Abstract
In a subgroup of children with chronic active hepatitis, circulating autoantibodies occur that bind to liver and kidney endoplasmic reticulum (anti-liver/kidney microsome antibody type I or anti-LKM1). Anti-LKM1 titers follow the severity of the disease and the presence of these antibodies serves as a diagnostic marker for this autoimmune hepatitis type II. We demonstrate that anti-LKM1 IgGs specifically inhibit the hydroxylation of bufuralol in human liver microsomes. Using two assay systems with different selectivity for the two cytochrome P-450 isozymes catalyzing bufuralol metabolism in human liver, we show that anti-LKM1 exclusively recognizes cytochrome P-450db1. Immunopurification of the LKM1 antigen from solubilized human liver microsomes resulted in an electrophoretically homogenous protein that had the same molecular mass (50 kDa) as purified P-450db1 and an identical N-terminal amino acid sequence. Recognition of both purified P-450db1 and the immunoisolated protein on western blots by several monoclonal antibodies confirmed the identity of the LKM1 antigen with cytochrome P-450db1. Cytochrome P-450db1 has been identified as the target of a common genetic polymorphism of drug oxidation. However, the relationship between the polymorphic cytochrome P-450db1 and the appearance of anti-LKM1 autoantibodies as well as their role in the pathogenesis of chronic active hepatitis remains speculative.
Full text
PDF

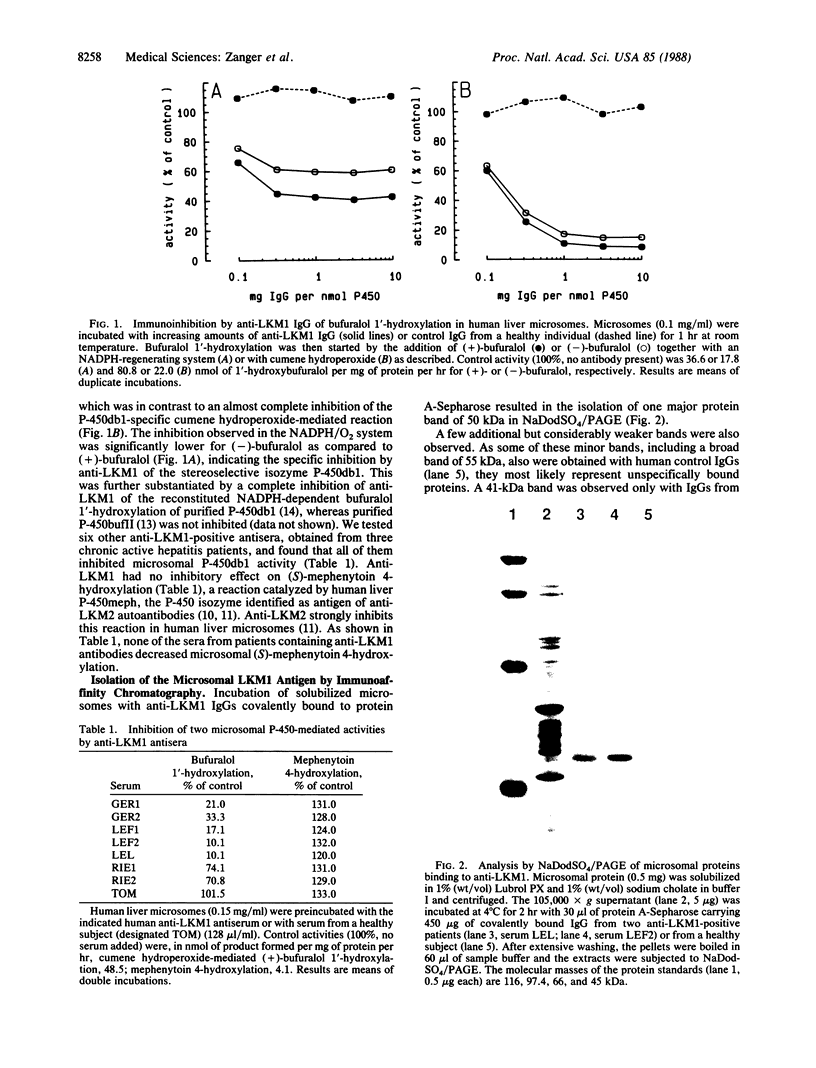

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez F., Bernard O., Homberg J. C., Kreibich G. Anti-liver-kidney microsome antibody recognizes a 50,000 molecular weight protein of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1231–1236. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaune P., Dansette P. M., Mansuy D., Kiffel L., Finck M., Amar C., Leroux J. P., Homberg J. C. Human anti-endoplasmic reticulum autoantibodies appearing in a drug-induced hepatitis are directed against a human liver cytochrome P-450 that hydroxylates the drug. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):551–555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crivelli O., Lavarini C., Chiaberge E., Amoroso A., Farci P., Negro F., Rizzetto M. Microsomal autoantibodies in chronic infection with the HBsAg associated delta (delta) agent. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):232–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lemos-Chiarandini C., Alvarez F., Bernard O., Homberg J. C., Kreibich G. Anti-liver-kidney microsome antibody is a marker for the rat hepatocyte endoplasmic reticulum. Hepatology. 1987 May-Jun;7(3):468–475. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distlerath L. M., Reilly P. E., Martin M. V., Davis G. G., Wilkinson G. R., Guengerich F. P. Purification and characterization of the human liver cytochromes P-450 involved in debrisoquine 4-hydroxylation and phenacetin O-deethylation, two prototypes for genetic polymorphism in oxidative drug metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):9057–9067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. A. Ethnic differences in reactions to drugs and xenobiotics. Therapy. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1986;214:491–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Matsunaga T., Nagata K., Meyer U. A., Nebert D. W., Pastewka J., Kozak C. A., Gillette J., Gelboin H. V., Hardwick J. P. Debrisoquine 4-hydroxylase: characterization of a new P450 gene subfamily, regulation, chromosomal mapping, and molecular analysis of the DA rat polymorphism. DNA. 1987 Apr;6(2):149–161. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Skoda R. C., Kimura S., Umeno M., Zanger U. M., Nebert D. W., Gelboin H. V., Hardwick J. P., Meyer U. A. Characterization of the common genetic defect in humans deficient in debrisoquine metabolism. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):442–446. doi: 10.1038/331442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gut J., Catin T., Dayer P., Kronbach T., Zanger U., Meyer U. A. Debrisoquine/sparteine-type polymorphism of drug oxidation. Purification and characterization of two functionally different human liver cytochrome P-450 isozymes involved in impaired hydroxylation of the prototype substrate bufuralol. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11734–11743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Sterchi E. E., Bienz D., Fransen J. A., Marxer A. Expression and intracellular transport of microvillus membrane hydrolases in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):838–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homberg J. C., Abuaf N., Bernard O., Islam S., Alvarez F., Khalil S. H., Poupon R., Darnis F., Lévy V. G., Grippon P. Chronic active hepatitis associated with antiliver/kidney microsome antibody type 1: a second type of "autoimmune" hepatitis. Hepatology. 