Abstract
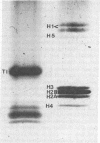
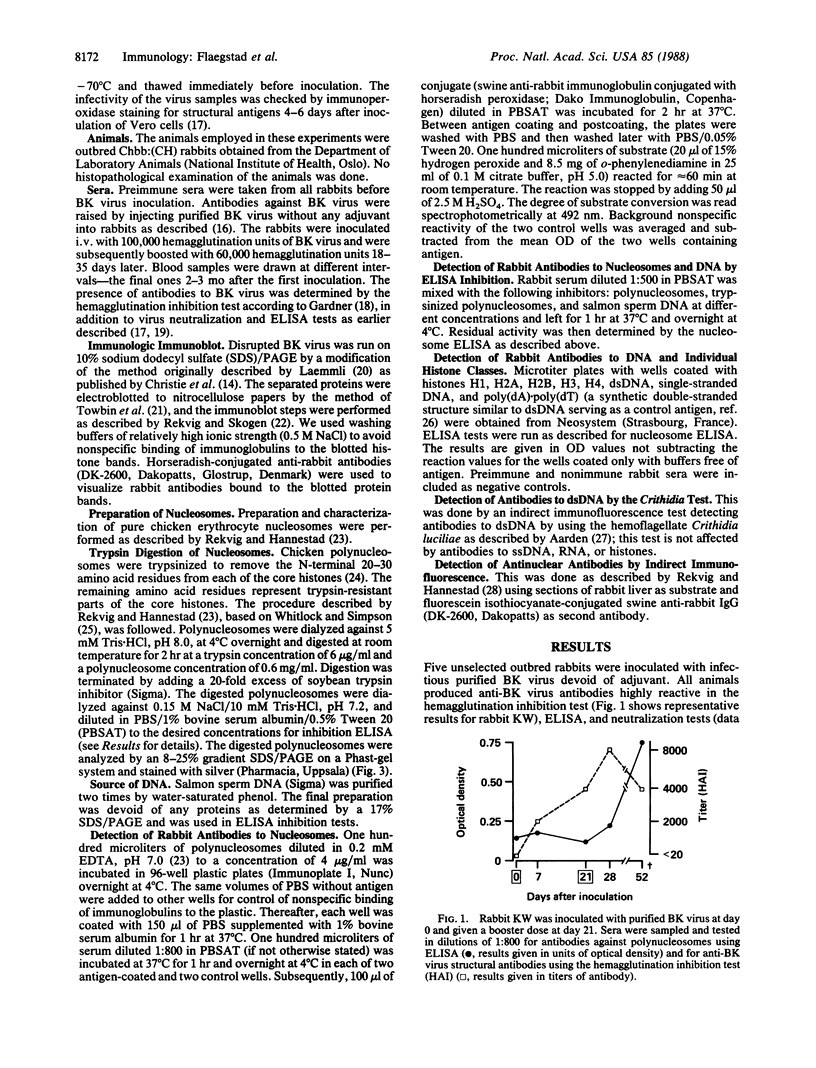
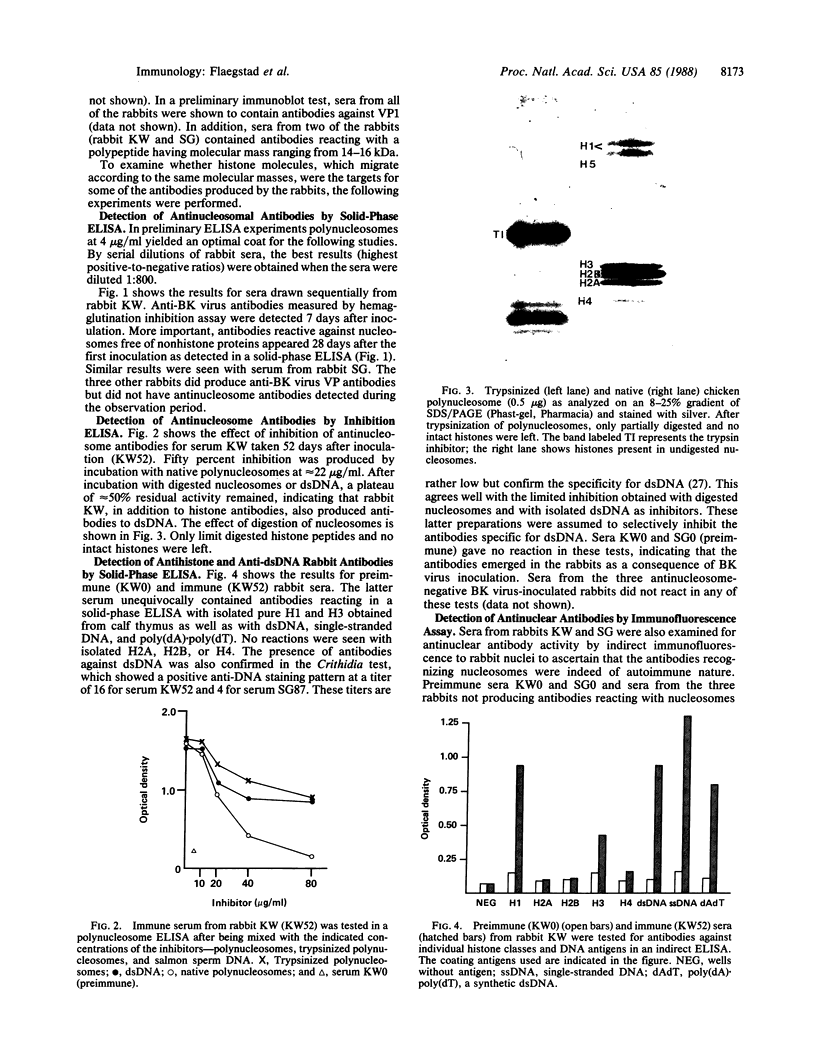
BK virus particles contain histones of host cell origin that combine with viral DNA to form minichromosomes. Data from earlier immunoblotting experiments demonstrated that rabbits inoculated i.v. with purified infectious BK virus produced antibodies not only to the viral structural protein VP1 but also to migrating polypeptides of a molecular mass ranging from 14-16 kDa. These proteins were believed to represent certain histone classes. To examine this hypothesis, sera from five rabbits inoculated with BK virus were analyzed by ELISA for antibodies against polynucleosomes, the individual histone classes, and double-stranded DNA, as well as against antigens carried by the structural viral proteins. Antibodies against polynucleosomes and also against histones H1 and H3 were found in sera from two of five inoculated rabbits. The same sera contained antibodies reacting with double-stranded DNA, whereas no antibodies against H2A, H2B, and H4 were detected. BK virus inoculation may thus lead to a break of tolerance, resulting in autoantibody production against highly conserved antigens that, in this context, may be regarded as "self-antigens", irrespective of the species in which they originate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brady J. N., Lavialle C. A., Radonovich M. F., Salzman N. P. Stable association of viral protein VP1 with simian virus 40 DNA. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):432–437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.432-437.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. N., Lavialle C., Salzman N. P. Efficient transcription of a compact nucleoprotein complex isolated from purified simian virus 40 virions. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):371–381. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.371-381.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P., Tsai T., Gajdusek D. C. Seroepidemiology of human papovaviruses. Discovery of virgin populations and some unusual patterns of antibody prevalence among remote peoples of the world. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Oct;102(4):331–340. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie K. E., Flaegstad T., Traavik T. Characterization of BK virus-specific antibodies in human sera by Western immunoblotting: use of a zwitterionic detergent for restoring the antibody-binding capacity of electroblotted proteins. J Med Virol. 1988 Feb;24(2):183–190. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890240207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. V., Wolfendale M. R., Daniel R. A., Dhanjal N. K., Gardner S. D., Gibson P. E., Field A. M. A prospective study of human polyomavirus infection in pregnancy. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):1–8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Gilchrist C., Allison A. C. Autoimmunity in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Apr;13(4):479–486. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaegstad T., Traavik T., Christie K. E., Joergensen J. Neutralization test for BK virus: plaque reduction detected by immunoperoxidase staining. J Med Virol. 1986 Jul;19(3):287–296. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890190311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaegstad T., Traavik T. Detection of BK virus IgM antibodies by two enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and a hemagglutination inhibition method. J Med Virol. 1985 Oct;17(2):195–204. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaegstad T., Traavik T. Detection of BK virus antibodies measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and two haemagglutination inhibition methods: a comparative study. J Med Virol. 1985 Aug;16(4):351–356. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaegstad T., Traavik T., Kolmannskog S., Stokland T. BK virus infection in children with cancer: serological response studied by haemagglutination inhibition, neutralization, and IgG- and IgM-class specific ELISA tests. J Med Virol. 1988 Jan;24(1):33–44. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890240106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournié G. J., Lambert P. H., Meischer P. A. Release of DNA in circulating blood and induction of anti-DNA antibodies after injection of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1189–1206. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner S. D., Field A. M., Coleman D. V., Hulme B. New human papovavirus (B.K.) isolated from urine after renal transplantation. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1253–1257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91776-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner S. D. Prevalence in England of antibody to human polyomavirus (B.k.). Br Med J. 1973 Jan 13;1(5845):77–78. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5845.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gohill J., Cary P. D., Couppez M., Fritzler M. J. Antibodies from patients with drug-induced and idiopathic lupus erythematosus react with epitopes restricted to the amino and carboxyl termini of histone. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3116–3121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gohill J., Fritzler M. J. Antibodies in procainamide-induced and systemic lupus erythematosus bind the C-terminus of histone 1 (H1). Mol Immunol. 1987 Mar;24(3):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halloran M. J., Parker C. W. The production of antibodies to mononucleotides, oligonucleotides and DNA. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Zaldivar N. M., Scher I., Lambert P. H. Mechanism for induction of anti-DNA antibodies by bacterial lipopolysaccharides in mice. I. Anti-DNA induction by LPS without significant release of DNA in circulating blood. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2151–2156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Bella F., Vesco C. Late modifications of simian virus 40 chromatin during the lytic cycle occur in an immature form of virion. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1138–1150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1138-1150.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1115–1156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneguzzi G., Pignatti P. F., Barbanti-Brodano G., Milanesi G. Minichromosome from BK virus as a template for transcription in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1126–1130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. L., Magilavy D. B., Warren R. W. The immunologic basis of lupus. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1986 Oct;33(5):1191–1202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portolani M., Borgatti M. Stable transformation of mouse, rabbit and monkey cells and abortive transformation of human cells by BK virus, a human papovavirus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Feb;38(2):369–374. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-2-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekvig O. P., Hannestad K. Certain polyclonal antinuclear antibodies cross-react with the surface membrane of human lymphocytes and granulocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(10):1041–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekvig O. P., Hannestad K. The specificity of human autoantibodies that react with both cell nuclei and plasma membranes: the nuclear antigen is present on core mononucleosomes. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2673–2681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes G., Rumpold H., Kurki P., Patrick K. M., Carson D. A., Vaughan J. H. Autoantibodies in infectious mononucleosis have specificity for the glycine-alanine repeating region of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):1026–1040. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D. Origins of anti-DNA autoantibodies. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):321–327. doi: 10.1172/JCI111704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. Antibodies to DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;20(1):1–36. doi: 10.3109/10409238609115899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D., Ward M. Rabbit antibodies to histone fractions as specific reagents for preparative and comparative studies. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 25;245(6):1261–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Allen P. M. The basis for the immunoregulatory role of macrophages and other accessory cells. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):551–557. doi: 10.1126/science.2437650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Van Lente F. Dissection of chromosome structure with trypsin and nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4249–4253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Simpson R. T. Localization of the sites along nucleosome DNA which interact with NH2-terminal histone regions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6516–6520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Elven E. H., van der Veen F. M., Rolink A. G., Issa P., Duin T. M., Gleichmann E. Diseases caused by reactions of T lymphocytes to incompatible structures of the major histocompatibility complex. V. High titers of IgG autoantibodies to double-stranded DNA. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2435–2438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rappard-van der Veen F. M., Rolink A. G., Gleichmann E. Diseases caused by reactions of T lymphocytes towards incompatible structures of the major histocompatibility complex. VI. Autoantibodies characteristic of systemic lupus erythematosus induced by abnormal T-B cell cooperation across I-E. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1555–1560. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]