Abstract
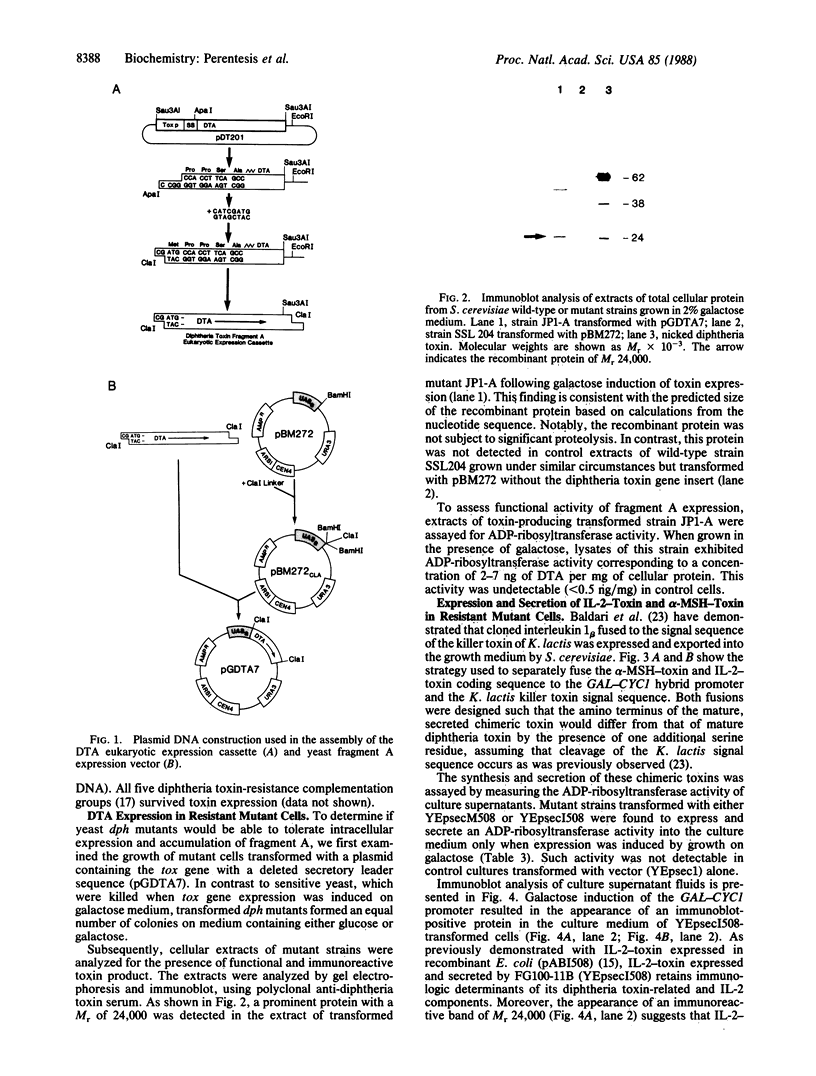
Mutants of the eukaryote Saccharomyces cerevisiae, previously selected for resistance to diphtheria toxin, were investigated for their suitability as hosts for the expression of tox-related proteins. The structural gene for the toxin, encoding the fragment A catalytic domain, was modified for efficient intracellular expression in eukaryotes and placed downstream of the yeast GAL1 promoter element in a plasmid. Transformed mutant yeast grown in galactose, which induces that promoter, were viable and contained active fragment A. In contrast, sensitive, wild-type cells harboring this plasmid grew normally under repressing conditions but were killed when the GAL1 promoter was induced. Additional constructions were also prepared that included sequences encoding either the lymphocyte growth factor interleukin 2 or alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone along with the lipid-associating domains of fragment B and the leader peptide of the Kluyveromyces lactis killer toxin. Resistant mutant strains transformed with these plasmids efficiently expressed and secreted the expected chimeric toxins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn B. Y., Livingston D. M. Mitotic gene conversion lengths, coconversion patterns, and the incidence of reciprocal recombination in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae plasmid system. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3685–3693. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacha P., Murphy J. R., Reichlin S. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-diphtheria toxin-related polypeptide conjugates. Potential role of the hydrophobic domain in toxin entry. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1565–1570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacha P., Williams D. P., Waters C., Williams J. M., Murphy J. R., Strom T. B. Interleukin 2 receptor-targeted cytotoxicity. Interleukin 2 receptor-mediated action of a diphtheria toxin-related interleukin 2 fusion protein. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):612–622. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldari C., Murray J. A., Ghiara P., Cesareni G., Galeotti C. L. A novel leader peptide which allows efficient secretion of a fragment of human interleukin 1 beta in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):229–234. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04743.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs J. D. Transformation of yeast by a replicating hybrid plasmid. Nature. 1978 Sep 14;275(5676):104–109. doi: 10.1038/275104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishai W. R., Miyanohara A., Murphy J. R. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of three fragments of diphtheria toxin truncated within fragment B. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1554–1563. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1554-1563.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishai W. R., Rappuoli R., Murphy J. R. High-level expression of a proteolytically sensitive diphtheria toxin fragment in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5140–5151. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5140-5151.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodley J. W., Upham R., Crow F. W., Tomer K. B., Gross M. L. Ribosyl-diphthamide: confirmation of structure by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 1;230(2):590–593. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90439-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. A., Bodley J. W. Primary structure at the site in beef and wheat elongation factor 2 of ADP-ribosylation by diphtheria toxin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 15;103(2):253–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bumol T. F., Wang Q. C., Reisfeld R. A., Kaplan N. O. Monoclonal antibody and an antibody-toxin conjugate to a cell surface proteoglycan of melanoma cells suppress in vivo tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):529–533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawley D. B., Simpson D. L., Herschman H. R. Asialoglycoprotein receptor mediates the toxic effects of an asialofetuin-diphtheria toxin fragment A conjugate on cultured rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3383–3387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., FitzGerald D. J., Adhya S., Pastan I. Activity of a recombinant fusion protein between transforming growth factor type alpha and Pseudomonas toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4538–4542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. Y., Bodley J. W., Livingston D. M. Diphtheria toxin-resistant mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3357–3360. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland D. G., Steplewski Z., Collier R. J., Mitchell K. F., Chang T. H., Koprowski H. Antibody-directed cytotoxic agents: use of monoclonal antibody to direct the action of toxin A chains to colorectal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4539–4543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Yocum R. R., Gifford P. A GAL10-CYC1 hybrid yeast promoter identifies the GAL4 regulatory region as an upstream site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley V. E., Bacha P., Pankewycz O., Nichols J. C., Murphy J. R., Strom T. B. Interleukin 2-diphtheria toxin fusion protein can abolish cell-mediated immunity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3980–3984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong D., Coleman K. D., Murphy J. R. Cloned fragment A of diphtheria toxin is expressed and secreted into the periplasmic space of Escherichia coli K12. Science. 1983 Apr 29;220(4596):515–517. doi: 10.1126/science.6403984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorberboum-Galski H., FitzGerald D., Chaudhary V., Adhya S., Pastan I. Cytotoxic activity of an interleukin 2-Pseudomonas exotoxin chimeric protein produced in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1922–1926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Bond M. W., Otsu K., Arai K., Arai N. Secretion of mature mouse interleukin-2 by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: use of a general secretion vector containing promoter and leader sequences of the mating pheromone alpha-factor. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):155–161. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90268-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J., Danley D. E. Posttranslational modification of elongation factor 2 in diphtheria-toxin-resistant mutants of CHO-K1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1010–1014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moonen P., Mermod J. J., Ernst J. F., Hirschi M., DeLamarter J. F. Increased biological activity of deglycosylated recombinant human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor produced by yeast or animal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4428–4431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Bishai W., Borowski M., Miyanohara A., Boyd J., Nagle S. Genetic construction, expression, and melanoma-selective cytotoxicity of a diphtheria toxin-related alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone fusion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8258–8262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeltmann T. N. Synthesis and in vitro activity of a hormone-diphtheria toxin fragment A hybrid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):430–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90924-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Dunlop P. C., Adolph K. W., Bodley J. W. Occurrence of diphthamide in archaebacteria. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1342–1347. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1342-1347.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Smith K. A. Heterogeneity of human T-cell growth factor(s) due to variable glycosylation. Mol Immunol. 1981 Dec;18(12):1087–1094. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge J. E. Immunoregulation and immunostimulation of murine lymphocytes by recombinant human interleukin-2. J Biol Response Mod. 1985 Feb;4(1):18–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Howard J. B., Bodley J. W. ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 by diphtheria toxin. Isolation and properties of the novel ribosyl-amino acid and its hydrolysis products. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10717–10720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. P., Parker K., Bacha P., Bishai W., Borowski M., Genbauffe F., Strom T. B., Murphy J. R. Diphtheria toxin receptor binding domain substitution with interleukin-2: genetic construction and properties of a diphtheria toxin-related interleukin-2 fusion protein. Protein Eng. 1987 Dec;1(6):493–498. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.6.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaizumi M., Mekada E., Uchida T., Okada Y. One molecule of diphtheria toxin fragment A introduced into a cell can kill the cell. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]