. H. Modes of attachment of acetylcholinesterase to the surface membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):11–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. B., Rieger F., Shelanski M. L., Greene L. A. Cellular localization of the multiple molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase in cultured neuronal cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3827–3830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]