Abstract
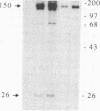
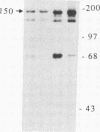
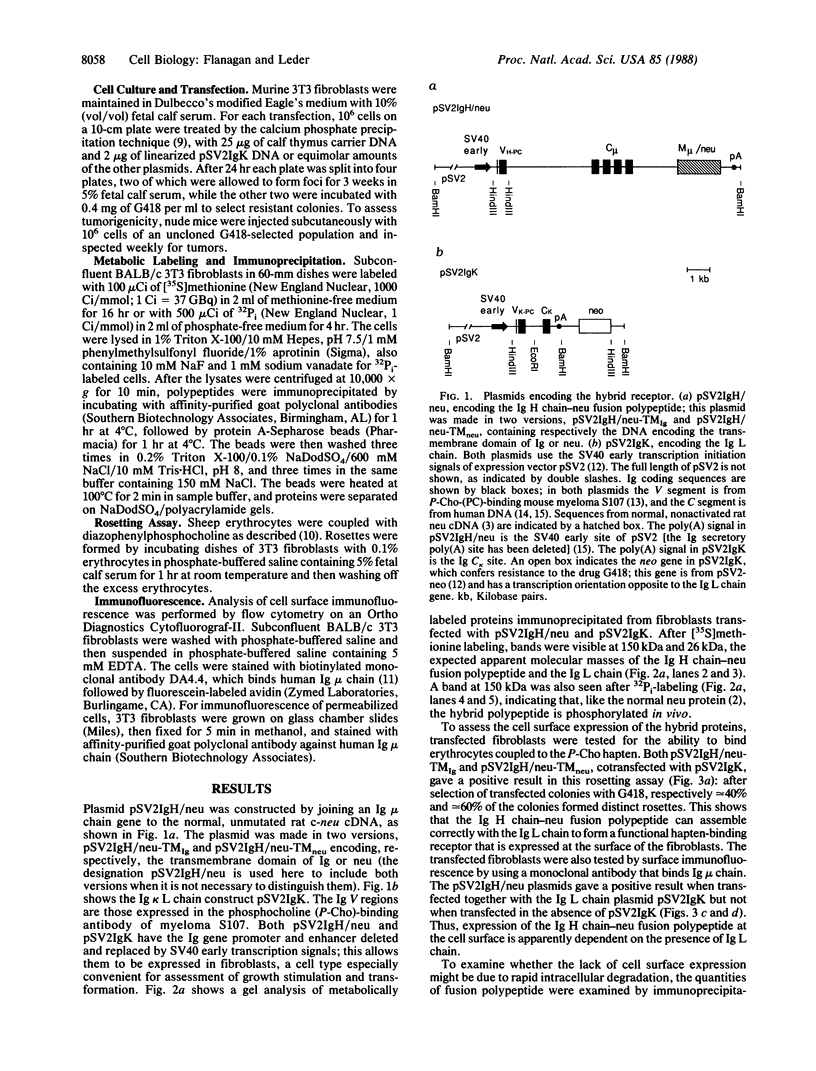
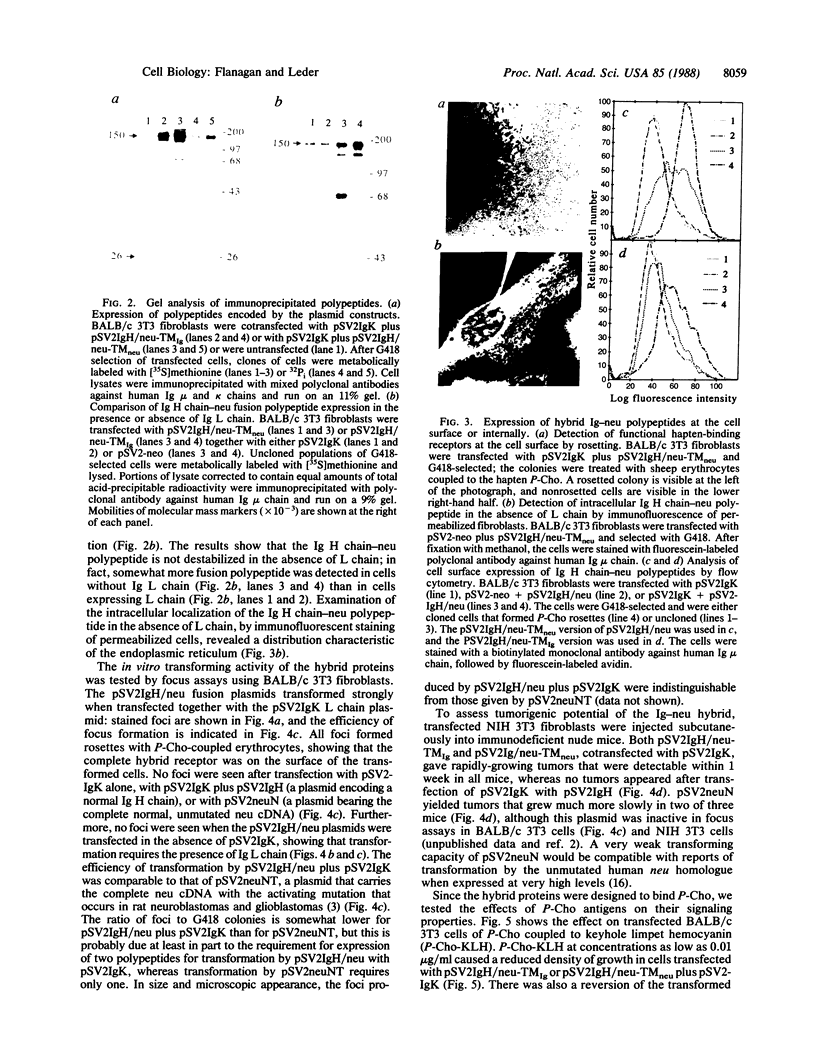
The protein encoded by the neu protooncogene (human gene symbol NGL for neuro/glioblastoma-derived) is a member of the surface receptor/tyrosine kinase family. Though its structure suggests that it can transduce a transmembrane signal, neither its extracellular ligand nor its critical intracellular substrates are known. To explore the functional properties of the protein encoded by neu, we created a fusion gene that joins the cytoplasmic domain of neu to the extracellular portion of an immunoglobulin heavy chain. The localization of the fusion polypeptide can then be controlled by coexpression with immunoglobulin light chain. In the absence of light chain, the heavy chain-neu polypeptide is expressed intracellularly and has no transforming activity. By contrast, in the presence of light chain the fusion polypeptide is expressed at the cell surface and produces tumorigenic foci. Thus, transformation apparently requires expression at the cell surface, where the neu intracellular domain can interact with components that are localized to the plasma membrane. The fusion protein is active in cellular transformation when the transmembrane domain is derived either from neu or from immunoglobulin, indicating that the neu transmembrane domain is not specifically required for transformation, although neu activation in tumors is known to result from a point mutation in this region. The extracellular immunoglobulin heavy and light chain domains of the fusion protein form a functional binding site that allows antigen to modulate its activity, reversing the transforming effect.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Chen K. C., Smith S. D., Rabbitts T. H. Fusion of an immunoglobulin variable gene and a T cell receptor constant gene in the chromosome 14 inversion associated with T cell tumors. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90243-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. The neu oncogene encodes an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):226–230. doi: 10.1038/319226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Neriah Y., Daley G. Q., Mes-Masson A. M., Witte O. N., Baltimore D. The chronic myelogenous leukemia-specific P210 protein is the product of the bcr/abl hybrid gene. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):212–214. doi: 10.1126/science.3460176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Fazekas de St Groth B., Ullrich A., Green W., Schlessinger J. High-affinity interleukin 2 binding by an oncogenic hybrid interleukin 2-epidermal growth factor receptor molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2125–2129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Neale M. J. Induction of clonally restricted thymus-dependent antibody responses in vitro using phosphorylcholine derivatized sheep erythrocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1980;38(3-4):231–238. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90271-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Receptors for epidermal growth factor and other polypeptide mitogens. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:881–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner D., Leder P. Role of an RNA cleavage/poly(A) addition site in the production of membrane-bound and secreted IgM mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8658–8662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny C. T., Yoshikai Y., Mak T. W., Smith S. D., Hollis G. F., Kirsch I. R. A chromosome 14 inversion in a T-cell lymphoma is caused by site-specific recombination between immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor loci. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):549–551. doi: 10.1038/320549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Pierce J. H., Kraus M. H., Segatto O., King C. R., Aaronson S. A. erbB-2 is a potent oncogene when overexpressed in NIH/3T3 cells. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):178–182. doi: 10.1126/science.2885917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drebin J. A., Link V. C., Stern D. F., Weinberg R. A., Greene M. I. Down-modulation of an oncogene protein product and reversion of the transformed phenotype by monoclonal antibodies. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):697–706. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. Cloned human and mouse kappa immunoglobulin constant and J region genes conserve homology in functional segments. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto T., Mendelsohn J., Le A., Sato G. H., Lazar C. S., Gill G. N. Relation of epidermal growth factor receptor concentration to growth of human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7761–7766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Kraus M. H., Aaronson S. A. Amplification of a novel v-erbB-related gene in a human mammary carcinoma. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):974–976. doi: 10.1126/science.2992089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan S. P., Rudikoff S., Seidman J. G., Leder P., Scharff M. D. Nucleic acid and protein sequences of phosphocholine-binding light chains. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1366–1370. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
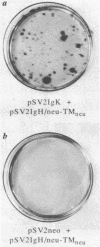
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Hughes S. H., Barbacid M. A human oncogene formed by the fusion of truncated tropomyosin and protein tyrosine kinase sequences. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):743–748. doi: 10.1038/319743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama S., Kubagawa H., Cooper M. D. Activation of human B cells and inhibition of their terminal differentiation by monoclonal anti-mu antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H., Alcaraz G., Hohman R., Kinet J. P., Pribluda V., Quarto R. The receptor with high affinity for immunoglobulin E. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:419–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols E. J., Manger R., Hakomori S., Herscovics A., Rohrschneider L. R. Transformation by the v-fms oncogene product: role of glycosylational processing and cell surface expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3467–3475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman S., Catovsky D. Prognostic significance of chromosome abnormalities in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1984 Dec;58(4):649–660. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb06112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel H., Dull T. J., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. A chimaeric receptor allows insulin to stimulate tyrosine kinase activity of epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):68–70. doi: 10.1038/324068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Dull T. J., Rettenmier C. W., Ralph P., Ullrich A., Sherr C. J. Transforming potential of the c-fms proto-oncogene (CSF-1 receptor). Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):549–552. doi: 10.1038/325549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Rettenmier C. W., Look A. T., Sherr C. J. Cell surface expression of v-fms-coded glycoproteins is required for transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1999–2009. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter A. L., Hung M. C., Vaidyanathan L., Weinberg R. A., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Ullrich A., Coussens L. The neu gene: an erbB-homologous gene distinct from and unlinked to the gene encoding the EGF receptor. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):976–978. doi: 10.1126/science.2992090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Libermann T. A., Lax I., Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Biological role of epidermal growth factor-receptor clustering. Investigation with monoclonal anti-receptor antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):846–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siden E., Alt F. W., Shinefeld L., Sato V., Baltimore D. Synthesis of immunoglobulin mu chain gene products precedes synthesis of light chains during B-lymphocyte development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1823–1827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinn E., Muller W., Pattengale P., Tepler I., Wallace R., Leder P. Coexpression of MMTV/v-Ha-ras and MMTV/c-myc genes in transgenic mice: synergistic action of oncogenes in vivo. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Heffernan P. A., Weinberg R. A. p185, a product of the neu proto-oncogene, is a receptorlike protein associated with tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1729–1740. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]