Abstract
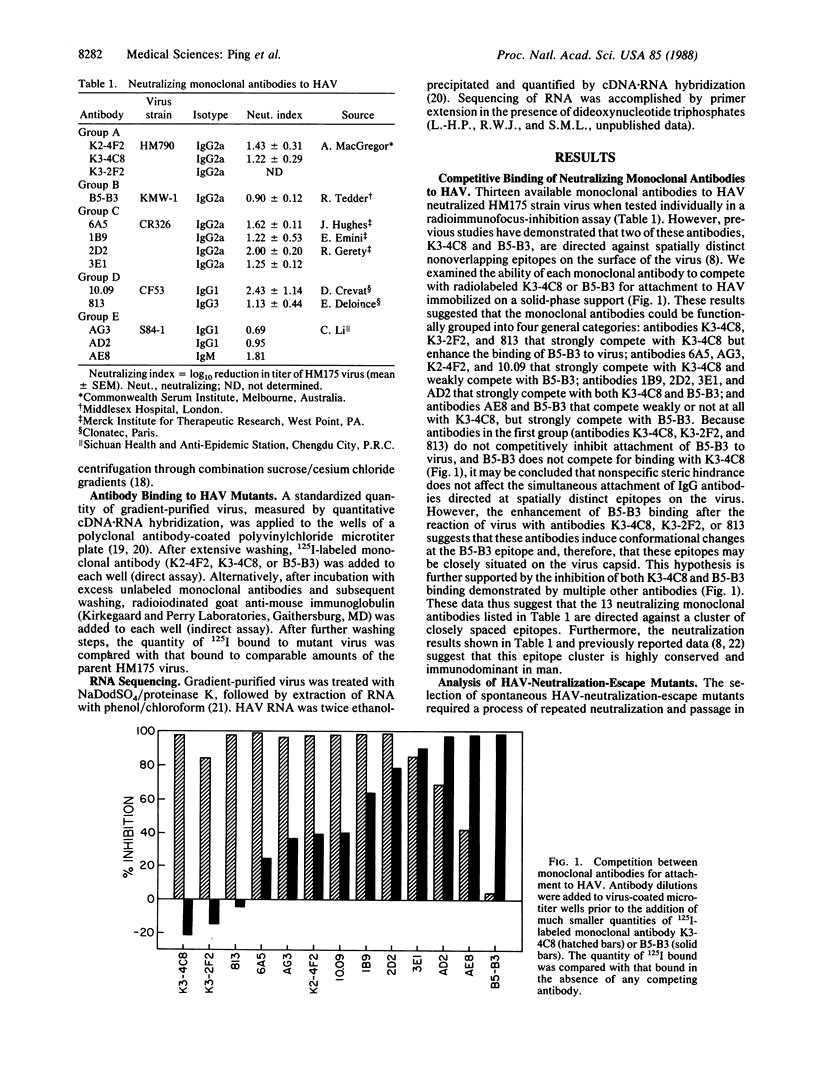
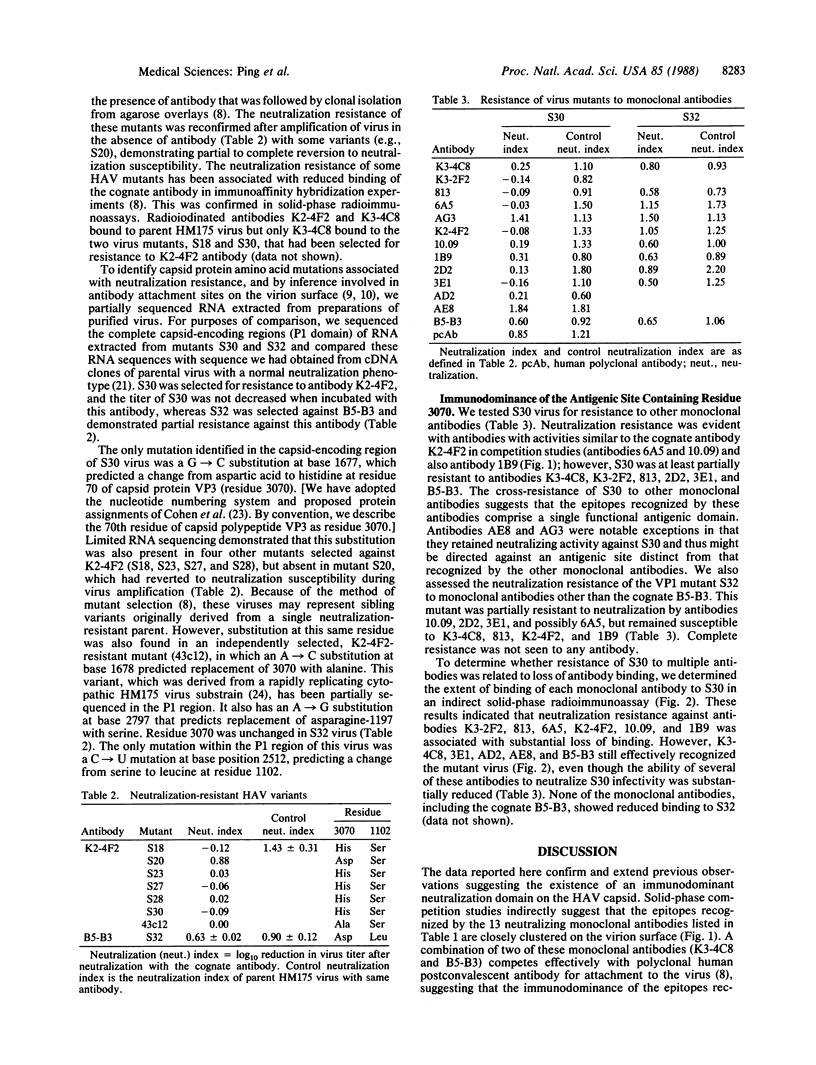
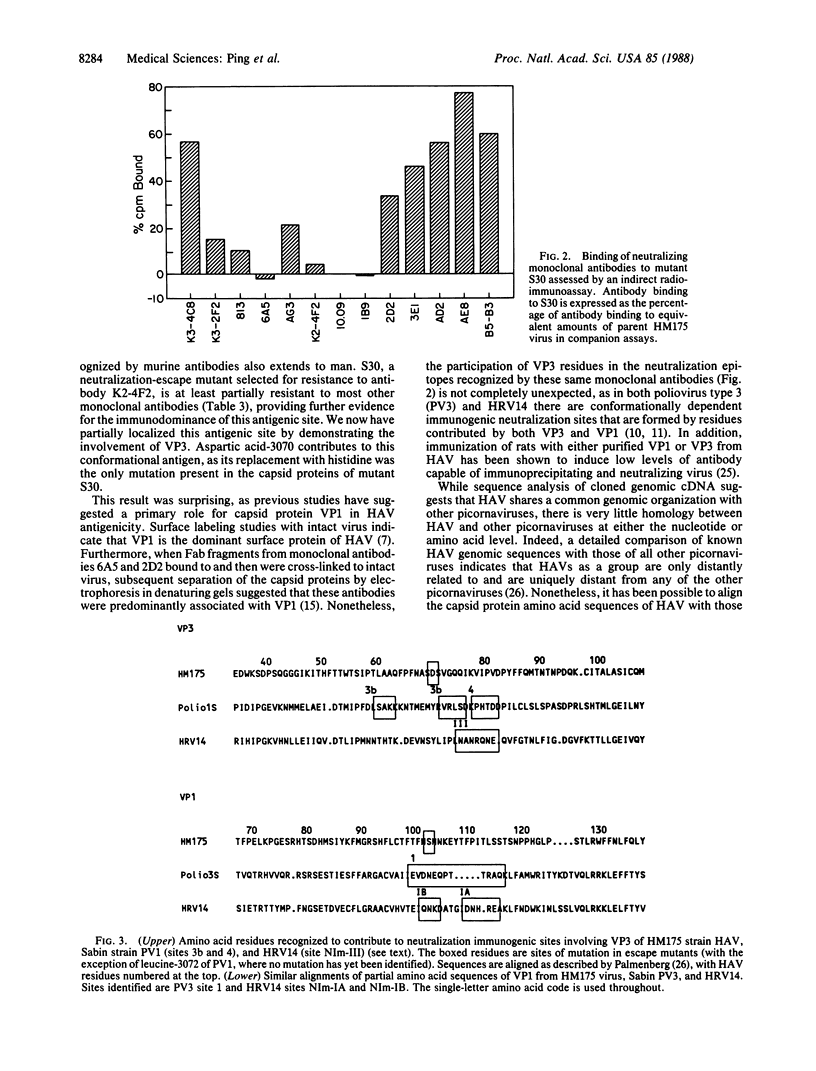
Hepatitis A virus, an hepatotropic picornavirus, is a common cause of acute hepatitis in man for which there is no available vaccine. Competitive binding studies carried out in solid phase suggest that neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to hepatitis A virus recognize a limited number of epitopes on the capsid surface, although the polypeptide locations of these epitopes are not well defined. Neutralization-escape mutants, selected for resistance to monoclonal antibodies, demonstrate broad cross-resistance to other monoclonal antibodies. Sequencing of virion RNA from several of these mutants demonstrated that replacement of aspartic acid residue 70 of capsid protein VP3 (residue 3070) with histidine or alanine confers resistance to neutralization by monoclonal antibody K2-4F2 and prevents binding of this antibody and other antibodies with similar solid-phase competition profiles. These results indicate that residue 3070 contributes to an immunodominant antigenic site. Mutation at residue 102 of VP1 (residue 1102) confers partial resistance against antibody B5-B3 and several other antibodies but does not prevent antibody attachment. Both VP3 and VP1 sites align closely in the linear peptide sequences with sites of neutralization-escape mutations in poliovirus and human rhinovirus, suggesting conservation of structure among these diverse picornaviruses. However, because partial neutralization resistance to several monoclonal antibodies (2D2, 3E1, and B5-B3) was associated with mutation at either residue 3070 or residue 1102, these sites appear more closely related functionally in hepatitis A virus than in these other picornaviruses.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binn L. N., Lemon S. M., Marchwicki R. H., Redfield R. R., Gates N. L., Bancroft W. H. Primary isolation and serial passage of hepatitis A virus strains in primate cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):28–33. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.28-33.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Ticehurst J. R., Purcell R. H., Buckler-White A., Baroudy B. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of wild-type hepatitis A virus: comparison with different strains of hepatitis A virus and other picornaviruses. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):50–59. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.50-59.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromeans T., Sobsey M. D., Fields H. A. Development of a plaque assay for a cytopathic, rapidly replicating isolate of hepatitis A virus. J Med Virol. 1987 May;22(1):45–56. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890220107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daemer R. J., Feinstone S. M., Gust I. D., Purcell R. H. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in African green monkey kidney cell culture: primary isolation and serial passage. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):388–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.388-393.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Chastonay J., Siegl G. Replicative events in hepatitis A virus-infected MRC-5 cells. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):268–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Ostapchuk P., Wimmer E. Bivalent attachment of antibody onto poliovirus leads to conformational alteration and neutralization. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):547–550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.547-550.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich W. H., Frösner G. G. Topology and immunoreactivity of capsid proteins in hepatitis A virus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1983;172(2):101–106. doi: 10.1007/BF02124510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. V., Stanton L. W., Tomassini J. E., Long W. J., Scolnick E. M. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to hepatitis A virus: partial localization of a neutralizing antigenic site. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):465–473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.465-473.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R. W., Newbold J. E., Lemon S. M. Combined immunoaffinity cDNA-RNA hybridization assay for detection of hepatitis A virus in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):984–989. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.984-989.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R. W., Newbold J. E., Lemon S. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of a cell culture-adapted variant of hepatitis A virus: comparison with wild-type virus with restricted capacity for in vitro replication. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90270-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. M., Harmon S. A., Binn L. N., Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E., Summers D. F. Antigenic and immunogenic properties of a hepatitis A virus capsid protein expressed in Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1203–1211. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Binn L. N. Incomplete neutralization of hepatitis A virus in vitro due to lipid-associated virions. J Gen Virol. 1985 Nov;66(Pt 11):2501–2505. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-11-2501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Binn L. N., Marchwicki R. H. Radioimmunofocus assay for quantitation of hepatitis A virus in cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):834–839. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.834-839.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Binn L. N. Serum neutralizing antibody response to hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1033–1039. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Chao S. F., Jansen R. W., Binn L. N., LeDuc J. W. Genomic heterogeneity among human and nonhuman strains of hepatitis A virus. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):735–742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.735-742.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Jansen R. W. A simple method for clonal selection of hepatitis A virus based on recovery of virus from radioimmunofocus overlays. J Virol Methods. 1985 Jun;11(2):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., LeDuc J. W., Binn L. N., Escajadillo A., Ishak K. G. Transmission of hepatitis A virus among recently captured Panamanian owl monkeys. J Med Virol. 1982;10(1):25–36. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890100105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M. Type A viral hepatitis. New developments in an old disease. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 24;313(17):1059–1067. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510243131706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor A., Kornitschuk M., Hurrell J. G., Lehmann N. I., Coulepis A. G., Locarnini S. A., Gust I. D. Monoclonal antibodies against hepatitis A virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1237–1243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1237-1243.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Ferguson M., Evans D. M., Almond J. W., Icenogle J. P. Antigenic structure of polioviruses of serotypes 1, 2 and 3. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1283–1291. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostermayr R., von der Helm K., Gauss-Müller V., Winnacker E. L., Deinhardt F. Expression of hepatitis A virus cDNA in Escherichia coli: antigenic VP1 recombinant protein. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3645–3647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3645-3647.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page G. S., Mosser A. G., Hogle J. M., Filman D. J., Rueckert R. R., Chow M. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus serotype 1 neutralizing determinants. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1781–1794. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1781-1794.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Hilleman M. R. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in cell culture in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Feb;160(2):213–221. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stapleton J. T., Lemon S. M. Neutralization escape mutants define a dominant immunogenic neutralization site on hepatitis A virus. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):491–498. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.491-498.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


