Abstract
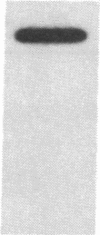
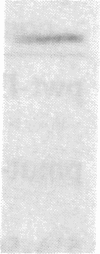
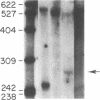
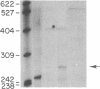
In this report, we determined that induction of the DR alpha-chain by recombinant human interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in a human glioblastoma multiform cell line is transcriptionally regulated and showed that protein synthesis is not necessary for this to occur. The regions of the DR alpha-chain gene that are responsible for basal and recombinant IFN-gamma-induced gene transcription have been determined by gene transfer of a series of 5' deletion mutants in which the upstream region of the DR alpha chain was linked to a reporter gene, chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase transcript and protein levels were determined by S1 nuclease protection and chloramphenicol acetyltransferase enzyme assays, respectively. By using these deletion mutants, we were able to draw the following conclusions. (i) One hundred and nine base pairs of upstream sequence contains the basic DR alpha-chain gene promoter and represents the minimal amount of sequence necessary for basal gene expression. (ii) An additional 9 base pairs of upstream sequence can mediate recombinant IFN-gamma induction. (iii) Maximal recombinant IFN-gamma induction requires at most an additional 23 base pairs of upstream sequence. (iv) The sequence between positions -267 and -141 does not appear to contain any additional positive or negative regulatory elements. These results suggest that the region between positions -141 and -109 contains a critical IFN-gamma-responsive element. Substitution mutagenesis was performed to confirm this suggestion.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basta P. V., Sherman P. A., Ting J. P. Identification of an interferon-gamma response region 5' of the human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen DR alpha chain gene which is active in human glioblastoma multiforme lines. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1275–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss J. M., Strominger J. L. Regulation of a transfected human class II major histocompatibility complex gene in human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9139–9143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., Lawrance S. K., Weissman S. M. Structure and nucleotide sequence of the heavy chain gene of HLA-DR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3543–3547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Durand B., Marfing C., Le Meur M., Benoist C., Mathis D. Conserved major histocompatibility complex class II boxes--X and Y--are transcriptional control elements and specifically bind nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6249–6253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folsom V., Gold D. P., White J., Marrack P., Kappler J., Tonegawa S. Functional and inducible expression of a transfected murine class II major histocompatibility complex gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2045–2049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Stark G. R. alpha-Interferon-induced transcription of HLA and metallothionein genes containing homologous upstream sequences. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):637–639. doi: 10.1038/314637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Folsom V., Tonegawa S. Cell type-specific enhancer element associated with a mouse MHC gene, E beta. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):594–597. doi: 10.1038/310594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling G. J. Tissue distribution of Ia antigens and their expression on lymphocyte subpopulations. Transplant Rev. 1976;30:64–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel A., Kimura A., Fournier A., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. Interferon response sequence potentiates activity of an enhancer in the promoter region of a mouse H-2 gene. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):743–746. doi: 10.1038/322743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A., Trowsdale J. Complete nucleotide sequence of a functional HLA-DP beta gene and the region between the DP beta 1 and DP alpha 1 genes: comparison of the 5' ends of HLA class II genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1607–1621. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Israël A., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. Detailed analysis of the mouse H-2Kb promoter: enhancer-like sequences and their role in the regulation of class I gene expression. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90760-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korber B., Hood L., Stroynowski I. Regulation of murine class I genes by interferons is controlled by regions located both 5' and 3' to the transcription initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3380–3384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korber B., Mermod N., Hood L., Stroynowski I. Regulation of gene expression by interferons: control of H-2 promoter responses. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1302–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.3125612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Boss J. M., Spies T., Sorrentino R., Okada K., Strominger J. L. Genetic complexity and expression of human class II histocompatibility antigens. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;85:45–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicholas J., Steinmetz M., Hunkapiller T., Jones P., Hood L. DNA sequence of the gene encoding the E alpha Ia polypeptide of the BALB/c mouse. Science. 1982 Dec 17;218(4578):1229–1232. doi: 10.1126/science.6815800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa K., Doyle C., Strominger J. L. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with conserved sequences of human class II major histocompatibility complex genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler P. I., Klingenstein R. J., Richman L. K., Ahmann G. B. The murine Kupffer cell. II. Accessory cell function in in vitro primary antibody responses, mitogen-induced proliferation, and stimulation of mixed lymphocyte responses. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2521–2525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Reiss C. S., Burakoff S. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A. Ia expression by vascular endothelium is inducible by activated T cells and by human gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1983 Apr 1;157(4):1339–1353. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F. M., Fellous M. Regulation of HLA-DR gene by IFN-gamma. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1660–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. S., Shevach E. M. Function of macrophages in antigen recognition by guinea pig T lymphocytes. I. Requirement for histocompatible macrophages and lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1194–1212. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Maki R. A., Clayton L. K., Tonegawa S. Complete primary structures of the E beta chain and gene of the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5520–5524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servenius B., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Class II genes of the human major histocompatibility complex. The DO beta gene is a divergent member of the class II beta gene family. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8759–8766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Basta P. V., Ting J. P. Upstream DNA sequences required for tissue-specific expression of the HLA-DR alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4254–4258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Katz S. I., Clement L., Green I., Shevach E. M. Immunologic functions of Ia-bearing epidermal Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2005–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita K., Miyazaki J., Appella E., Ozato K. Interferons increase transcription of a major histocompatibility class I gene via a 5' interferon consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2625–2630. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiguchi M., Ting J. P., Buessow S. C., Boyer C., Gillespie Y., Frelinger J. A. Response of glioma cells to interferon-gamma: increase in class II RNA, protein and mixed lymphocyte reaction-stimulating ability. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Aug;15(8):809–814. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting J. P., Shigekawa B. L., Linthicum D. S., Weiner L. P., Frelinger J. A. Expression and synthesis of murine immune response-associated (Ia) antigens by brain cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3170–3174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Larsen A. S., Peterlin B. M. A tissue-specific transcriptional enhancer is found in the body of the HLA-DR alpha gene. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):625–636. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikstrand C. J., Grahmann F. C., McComb R. D., Bigner D. D. Antigenic heterogeneity of human anaplastic gliomas and glioma-derived cell lines defined by monoclonal antibodies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1985 May;44(3):229–241. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198505000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter E., Yamamoto F., Almoguera C., Perucho M. A method to detect and characterize point mutations in transcribed genes: amplification and overexpression of the mutant c-Ki-ras allele in human tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7575–7579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota S., Yuan D., Katagiri T., Eisenberg R. A., Cohen P. L., Ting J. P. The expression and regulation of c-myb transcription in B6/lpr Lyt-2-, L3T4-T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2810–2817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan D., Tucker P. W. Transcriptional regulation of the mu-delta heavy chain locus in normal murine B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):564–583. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]