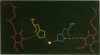Abstract
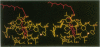
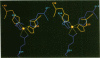
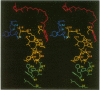
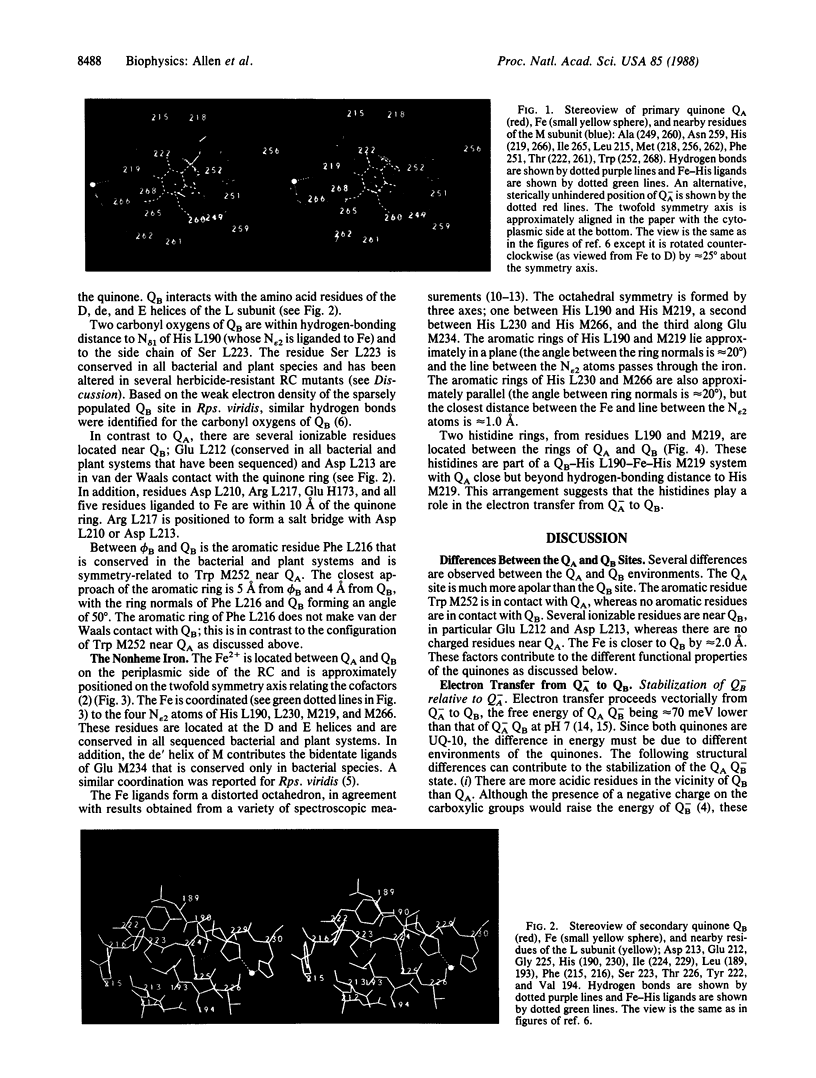
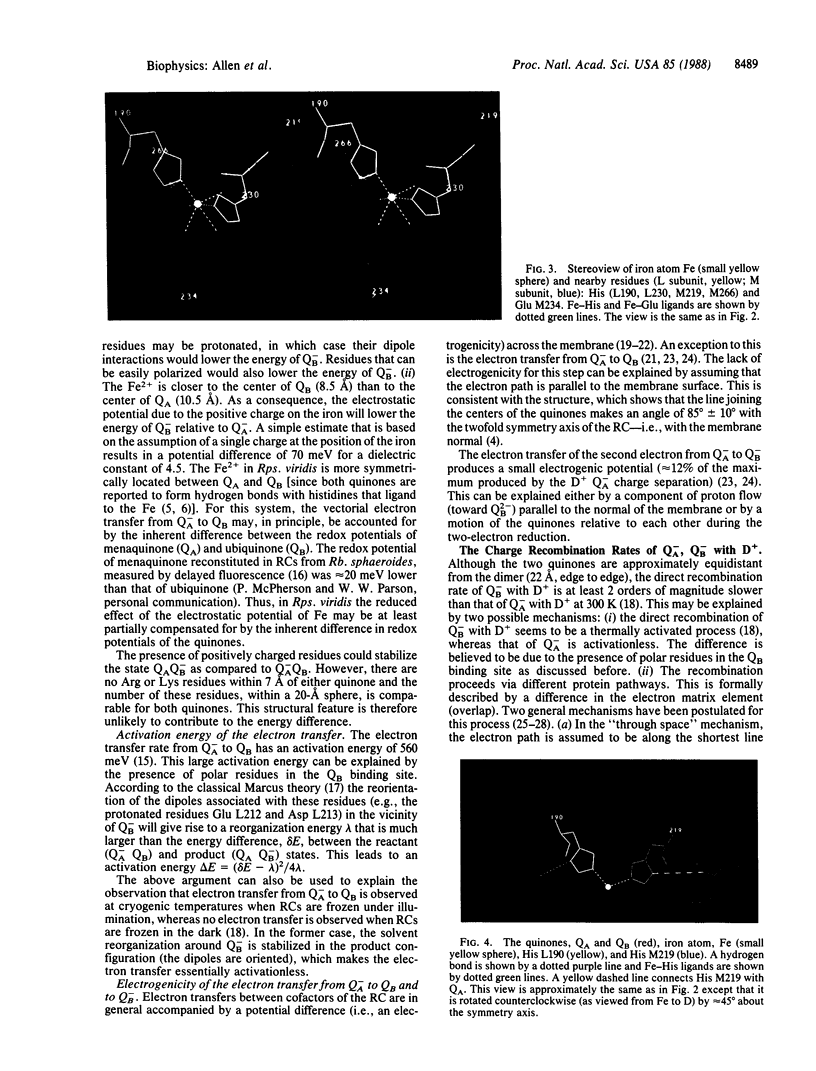
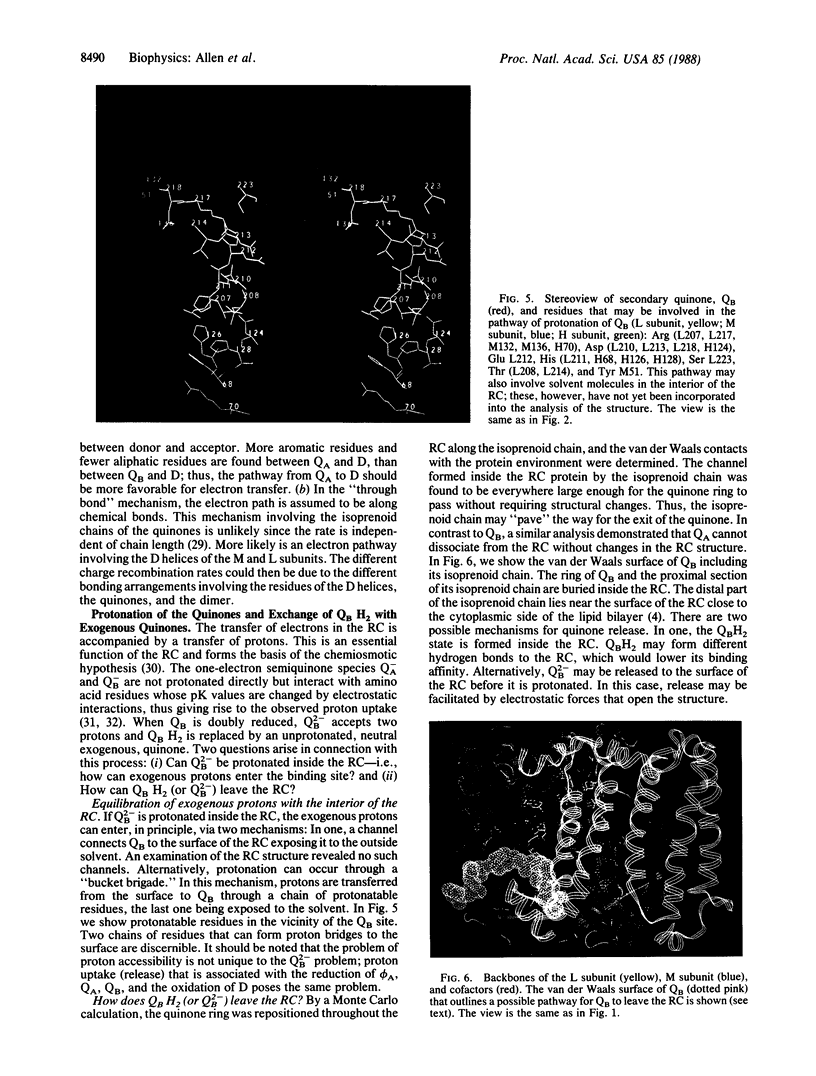
The three-dimensional structure of the reaction center (RC) from Rhodobacter sphaeroides has been determined by x-ray diffraction to a resolution of 2.8 A with an R value of 24%. The interactions of the protein with the primary quinone, QA, secondary quinone, QB, and the nonheme iron are described and compared to those of RCs from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Structural differences between the QA and QB environments that contribute to the function of the quinones (the electron transfer from QA- to QB and the charge recombination of QA-, QB- with the primary donor) are delineated. The protein residues that may be involved in the protonation of QB are identified. A pathway for the doubly reduced QB to dissociate from the RC is proposed. The interactions between QB and the residues that have been changed in herbicide-resistant mutants are described. The environment of the nonheme iron is compared to the environments of metal ions in other proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. P., Feher G., Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Rees D. C. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26: the cofactors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5730–5734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. P., Feher G., Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Rees D. C. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26: the protein subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6162–6166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunker G., Stern E. A., Blankenship R. E., Parson W. W. An x-ray absorption study of the iron site in bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers. Biophys J. 1982 Feb;37(2):539–551. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84699-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. F., Calvo R., Fredkin D. R., Isaacson R. A., Okamura M. Y., Feher G. The electronic structure of Fe2+ in reaction centers from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. III. EPR measurements of the reduced acceptor complex. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):947–973. