Abstract
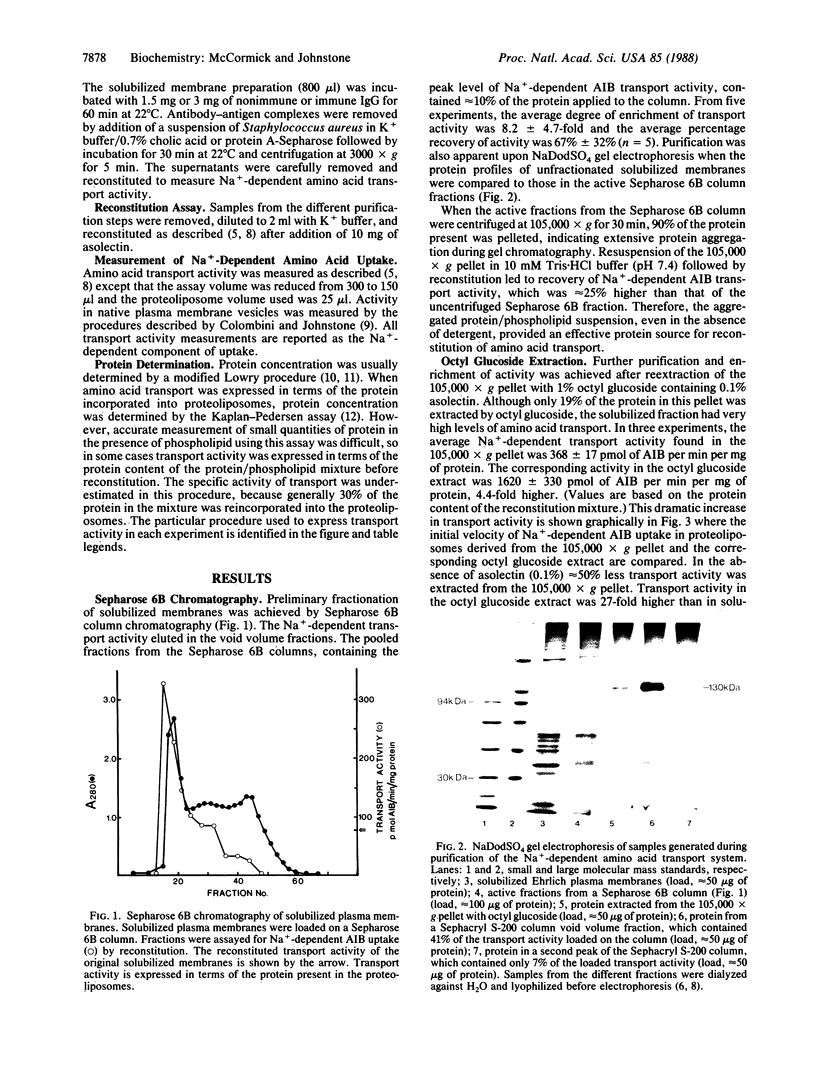
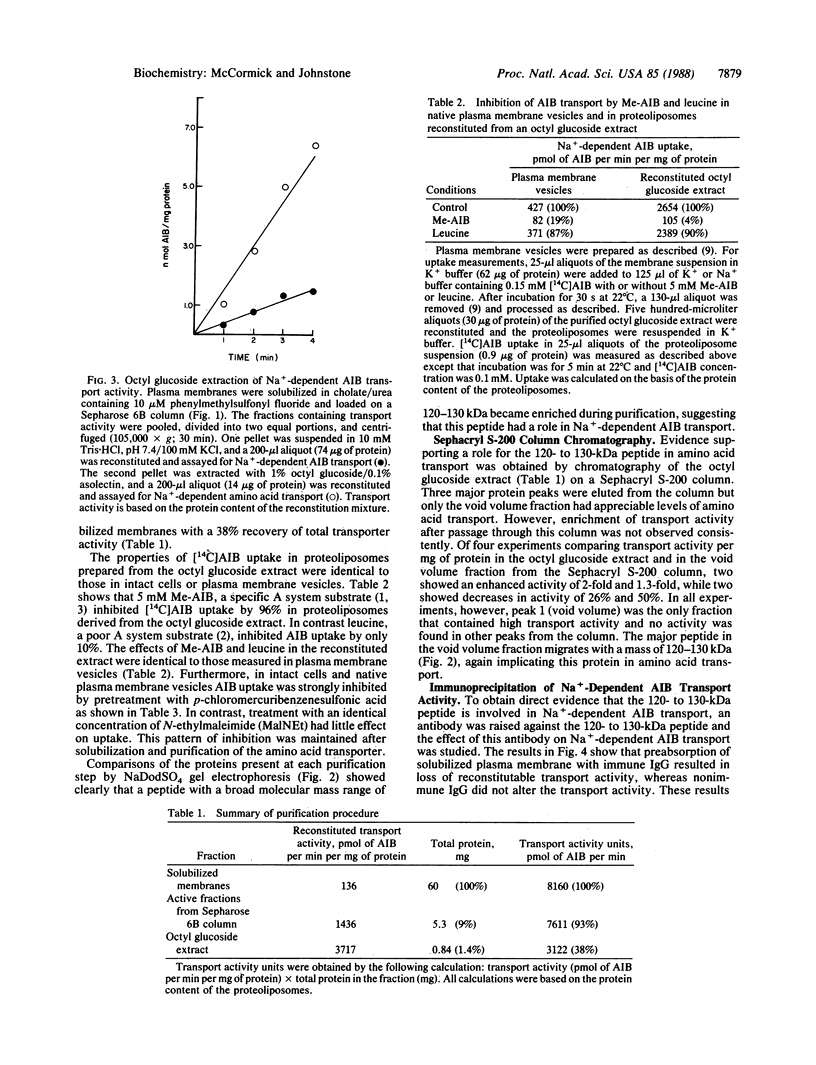
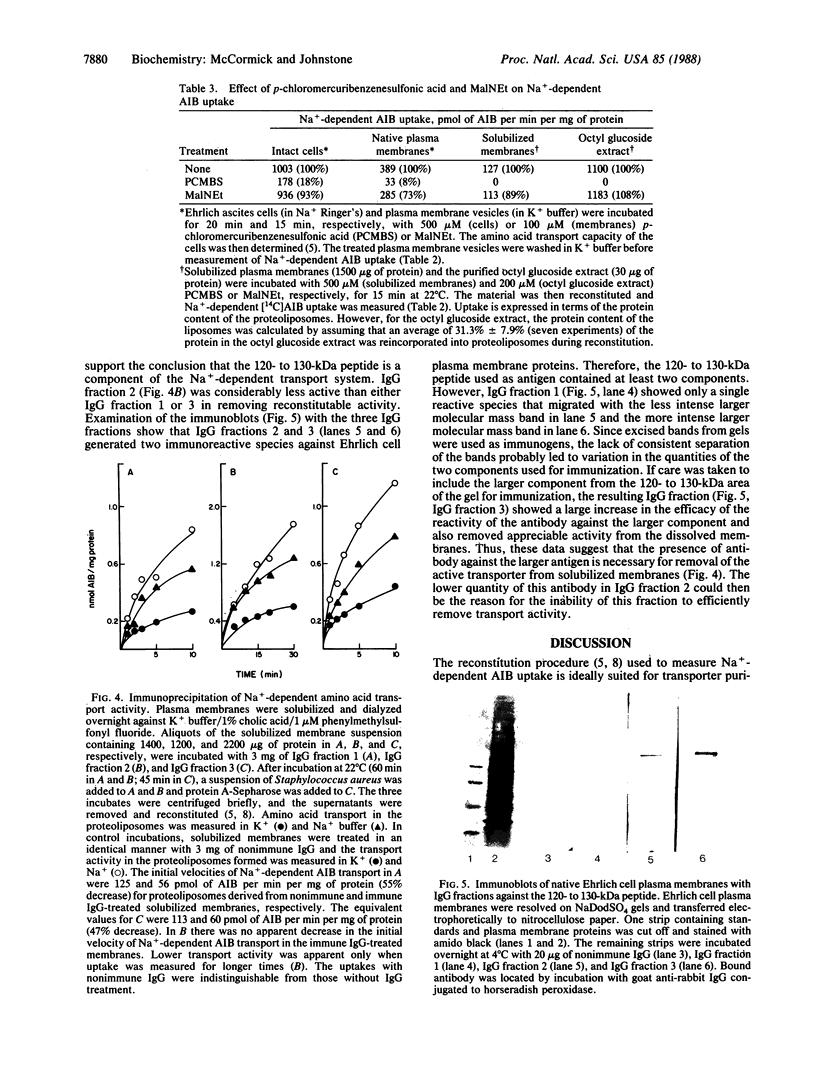
A reconstitution assay was used to measure transport activity during purification of a Na+-dependent amino acid transporter from Ehrlich cell plasma membrane. Cholate/urea-solubilized membranes were fractionated on a Sepharose 6B column and transport activity was recovered in the column void volume. Centrifugation of the void volume fraction at 105,000 X g and reextraction of the pellet with 1% octyl glucoside led to recovery of an extract whose specific transport activity was nearly 30-fold higher than that of the original solubilized extract with a recovery of 38% of the original activity. The properties of amino acid uptake in the purified reconstituted transporter were identical to those in native plasma membrane vesicles. The major component present in the purified fraction had a molecular mass of 120-130 kDa. Strong evidence that this 120- to 130-kDa peptide contains a component of the amino acid transporter was obtained by immunoprecipitation of transport activity from solubilized membranes with an antibody against the 120- to 130-kDa peptide. This study tentatively identifies a component of the Na+-dependent amino acid transporter as a peptide with an apparent molecular mass of 120-130 kDa.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barzilai A., Spanier R., Rahamimoff H. Immunological identification of the synaptic plasma membrane Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10315–10320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N., Liang M., Archer E. G. A distinct Na+-requiring transport system for alanine, serine, cysteine, and similar amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5237–5246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombini M., Johnstone R. M. Na+-dependent amino acid transport in plasma membrane vesicles from Ehrlich ascites cells. J Membr Biol. 1974;15(3):261–276. doi: 10.1007/BF01870091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudeck K. L., Dudenhausen E. E., Chiles T. C., Fafournoux P., Kilberg M. S. Evidence for inherent differences in the system A carrier from normal and transformed liver tissue. Differential inactivation and substrate protection in membrane vesicles and reconstituted proteoliposomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12565–12569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes M. R., McGivan J. D. Comparison of the effects of certain thiol reagents on alanine transport in plasma membrane vesicles from rat liver and their use in identifying the alanine carrier. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 15;214(2):489–495. doi: 10.1042/bj2140489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im W. B., Spector A. A. Sodium-dependent neutral amino acid transport in native and reconstituted membrane vesicles from Ehrlich cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):764–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone R. M. Electrogenic amino acid transport. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;57(1):1–15. doi: 10.1139/y79-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R. S., Pedersen P. L. Determination of microgram quantities of protein in the presence of milligram levels of lipid with amido black 10B. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsell H., Korn K., Ferguson D., Menuhr H., Ollig D., Haase W. Reconstitution and partial purification of several Na+ cotransport systems from renal brush-border membranes. Properties of the L-glutamate transporter in proteoliposomes. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6548–6558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Tolbert N. E., Bieber L. L. Protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples: manual and automated procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;72:296–303. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)72018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. I., Silvius J. R., Johnstone R. M. Effect of alkali cations on freeze-thaw-dependent reconstitution of amino acid transport from Ehrlich ascites cell plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5706–5714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. I., Tsang D., Johnstone R. M. A simple and efficient method for reconstitution of amino acid and glucose transport systems from Ehrlich ascites cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jun;231(2):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90398-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OXENDER D. L., CHRISTENSEN H. N. DISTINCT MEDIATING SYSTEMS FOR THE TRANSPORT OF NEUTRAL AMINO ACIDS BY THE EHRLICH CELL. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3686–3699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotwell M. A., Kilberg M. S., Oxender D. L. The regulation of neutral amino acid transport in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
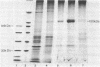
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M., Peerce B. E. Identification and conformational changes of the intestinal proline carrier. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):14993–14996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]