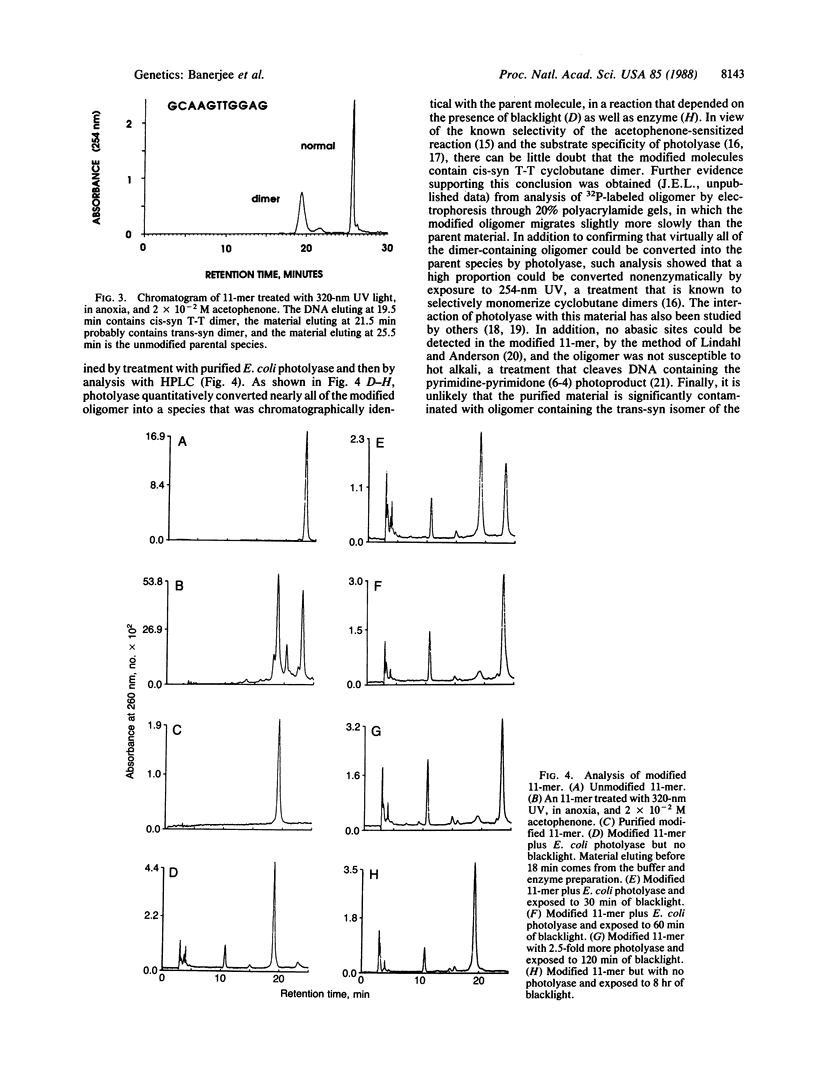
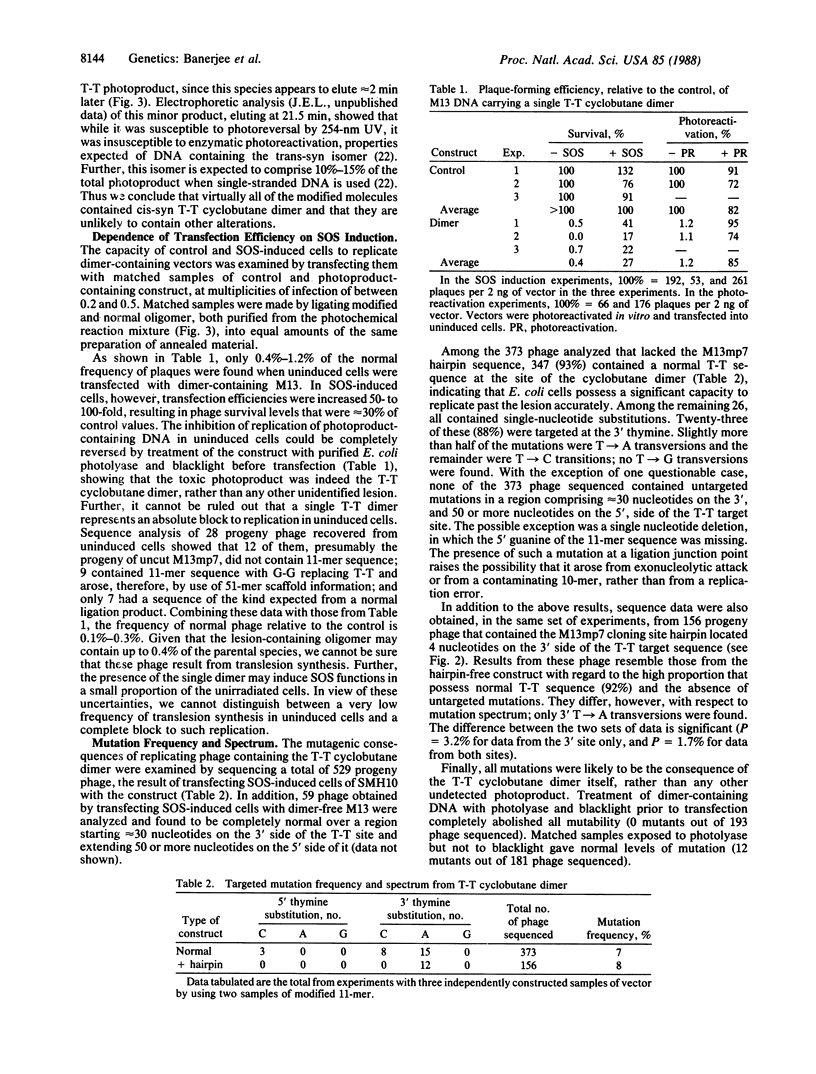
Abstract
We have constructed a single-stranded vector that contains a uniquely located cis-syn T-T cyclobutane dimer by ligating a synthetic oligomer containing this UV photoproduct into M13mp7 viral DNA linearized with EcoRI. In the absence of SOS induction, transfection of a uvrA6 mutant of Escherichia coli with this vector gave very few progeny plaques, and the data imply that a single dimer blocks replication in at least 99.5% of the molecules. In vitro photoreactivation completely abolished this inhibition. Transfection of cells irradiated with UV at 4 J.m-2 to induce the SOS response gave 27% of the number of plaques found with a dimer-free control. Nucleotide sequence analysis of 529 progeny phage showed that translesion synthesis was usually accurate: the normal sequence was found in 93% of them. Where mutations occurred, all were targeted single-nucleotide substitutions, with approximately 90% being targeted at the 3' nucleotide of the lesion: of a total of 26 mutations, 15 were 3' T----A, 8 were 3' T----C, and 3 were 5' T----C. No T----G mutations were found. In addition to these results with the normal construct, data were also obtained from vectors in which the M13mp7 cloning site, which forms a hairpin in single-stranded DNA, was present 4 nucleotides on the 3' side of the T-T dimer. These hairpin-containing vectors gave a very similar mutation frequency (8% versus 7%) but altered mutation spectrum: all 12 mutations detected were 3' T----A transversions, a difference from the previous set of data that is significant (P = 0.03).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu A. K., Essigmann J. M. Site-specifically modified oligodeoxynucleotides as probes for the structural and biological effects of DNA-damaging agents. Chem Res Toxicol. 1988 Jan-Feb;1(1):1–18. doi: 10.1021/tx00001a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Champoux J. J. Cutting of M13mp7 phage DNA and excision of cloned single-stranded sequences by restriction endonucleases. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:90–98. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brash D. E., Franklin W. A., Sancar G. B., Sancar A., Haseltine W. A. Escherichia coli DNA photolyase reverses cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers but not pyrimidine-pyrimidone (6-4) photoproducts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11438–11441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brash D. E., Haseltine W. A. UV-induced mutation hotspots occur at DNA damage hotspots. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):189–192. doi: 10.1038/298189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin W. A., Haseltine W. A. The role of the (6-4) photoproduct in ultraviolet light-induced transition mutations in E. coli. Mutat Res. 1986 Jan;165(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(86)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman B. W., Schaaper R. M., Haseltine W. A., Dunn R. L., Brash D. E. The C-C (6-4) UV photoproduct is mutagenic in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6945–6949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Sancar A. Binding of E. coli DNA photolyase to a defined substrate containing a single T mean value of T dimer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1109–1120. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Sancar G. B., Holbrook S. R., Sancar A. Mechanism of damage recognition by Escherichia coli DNA photolyase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13188–13197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemmink J., Boelens R., Koning T., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Kaptein R. 1H NMR study of the exchangeable protons of the duplex d(GCGTTGCG).d(CGCAACGC) containing a thymine photodimer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4645–4653. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Mutational specificity of depurination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1494–1498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamola A. A. Specific formation of thymine dimers in DNA. Photochem Photobiol. 1969 Mar;9(3):291–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1969.tb07292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C. W. Are pyrimidine dimers non-instructive lesions? Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(3):511–513. doi: 10.1007/BF00293945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C. W., Christensen R. B., Christensen J. R. Identity of the photoproduct that causes lacI mutations in UV-irradiated Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):767–768. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.767-768.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClerc J. E., Istock N. L., Saran B. R., Allen R., Jr Sequence analysis of ultraviolet-induced mutations in M13lacZ hybrid phage DNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):217–237. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClerc J. E., Istock N. L. Specificity of UV mutagenesis in the lac promoter of M13lac hybrid phage DNA. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):596–598. doi: 10.1038/297596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Andersson A. Rate of chain breakage at apurinic sites in double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3618–3623. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippke J. A., Gordon L. K., Brash D. E., Haseltine W. A. Distribution of UV light-induced damage in a defined sequence of human DNA: detection of alkaline-sensitive lesions at pyrimidine nucleoside-cytidine sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3388–3392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H. Mutagenic specificity of ultraviolet light. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 5;182(1):45–65. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B., Smith F. W., Sancar A. Binding of Escherichia coli DNA photolyase to UV-irradiated DNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):1849–1855. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaaper R. M., Dunn R. L., Glickman B. W. Mechanisms of ultraviolet-induced mutation. Mutational spectra in the Escherichia coli lacI gene for a wild-type and an excision-repair-deficient strain. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):187–202. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90305-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss B., Rabkin S., Sagher D., Moore P. The role of DNA polymerase in base substitution mutagenesis on non-instructional templates. Biochimie. 1982 Aug-Sep;64(8-9):829–838. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang M. S., Hrncir J., Mitchell D., Ross J., Clarkson J. The relative cytotoxicity and mutagenicity of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers and (6-4) photoproducts in Escherichia coli cells. Mutat Res. 1986 Jun;161(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(86)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. D., Skopek T. R., Hutchinson F. Changes in DNA base sequence induced by targeted mutagenesis of lambda phage by ultraviolet light. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 5;173(3):273–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



