Abstract
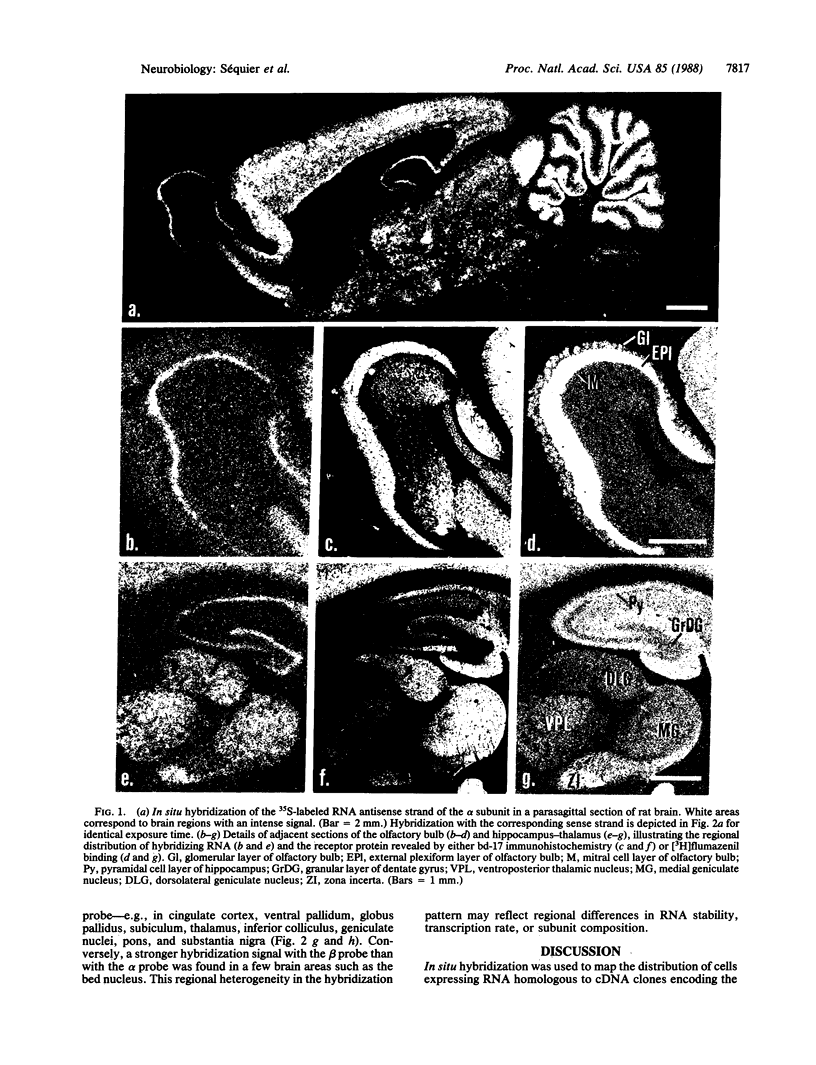
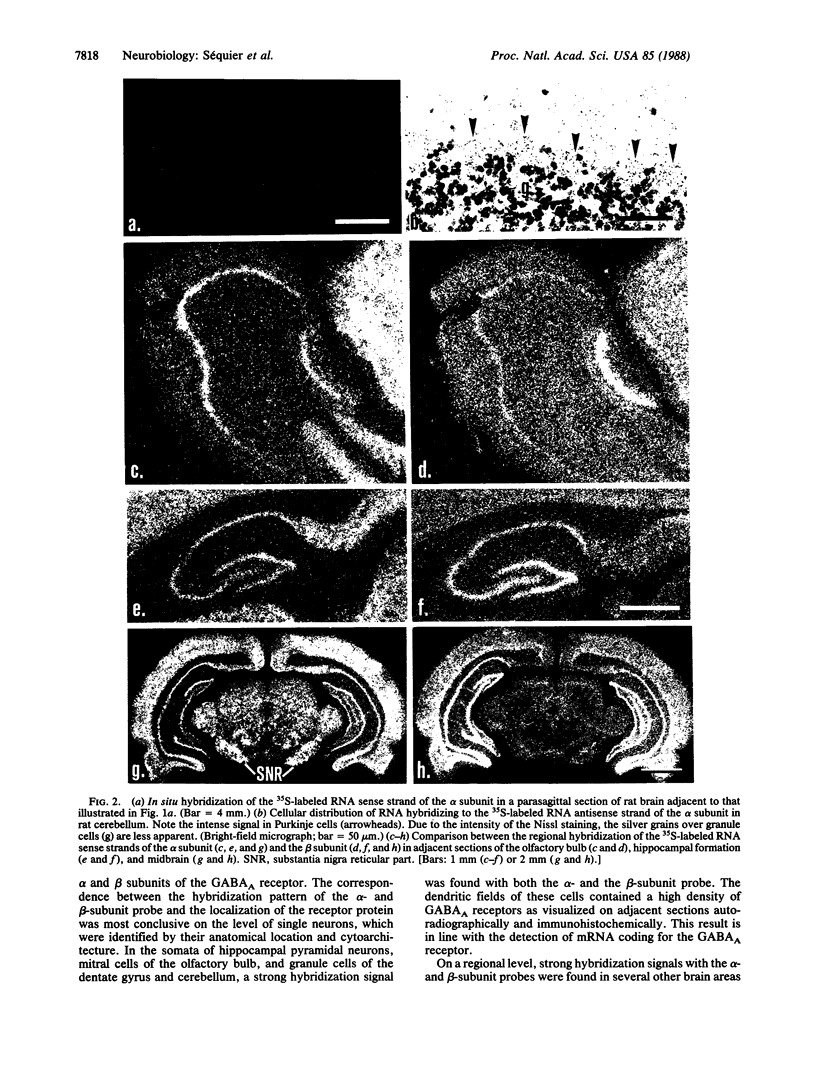
An in situ hybridization technique was used to determine the distribution in rat brain of RNA homologous to cDNA clones encoding the alpha and beta subunits of the rat brain GABAA gamma-aminobutyrate receptor. The subunit proteins were mapped in adjacent sections autoradiographically and immunohistochemically. Many brain areas containing high densities of GABAA receptors showed strong hybridization signals with both the alpha- and the beta-subunit antisense RNA probe--e.g., cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum. On a cellular level, a dense dendritic localization of GABAA receptors was correlated with a strong hybridization in the corresponding somata--e.g., in mitral cells of the olfactory bulb, pyramidal cells of hippocampus, granule cells of the dentate gyrus, and Purkinje and granule cells of the cerebellum. In some brain areas--e.g., substantia nigra--the intensity of the hybridization signal with the beta-subunit probe was much weaker than that with the alpha-subunit probe, whereas the inverse ratio of hybridization intensity was found in others--e.g., in bed nucleus. This regional heterogeneity in the hybridization pattern may reflect regional differences in RNA stability, transcription rate, or subunit composition. The results open the way for studies on the regulation of GABAA-receptor gene expression in normal and pathological brain in situ.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloch B., Popovici T., Le Guellec D., Normand E., Chouham S., Guitteny A. F., Bohlen P. In situ hybridization histochemistry for the analysis of gene expression in the endocrine and central nervous system tissues: a 3-year experience. J Neurosci Res. 1986;16(1):183–200. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490160117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodkin D. K., Knudson D. L. Sequence relatedness of Palyam virus genes to cognates of the Palyam serogroup viruses by RNA-RNA blot hybridization. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., DeLeon D. V., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of mrnas in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):485–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Deneris E., Luyten W., Kochhar A., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Members of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family are expressed in different regions of the mammalian central nervous system. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):965–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90705-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Simmons D., Swanson L. W., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Mapping of brain areas expressing RNA homologous to two different acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit cDNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4076–4080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Rienitz A., Schmitt B., Methfessel C., Zensen M., Beyreuther K., Gundelfinger E. D., Betz H. The strychnine-binding subunit of the glycine receptor shows homology with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):215–220. doi: 10.1038/328215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häring P., Stähli C., Schoch P., Takács B., Staehelin T., Möhler H. Monoclonal antibodies reveal structural homogeneity of gamma-aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptors in different brain areas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4837–4841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Wamsley J. K., Kuhar M. J. High affinity GABA receptors-autoradiographic localization. Brain Res. 1981 Oct 19;222(2):285–307. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst A., Cortés R., Palacios J. M. The distribution of glycine receptors in the human brain. A light microscopic autoradiographic study using [3H]strychnine. Neuroscience. 1986;17(1):11–35. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rentrop M., Knapp B., Winter H., Schweizer J. Aminoalkylsilane-treated glass slides as support for in situ hybridization of keratin cDNAs to frozen tissue sections under varying fixation and pretreatment conditions. Histochem J. 1986 May;18(5):271–276. doi: 10.1007/BF01676237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. G., Schoch P., Häring P., Takacs B., Möhler H. Resolving GABAA/benzodiazepine receptors: cellular and subcellular localization in the CNS with monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci. 1987 Jun;7(6):1866–1886. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-06-01866.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoch P., Häring P., Takacs B., Stähli C., Möhler H. A GABA/benzodiazepine receptor complex from bovine brain: purification, reconstitution and immunological characterization. J Recept Res. 1984;4(1-6):189–200. doi: 10.3109/10799898409042549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoch P., Richards J. G., Häring P., Takacs B., Stähli C., Staehelin T., Haefely W., Möhler H. Co-localization of GABA receptors and benzodiazepine receptors in the brain shown by monoclonal antibodies. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):168–171. doi: 10.1038/314168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Darlison M. G., Fujita N., Burt D. R., Stephenson F. A., Rodriguez H., Rhee L. M., Ramachandran J., Reale V., Glencorse T. A. Sequence and functional expression of the GABA A receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):221–227. doi: 10.1038/328221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh B. H., Ballivet M., Schmidt J. Acetylcholine receptor synthesis rate and levels of receptor subunit messenger RNAs in chick muscle. Neuroscience. 1988 Jan;24(1):175–187. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Barnard E. A. A gamma-aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptor complex from bovine cerebral cortex. Improved purification with preservation of regulatory sites and their interactions. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7219–7223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Brastrup C. Benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):732–734. doi: 10.1038/266732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séquier J. M., Hunziker W., Richards G. Localization of calbindin D28 mRNA in rat tissues by in situ hybridization. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Mar 31;86(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90563-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. A new method for receptor autoradiography: [3H]opioid receptors in rat brain. Brain Res. 1979 Dec 28;179(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90442-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. Radiohistochemical localization of benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Feb;212(2):337–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]