1987 Nov-Dec;7(6):1333–1339. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homberg J. C., Abuaf N., Helmy-Khalil S., Biour M., Poupon R., Islam S., Darnis F., Levy V. G., Opolon P., Beaugrand M. Drug-induced hepatitis associated with anticytoplasmic organelle autoantibodies. Hepatology. 1985 Sep-Oct;5(5):722–727. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homberg J. C., Andre C., Abuaf N. A new anti-liver-kidney microsome antibody (anti-LKM2) in tienilic acid-induced hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Mar;55(3):561–570. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronbach T., Mathys D., Gut J., Catin T., Meyer U. A. High-performance liquid chromatographic assays for bufuralol 1'-hydroxylase, debrisoquine 4-hydroxylase, and dextromethorphan O-demethylase in microsomes and purified cytochrome P-450 isozymes of human liver. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrey D., Distlerath L. M., Dannan G. A., Wilkinson G. R., Guengerich F. P. Purification and characterization of the rat liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 involved in the 4-hydroxylation of debrisoquine, a prototype for genetic variation in oxidative drug metabolism. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 5;23(12):2787–2795. doi: 10.1021/bi00307a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggiore G., Bernard O., Homberg J. C., Hadchouel M., Alvarez F., Hadchouel P., Odièvre M., Alagille D. Liver disease associated with anti-liver-kidney microsome antibody in children. J Pediatr. 1986 Mar;108(3):399–404. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80880-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier U. T., Kronbach T., Meyer U. A. Assay of mephenytoin metabolism in human liver microsomes by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1985 Dec;151(2):286–291. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier U. T., Meyer U. A. Genetic polymorphism of human cytochrome P-450 (S)-mephenytoin 4-hydroxylase. Studies with human autoantibodies suggest a functionally altered cytochrome P-450 isozyme as cause of the genetic deficiency. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8466–8474. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Van Keuren M. L. Gel protein stains: silver stain. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:441–447. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Adesnik M., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F., Kemper B., Levin W. The P450 gene superfamily: recommended nomenclature. DNA. 1987 Feb;6(1):1–11. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. I. EVIDENCE FOR ITS HEMOPROTEIN NATURE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2370–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odièvre M., Maggiore G., Homberg J. C., Saadoun F., Couroucé A. M., Yvart J., Hadchouel M., Alagille D. Seroimmunologic classification of chronic hepatitis in 57 children. Hepatology. 1983 May-Jun;3(3):407–409. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzetto M., Bianchi F. B., Doniach D. Characterization of the microsomal antigen related to a subclass of active chronic hepatitis. Immunology. 1974 Mar;26(3):589–601. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzetto M., Swana G., Doniach D. Microsomal antibodies in active chronic hepatitis and other disorders. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Nov;15(3):331–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah R. R., Oates N. S., Idle J. R., Smith R. L., Lockhart J. D. Impaired oxidation of debrisoquine in patients with perhexiline neuropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jan 30;284(6312):295–299. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6312.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vento S., Eddleston A. L. Immunological aspects of chronic active hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 May;68(2):225–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukochi Y., Masters B. S. Some properties of a detergent-solubilized NADPH-cytochrome c(cytochrome P-450) reductase purified by biospecific affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5337–5344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanger U. M., Vilbois F., Hardwick J. P., Meyer U. A. Absence of hepatic cytochrome P450bufI causes genetically deficient debrisoquine oxidation in man. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 26;27(15):5447–5454. doi: 10.1021/bi00415a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]