Abstract
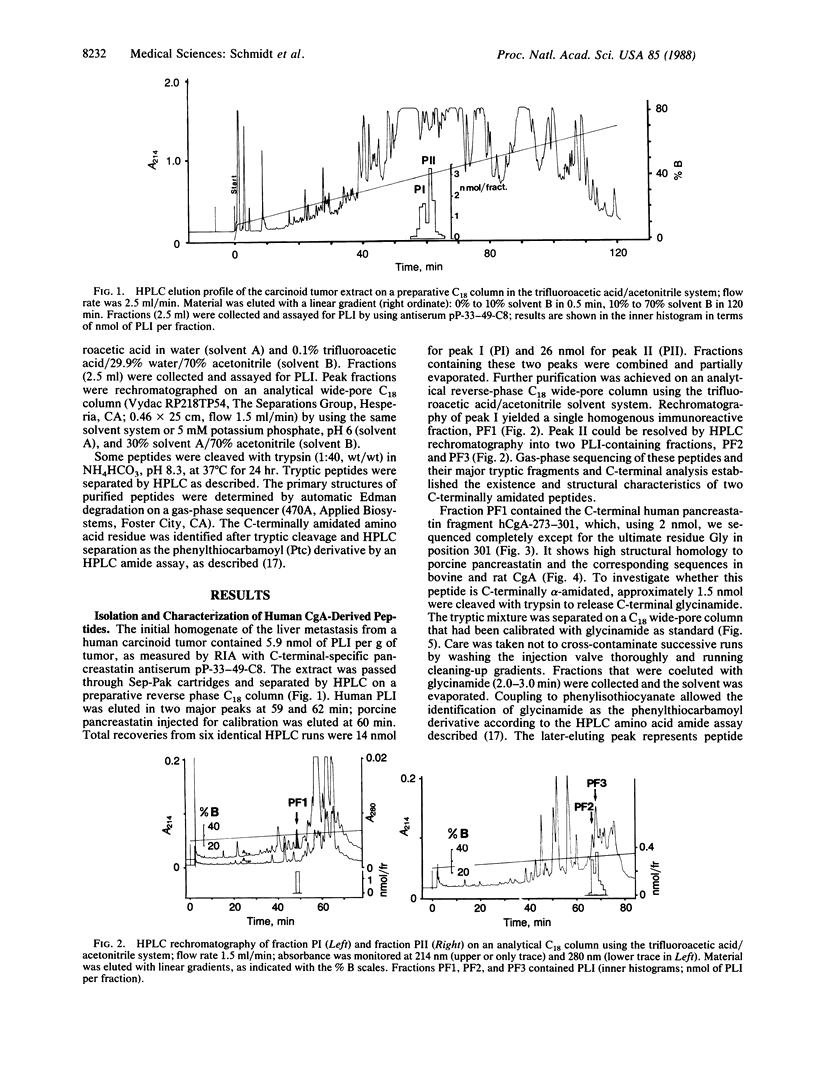
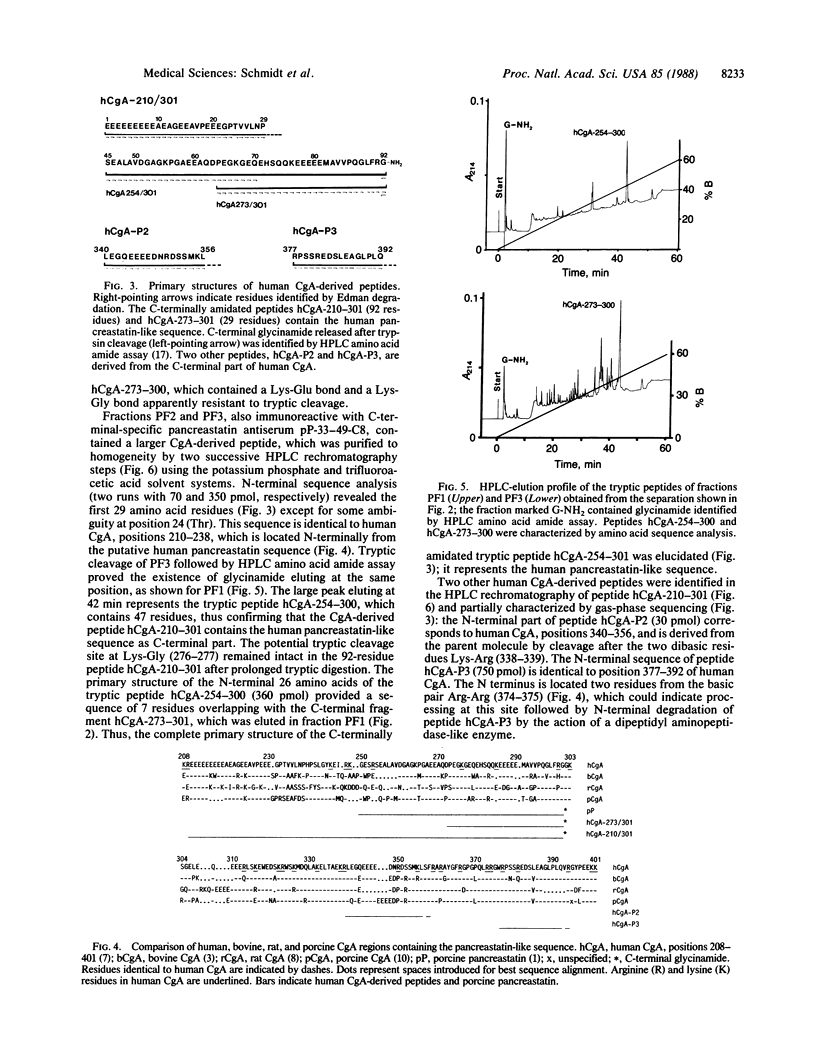
Using an antiserum raised against a synthetic C-terminal peptide of porcine pancreastatin, we detected pancreastatin-like immunoreactivity (PLI) in human pancreatic islets, adrenal medulla, and endocrine tumors. From a carcinoid liver metastasis, human PLI was extracted and purified by HPLC. Two C-terminally amidated peptides were isolated and characterized by sequence analysis. The first peptide, hCgA-210-301, consists of 92 amino acid residues with glycinamide as C terminus. It is identical to the cDNA-derived sequence of human chromogranin A, positions 210-301, which is preceded by two basic residues indicating a putative processing site. The C-terminal part, positions 250-301, shows 70% sequence identity to porcine pancreastatin and represents the human pancreastatin-like sequence. The second peptide, hCgA-273-301, represents a C-terminally amidated fragment of the human pancreastatin sequence, generated by an Asp-Pro cleavage at the N terminus. Peptide hCgA-273-301 was synthesized to confirm the structure of the natural peptide. Two other peptides derived from human chromogranin A were isolated and partially characterized. They are generated by proteolytic cleavage after dibasic amino acids Lys-Arg (positions 338-339) and after Trp-376 of the human chromogranin A sequence, respectively. These results indicate that chromogranin A may represent the precursor for pancreastatin-related and possibly other yet-unidentified peptides of unknown physiological function.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn T. G., Cohn D. V., Gorr S. U., Ornstein D. L., Kashdan M. A., Levine M. A. Primary structure of bovine pituitary secretory protein I (chromogranin A) deduced from the cDNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5043–5047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahrén B., Lindskog S., Tatemoto K., Efendić S. Pancreastatin inhibits insulin secretion and stimulates glucagon secretion in mice. Diabetes. 1988 Mar;37(3):281–285. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.3.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedum U. M., Baeuerle P. A., Konecki D. S., Frank R., Powell J., Mallet J., Huttner W. B. The primary structure of bovine chromogranin A: a representative of a class of acidic secretory proteins common to a variety of peptidergic cells. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1495–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackstone C. D., Seino S., Takeuchi T., Yamada T., Steiner D. F. Novel organization and processing of the guinea pig pancreatic polypeptide precursor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2911–2916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. V., Elting J. J., Frick M., Elde R. Selective localization of the parathyroid secretory protein-I/adrenal medulla chromogranin A protein family in a wide variety of endocrine cells of the rat. Endocrinology. 1984 Jun;114(6):1963–1974. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-6-1963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efendić S., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Quan C., Chang D., Ostenson C. G. Pancreastatin and islet hormone release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7257–7260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhart M., Grube D., Bader M. F., Aunis D., Gratzl M. Chromogranin A in the pancreatic islet: cellular and subcellular distribution. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Dec;34(12):1673–1682. doi: 10.1177/34.12.2878021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E. Is chromogranin a prohormone? Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):301–301. doi: 10.1038/325301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Benedum U. M. Chromogranin A and pancreastatin. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):305–305. doi: 10.1038/325305b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Davidson H. W., Grimaldi K. A., Peshavaria M. Biosynthesis of betagranin in pancreatic beta-cells. Identification of a chromogranin A-like precursor and its parallel processing with proinsulin. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):449–456. doi: 10.1042/bj2440449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Davidson H. W., Peshavaria M. Proteolytic processing of chromogranin A in purified insulin granules. Formation of a 20 kDa N-terminal fragment (betagranin) by the concerted action of a Ca2+-dependent endopeptidase and carboxypeptidase H (EC 3.4.17.10). Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):457–464. doi: 10.1042/bj2440457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Hansen F., Peshavaria M. beta-Granins: 21 kDa co-secreted peptides of the insulin granule closely related to adrenal medullary chromogranin A. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 2;188(2):336–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A. L., Fischer-Colbrie R., Koller K. J., Brownstein M. J., Eiden L. E. The sequence of porcine chromogranin A messenger RNA demonstrates chromogranin A can serve as the precursor for the biologically active hormone, pancreastatin. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2339–2341. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A., Affolter H. U., Eiden L. E., Herbert E., Grimes M. Bovine chromogranin A sequence and distribution of its messenger RNA in endocrine tissues. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):82–86. doi: 10.1038/323082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A., Okayama H., Eiden L. E. Primary structure of rat chromogranin A and distribution of its mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 25;227(2):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80880-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konecki D. S., Benedum U. M., Gerdes H. H., Huttner W. B. The primary structure of human chromogranin A and pancreastatin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17026–17030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T., Burton D., Deftos L. J. Chromogranin A: immunohistology reveals its universal occurrence in normal polypeptide hormone producing endocrine glands. Life Sci. 1983 Oct 24;33(17):1657–1663. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90721-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Hille A., Lee R. W., Zanini A., De Camilli P., Huttner W. B. Secretogranins I and II: two tyrosine-sulfated secretory proteins common to a variety of cells secreting peptides by the regulated pathway. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1999–2011. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. E., Conlon J. M., Mutt V., Carlquist M., Gallwitz B., Creutzfeldt W. Identification of the C-terminally alpha-amidated amino acid in peptides by high-performance liquid chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 2;162(3):467–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. E., Siegel E. G., Lamberts R., Gallwitz B., Creutzfeldt W. Pancreastatin: molecular and immunocytochemical characterization of a novel peptide in porcine and human tissues. Endocrinology. 1988 Sep;123(3):1395–1404. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-3-1395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Hendy G. N., Hamelin J., Paquin J., Lazure C., Metters K. M., Rossier J., Chrétien M. Chromogranin A can act as a reversible processing enzyme inhibitor. Evidence from the inhibition of the IRCM-serine protease 1 cleavage of pro-enkephalin and ACTH at pairs of basic amino acids. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):144–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81425-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya K., Ghatei M. A., Minamino N., Bretherton-Watt D., Matsuo H., Bloom S. R. Isolation of human pancreastatin fragment containing the active sequence from a glucagonoma. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 8;228(1):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80606-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., Fonseca R., Nolan J., Angeletti R. H. Relationship of multiple forms of chromogranin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1645–1651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. P., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Secretion from chromaffin cells is controlled by chromogranin A-derived peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1712–1716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Efendić S., Mutt V., Makk G., Feistner G. J., Barchas J. D. Pancreastatin, a novel pancreatic peptide that inhibits insulin secretion. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):476–478. doi: 10.1038/324476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig R., Scheller R. H. The Aplysia FMRFamide gene encodes sequences related to mammalian brain peptides. DNA. 1986 Dec;5(6):453–461. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1986.5.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]