Abstract
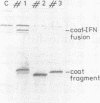
We have inserted the sequence 5'-AAG-GAGGU-3', which is complementary to the 3' terminus of Escherichia coli 16S rRNA, in a reading frame and analyzed its effect on the accuracy and overall rate of translation in vivo. Translation over the sequence yields a 50% ribosomal frameshift if the reading phase is A-AGG-AGG-U. The other two possible frames do not give shifts. The introduction of a UAA stop codon before (UAA-AGG-AGG-U) but not after (A-AGG-AGG-UAA) the AGG codons abolishes the frameshift. The change in the reading phase occurs exclusively to the +1 direction. Efficient frameshifting is also induced by the sequence A-AGA-AGA-U. The arginine codons AGG and AGA are read by minor tRNA. Suppression of frameshifting takes place when a gene for minor tRNA(Arg) is introduced on a multicopy plasmid. We suggest that frameshifting during translation of the A-AGG-AGG-U sequence is due to the erroneous decoding of the tandem AGG codons and arises by depletion of tRNA(Arg). The complementarity of tandem AGG codons to the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA is a coincidence and apparently not related to the shift. Replacing the AGG-AGG sequence by the optimal arginine codons CGU-CGU does not increase the overall rate of translation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F., Reid B. R., Anderson C. W. Normal tRNAs promote ribosomal frameshifting. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1119–1131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90225-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Schmidt B. F., van Strien A., van Boom J., van Westrenen J., van Duin J. Lysis gene of bacteriophage MS2 is activated by translation termination at the overlapping coat gene. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigen W. J., Caskey C. T. Expression of peptide chain release factor 2 requires high-efficiency frameshift. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):273–275. doi: 10.1038/322273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigen W. J., Caskey C. T. Translational frameshifting: where will it stop? Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90652-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A., Yanofsky C. A ribosome binding site sequence is necessary for efficient expression of the distal gene of a translationally-coupled gene pair. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4757–4768. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix D. B., Thompson R. C. Elongation factor Tu.guanosine 3'-diphosphate 5'-diphosphate complex increases the fidelity of proofreading in protein biosynthesis: mechanism for reducing translational errors introduced by amino acid starvation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2027–2031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelmann P., Gallant J. Mistranslation in E. coli. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Duerinck F., Haegeman G., Iserentant D., Merregaert J., Min Jou W., Molemans F., Raeymaekers A., Van den Berghe A. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage MS2 RNA: primary and secondary structure of the replicase gene. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):500–507. doi: 10.1038/260500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean H. J., de Henau S., Crothers D. M. On the physical basis for ambiguity in genetic coding interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):610–614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm L. Codon usage and gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):3075–3087. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.3075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. J. Kinetic proofreading: a new mechanism for reducing errors in biosynthetic processes requiring high specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4135–4139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 15;146(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90363-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Townsley K., Varmus H. E., Majors J. Two efficient ribosomal frameshifting events are required for synthesis of mouse mammary tumor virus gag-related polyproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4298–4302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Varmus H. E. Expression of the Rous sarcoma virus pol gene by ribosomal frameshifting. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1237–1242. doi: 10.1126/science.2416054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzara G. P., Plunkett G., 3rd, McClain W. H. DNA sequence of the transfer RNA region of bacteriophage T4: implications for transfer RNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):889–892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzara G. P., Seidman J. G., McClain W. H., Yesian H., Abelson J., Guthrie C. Nucleotide sequence of an arginine transfer ribonucleic acid from bacteriophage T4. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8245–8253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menninger J. R., Caplan A. B., Gingrich P. K., Atherly A. G. Tests of the ribosome editor hypothesis. II. Relaxed (relA) and stringent (relA+) E. coli differ in rates of dissociation of peptidyl-tRNA from ribosomes. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(2):215–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00330642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra R., Reeves P. Intermediates in the synthesis of TolC protein include an incomplete peptide stalled at a rare Arg codon. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):151–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninio J. Kinetic amplification of enzyme discrimination. Biochimie. 1975;57(5):587–595. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaut E., Stanssens P., Fiers W. Plasmid vectors for high-efficiency expression controlled by the PL promoter of coliphage lambda. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M., Lilley R., Little S., Emtage J. S., Yarranton G., Stephens P., Millican A., Eaton M., Humphreys G. Codon usage can affect efficiency of translation of genes in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6663–6671. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruusala T., Ehrenberg M., Kurland C. G. Is there proofreading during polypeptide synthesis? EMBO J. 1982;1(6):741–745. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner B. E., Hsiung H. M., Belagaje R. M., Mayne N. G., Schoner R. G. Role of mRNA translational efficiency in bovine growth hormone expression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5403–5407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Li W. H. Codon usage in regulatory genes in Escherichia coli does not reflect selection for 'rare' codons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7737–7749. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Stone P. J. Proofreading of the codon-anticodon interaction on ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):198–202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varenne S., Lazdunski C. Effect of distribution of unfavourable codons on the maximum rate of gene expression by an heterologous organism. J Theor Biol. 1986 May 7;120(1):99–110. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(86)80020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. G., Kurland C. G. Translational accuracy enhanced in vitro by (p)ppGpp. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(1):139–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00267363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. B., Dunn D. M., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. Slippery runs, shifty stops, backward steps, and forward hops: -2, -1, +1, +2, +5, and +6 ribosomal frameshifting. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:687–693. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. B., Dunn D. M., Dahlberg A. E., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. Reading frame switch caused by base-pair formation between the 3' end of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during elongation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1503–1507. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02969.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R., Gallant J. Mechanism of ribosome frameshifting during translation of the genetic code. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):389–393. doi: 10.1038/302389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Nomura M. Feedback regulation of ribosomal protein synthesis in E. coli: localization of the mRNA target sites for repressor action of ribosomal protein L1. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):243–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90520-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]