Abstract
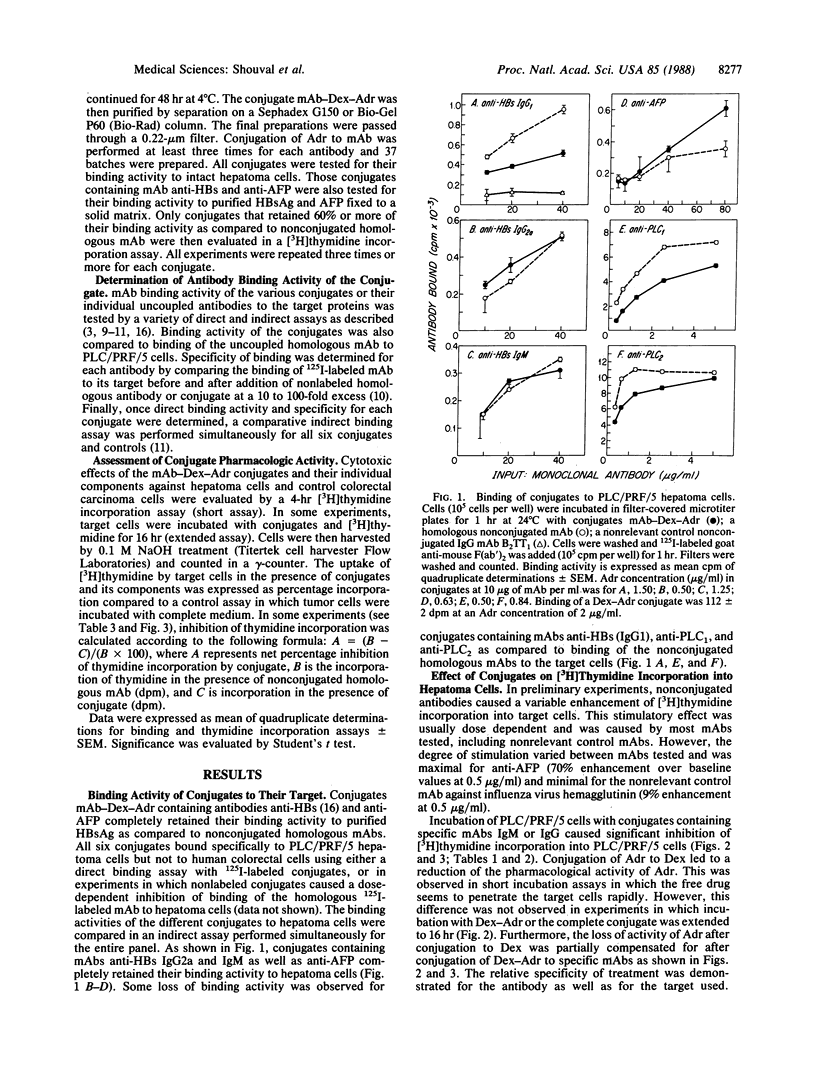
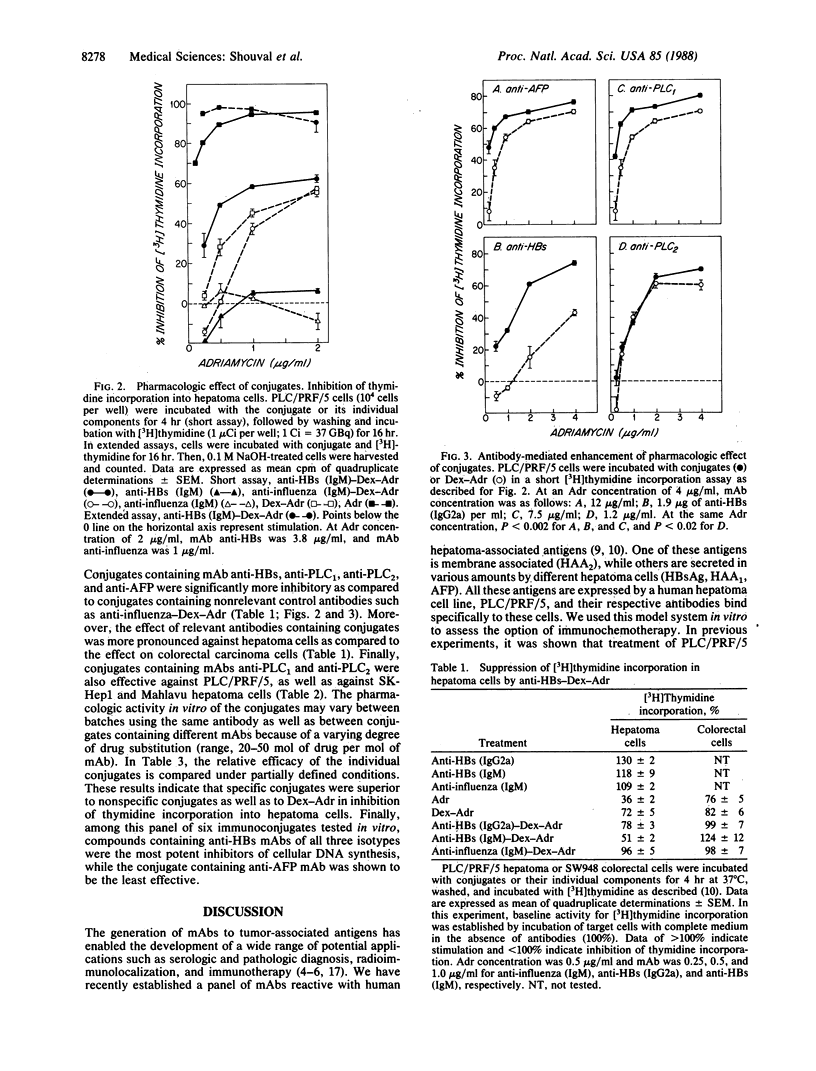
A panel of six murine monoclonal antibodies against hepatocellular carcinoma-associated antigens, reactive with PLC/PRF/5 human hepatoma cells, was conjugated to Adriamycin (doxorubicin) via a dextran bridge. This library of antibodies includes three monoclonal antibodies against hepatitis B virus surface antigen, one anti-alpha-fetoprotein, and two other IgG2a antibodies against PLC/PRF/5 hepatoma-associated antigens. The use of dextran for conjugation of Adriamycin to antibodies enabled a 5- to 10-fold amplification of the number of drug molecules linked to antibody. Conjugation of Adriamycin to dextran caused an occasional reduction in the pharmacologic activity of dextran-Adriamycin in [3H]thymidine incorporation assays in hepatoma cells as compared to nonconjugated Adriamycin. This loss of anticellular activity was partially compensated for by conjugation of specific antibodies to the dextran-Adriamycin conjugate. Conjugated compounds completely retained their binding activity to purified hepatitis B virus surface antigen and alpha-fetoprotein fixed to a solid matrix as compared to binding of homologous nonconjugated antibodies. However, some reduction of the binding activity to intact hepatoma cells was observed in three of six conjugates. Binding activity to hepatoma cells and, as a consequence, suppression of tumor cell DNA synthesis by the various conjugates was enhanced as compared to the same effect in treated colorectal carcinoma cells that do not express the relevant hepatoma-associated proteins. Furthermore, two conjugates containing nonspecific antibodies did not bind to hepatoma cells and caused minimal suppression of DNA synthesis. These results suggest that this panel of monoclonal antibody-dextran-Adriamycin conjugates was effective in suppression of PLC/PRF/5 cell growth in vitro.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon R., Sela M. In vitro and in vivo efficacy of conjugates of daunomycin with anti-tumor antibodies. Immunol Rev. 1982;62:5–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. I., Ben-Porath E., Shouval D., Strauss W., Isselbacher K. J., Wands J. R. Antigenic characterization of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Development of in vitro and in vivo immunoassays that use monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):40–51. doi: 10.1172/JCI111975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi T. K., Lee N. W., Wong J. Chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Adriamycin versus quadruple chemotherapy. Cancer. 