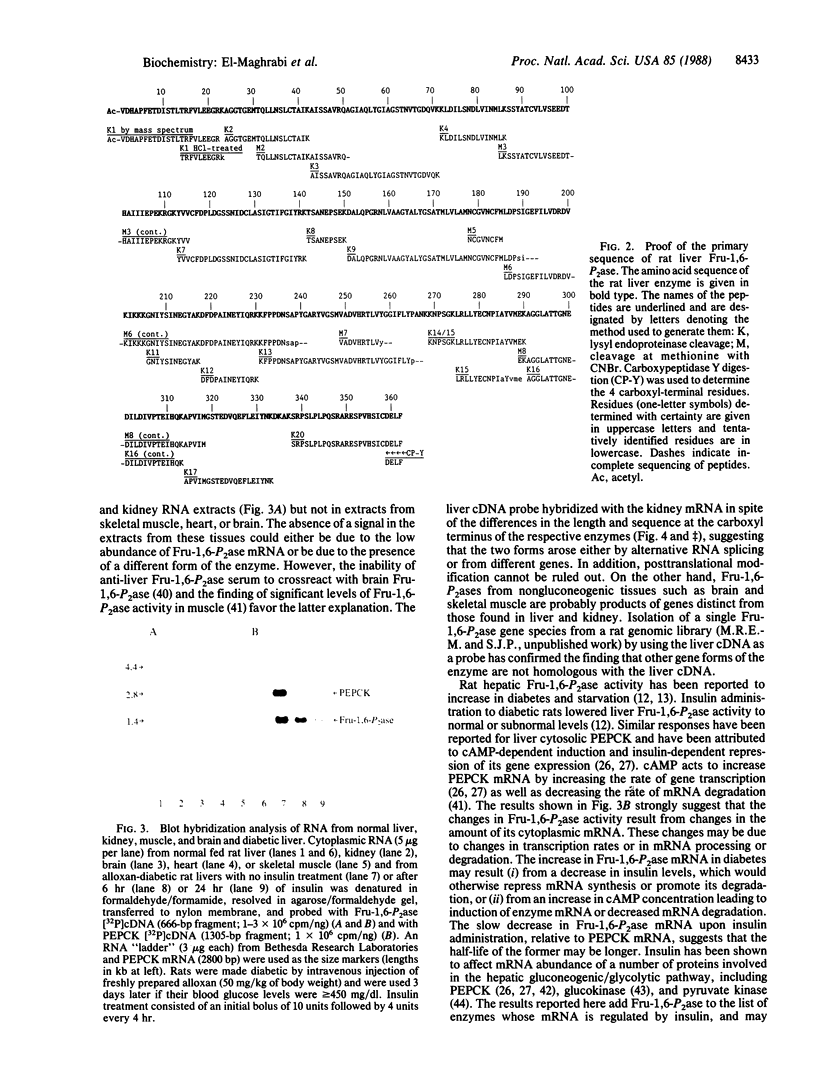
Abstract
A coding-length clone of rat liver fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (EC 3.1.3.11) was isolated by immunological screening of a cDNA library in lambda gt11. Its identity was verified by comparing the deduced amino acid sequence with that obtained by direct sequencing of a complete set of CNBr and proteolytic peptides from the purified protein. The enzyme subunit is composed of 362 amino acids and has N-acetylvaline as the amino-terminal residue. The cDNA, 1255 base pairs (bp) long, consisted of 1086 bp of coding region, 15 bp of 5' untranslated sequence, and 154 bp at the 3' untranslated end. The 3' untranslated sequence contained a polyadenylylation signal (AATAAA) followed after 30 bp by a stretch of 7 adenines at the end of the clone. The deduced amino acid sequence was identical to the primary sequence of the protein and confirmed the alignment of five nonoverlapping peptides. It also confirmed the 27-residue extension, unique to the rat liver subunit, ending with a carboxyl-terminal phenylalanine. RNA blot analyses using the radiolabeled liver cDNA as a probe revealed a single band of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase mRNA, 1.4 kilobases long, in liver and kidney but not in nongluconeogenic tissues. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase mRNA was increased 10-fold in livers from diabetic rats and was reduced to control levels after 24 hr of insulin treatment, suggesting that the changes in enzyme activity observed in diabetes and after insulin treatment are due to alterations in mRNA abundance.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergström G., Ekman P., Dahlqvist U., Humble E., Engström L. Subtilisin-catalyzed removal of phosphorylated site of pig liver pyruvate kinase without inactivation of the enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):288–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee T., Rittenhouse J., Marcus F., Reardon I., Heinrikson R. L. Identification of the in vivo and in vitro phosphorylation sites of rat liver fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3831–3833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimbala M. A., van Lelyveld P., Hanson R. W. Regulation of the levels of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) mRNA in rat liver by insulin and glucagon. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1980;19:205–214. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(81)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Watson D. C., Dixon G. H. The hormonal control of activity of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. Amino-acid sequences at the two sites of action of adenosine-3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 3;51(1):79–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekdahl K. N., Ekman P. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from rat liver. A comparison of the kinetics of the unphosphorylated enzyme and the enzyme phosphorylated by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14173–14179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHER E. H., KREBS E. G. The isolation and crystallization of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase b. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher W. K., Thompson E. O. Amino acid sequence studies on sheep liver fructose-bisphosphatase. I. The S-peptide. Aust J Biol Sci. 1980 Dec;33(6):665–674. doi: 10.1071/bi9800665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funayama S., Molano J., Gancedo C. Purification and properties of a D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Oct 1;197(1):170–177. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D. K., Andreone T. L. Insulin modulation of gene expression. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1985;1(1-2):139–170. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hod Y., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP stabilizes the mRNA for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) against degradation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7747–7752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horecker B. L., Melloni E., Pontremoli S. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase: properties of the neutral enzyme and its modification by proteolytic enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;42:193–226. doi: 10.1002/9780470122877.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Analysis of phenylthiohydantoins by ultrasensitive gradient high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:486–493. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima S., Uyeda K. A binding study of the interaction of beta-D-fructose 2,6-bisphosphate with phosphofructokinase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7352–7357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lively M. O., el-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis J., D'Angelo G., Colosia A. D., Ciavola J. A., Fraser B. A., Pilkis S. J. Complete amino acid sequence of rat liver 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):839–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumder A. L., Eisenberg F., Jr Unequivocal demonstration of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3222–3225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus F., Edelstein I., Reardon I., Heinrikson R. L. Complete amino acid sequence of pig kidney fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7161–7165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez J., Cid H. A model for the structure of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from pig kidney. Arch Biol Med Exp (Santiago) 1986 Jan;19(1):77–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzotta M. Y., Veneziale C. M. Concentration of liver and kidney fructose-1,6-diphosphatase determined by specific radioimmunoassay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 11;611(1):156–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek D. W., Nimmo H. G. The interaction of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate with an allosteric site of rat liver fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 22;160(1-2):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80946-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Carter J. K., Moyer R. W. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against two subunits of rabbit poxvirus-associated, DNA-directed RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):670–680. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.670-680.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller D., Holzer H. Regulation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in yeast by phosphorylation/dephosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 15;103(3):926–933. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90899-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi T., Inoue H., Tanaka T. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of L-type pyruvate kinase in diabetic rat liver by insulin and dietary fructose. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14393–14397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson B., Flinta C., von Heijne G., Jörnvall H. Structures of N-terminally acetylated proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 4;152(3):523–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riou J. P., Claus T. H., Flockhart D. A., Corbin J. D., Pilkis S. J. In vivo and in vitro phosphorylation of rat liver fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4615–4619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse J., Chatterjee T., Marcus F., Reardon I., Heinrikson R. L. Amino acid sequence of the COOH-terminal region of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatases in relation to cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7648–7652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse J., Harrsch P. B., Kim J. N., Marcus F. Amino acid sequence of the phosphorylation site of yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):3939–3943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. T., Hiller E., Mitsock L., Orr E. Characterization of the gene for fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Sequence, protein homology, and expression during growth on glucose. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6051–6057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibrowski W., Seitz H. J. Rapid action of insulin and cyclic AMP in the regulation of functional messenger RNA coding for glucokinase in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):343–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soderling T. R. Regulation of glycogen synthetase. Effects of trypsin on the structure, activity, and phosphorylation of the skeletal muscle enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4359–4364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tejwani G. A., Pedrosa F. O., Pontremoli S., Horecker B. L. The purification of properties of rat liver fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Nov;177(1):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90435-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tejwani G. A. Regulation of fructose-bisphosphatase activity. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1983;54:121–194. doi: 10.1002/9780470122990.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. Inhibition of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by fructose 2,6-biphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2861–2863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G., SINGHAL R. L., SRIVASTAVA S. K. INSULIN: SUPPRESSOR OF BIOSYNTHESIS OF HEPATIC GLUCONEOGENIC ENZYMES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jan;53:96–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. J., Datta A. G., Singh V. N., Suda H., Pontremoli S., Horecker B. L. Rabbit liver fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase: labeling of the active and allosteric sites with pyridoxal 5-phosphate and sequence of a nonapeptide from the active site. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Aug;210(1):98–103. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Maghrabi M. R., Correia J. J., Heil P. J., Pate T. M., Cobb C. E., Pilkis S. J. Tissue distribution, immunoreactivity, and physical properties of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5005–5009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