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84241-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Closs G. L., Miller J. R. Intramolecular long-distance electron transfer in organic molecules. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):440–447. doi: 10.1126/science.240.4851.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus R. J., Feher G., Okamura M. Y. Iron-depleted reaction centers from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides R-26.1: characterization and reconstitution with Fe2+, Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):2276–2287. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberger P., Okamura M. Y., Feher G. The electronic structure of Fe2+ in reaction centers from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. II. Extended x-ray fine structure studies. Biophys J. 1982 Feb;37(2):523–538. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84698-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinfeld D., Okamura M. Y., Feher G. Electron transfer in reaction centers of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. I. Determination of the charge recombination pathway of D+QAQ(-)B and free energy and kinetic relations between Q(-)AQB and QAQ(-)B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 27;766(1):126–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(84)90224-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinfeld D., Okamura M. Y., Feher G. Electron-transfer kinetics in photosynthetic reaction centers cooled to cryogenic temperatures in the charge-separated state: evidence for light-induced structural changes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5780–5786. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuki A., Wolynes P. G. Electron tunneling paths in proteins. Science. 1987 Jun 26;236(4809):1647–1652. doi: 10.1126/science.3603005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo S. L., Ellis W. R., Jr, Crutchley R. J., Gray H. B. Long-range electron transfer in heme proteins. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):948–952. doi: 10.1126/science.3016897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel H., Epp O., Deisenhofer J. Pigment-protein interactions in the photosynthetic reaction centre from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2445–2451. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura M. Y., Isaacson R. A., Feher G. Primary acceptor in bacterial photosynthesis: obligatory role of ubiquinone in photoactive reaction centers of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3491–3495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham N. K., Dutton P. L., Mueller P. Photoelectric currents across planar bilayer membranes containing bacterial reaction centers. Response under conditions of single electron turnover. Biophys J. 1982 Feb;37(2):465–473. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84693-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham N. K., Packham C., Mueller P., Tiede D. M., Dutton P. L. Reconstitution of photochemically active reaction centers in planar phospholipid membranes. Light-induced electrical currents under voltage-clamped conditions. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 28;110(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönfeld M., Montal M., Feher G. Functional reconstitution of photosynthetic reaction centers in planar lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6351–6355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon S. F., Morgan R. S., Brooks C. L., 3rd A new classification of the amino acid side chains based on doublet acceptor energy levels. Biophys J. 1988 Jan;53(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83068-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissl H. W. Spatial correlation between primary redox components in reaction centers of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides measured by two electrical methods in the nanosecond range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7173–7177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury N. W., Parson W. W., Gunner M. R., Prince R. C., Dutton P. L. Radical-pair energetics and decay mechanisms in reaction centers containing anthraquinones, naphthoquinones or benzoquinones in place of ubiquinone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 13;851(1):6–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(86)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Chirino A., Rees D. C., Allen J. P., Feher G. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26 and 2.4.1: protein-cofactor (bacteriochlorophyll, bacteriopheophytin, and carotenoid) interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7993–7997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Rees D. C., Allen J. P., Feher G. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26: membrane-protein interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6438–6442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]