1984 Feb 1;53(3):401–405. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19840201)53:3<401::aid-cncr2820530306>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogh J., Wright W. C., Loveless J. D. Absence of HeLa cell contamination in 169 cell lines derived from human tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Feb;58(2):209–214. doi: 10.1093/jnci/58.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz E., Levy R., Maron R., Wilchek M., Arnon R., Sela M. The covalent binding of daunomycin and adriamycin to antibodies, with retention of both drug and antibody activities. Cancer Res. 1975 May;35(5):1175–1181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shouval D., Eilat D., Carlson R. I., Adler R., Livni N., Wands J. R. Human hepatoma-associated cell surface antigen: identification and characterization by means of monoclonal antibodies. Hepatology. 1985 May-Jun;5(3):347–356. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shouval D., Reid L. M., Chakraborty P. R., Ruiz-Opazo N., Morecki R., Gerber M. A., Thung S. N., Shafritz D. A. Tumorigenicity in nude mice of a human hepatoma cell line containing hepatitis B virus DNA. Cancer Res. 1981 Apr;41(4):1342–1350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shouval D., Shafritz D. A., Zurawski V. R., Jr, Isselbacher K. J., Wands J. R. Immunotherapy in nude mice of human hepatoma using monoclonal antibodies against hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):567–569. doi: 10.1038/298567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shouval D., Wands J. R., Zurawski V. R., Jr, Isselbacher K. J., Shafritz D. A. Selecting binding and complement-mediated lysis of human hepatoma cells (PLC/PRF/5) in culture by monoclonal antibodies to hepatitis B surface antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):650–654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada Y., Bischof W. K., Hibi N., Hirai H., Hurwitz E., Sela M. Effect of a conjugate of daunomycin and antibodies to rat alpha-fetoprotein on the growth of alpha-fetoprotein-producing tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):621–625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada Y., Hurwitz E., Kashi R., Sela M., Hibi N., Hara A., Hirai H. Chemotherapy by intravenous administration of conjugates of daunomycin with monoclonal and conventional anti-rat alpha-fetoprotein antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7896–7899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


