Abstract
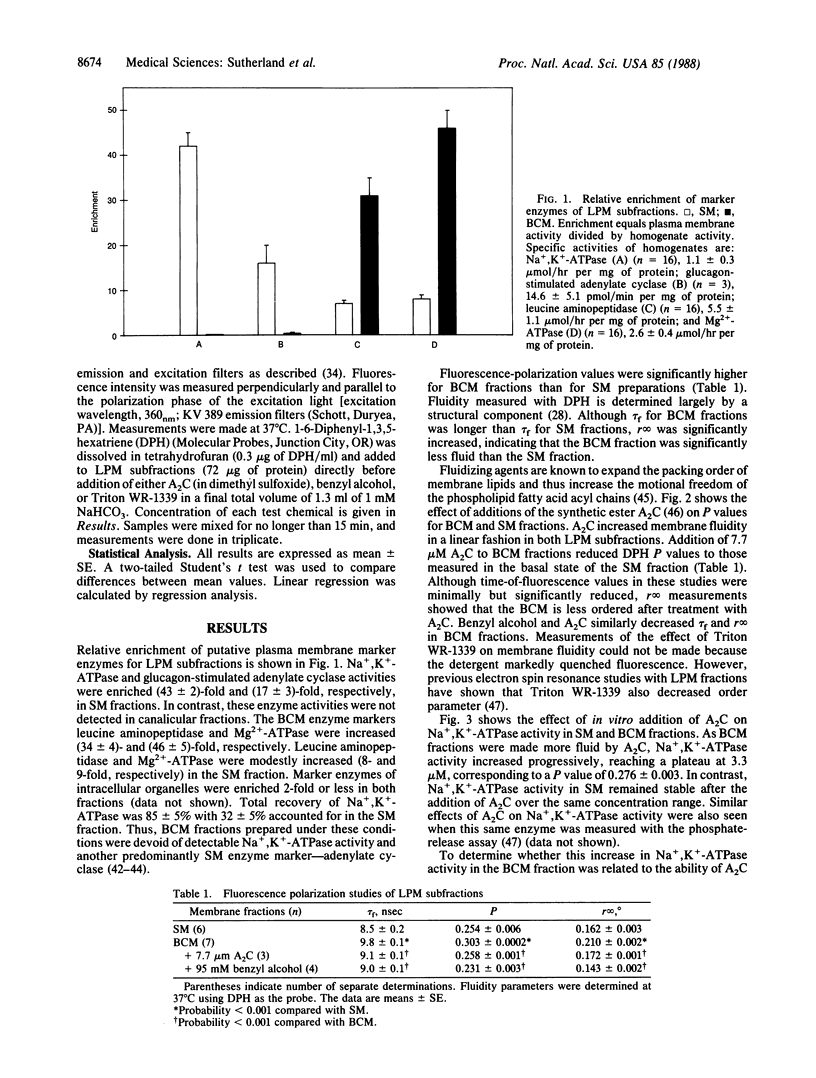
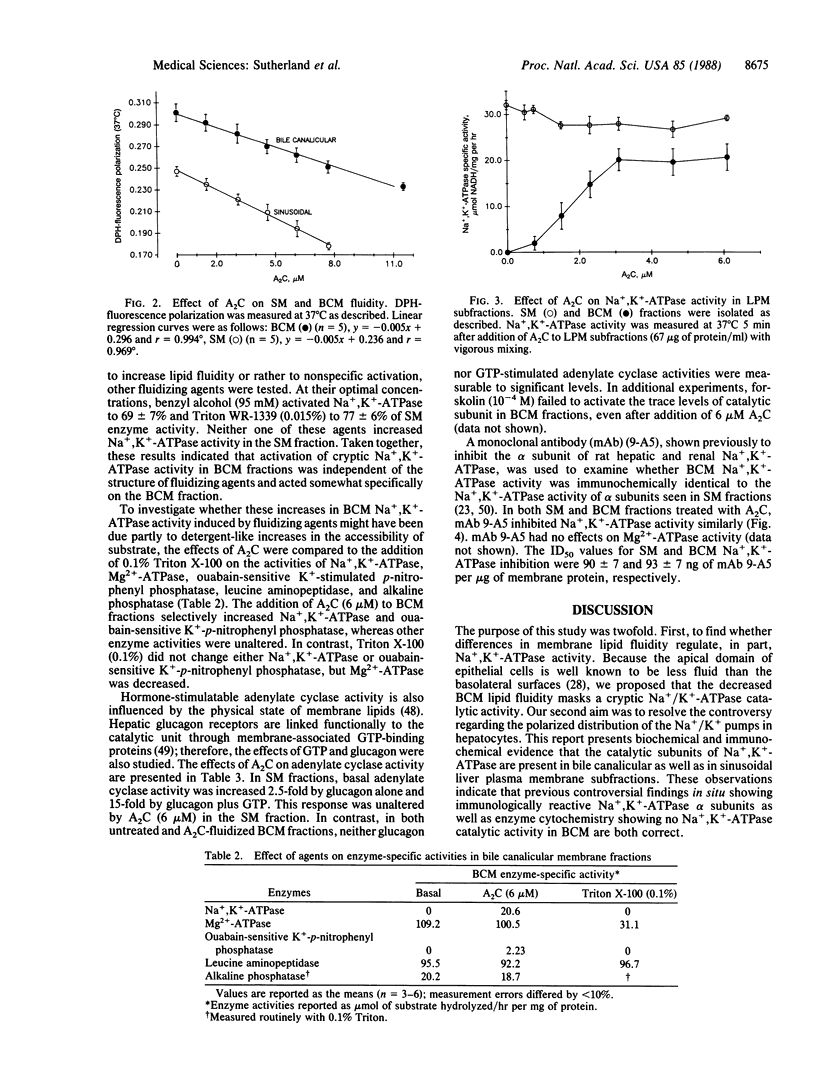
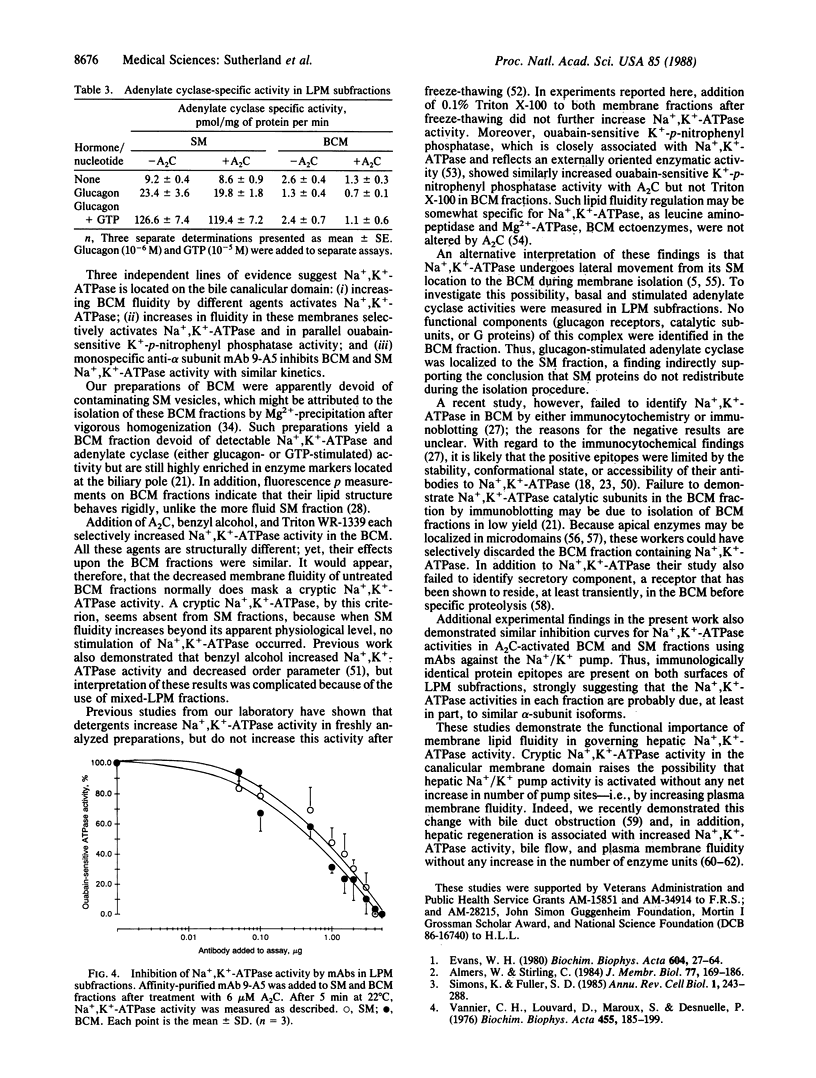
Membrane proteins of transporting epithelia are often distributed between apical and basolateral surfaces to produce a functionally polarized cell. The distribution of Na+,K+-ATPase [ATP phosphohydrolase (Na+/K+-transporting), EC 3.6.1.37] between apical and basolateral membranes of hepatocytes has been controversial. Because Na+,K+-ATPase activity is fluidity dependent and the physiochemical properties of the apical membrane reduces its fluidity, we investigated whether altering membrane fluidity might uncover cryptic Na+,K+-ATPase in bile canalicular (apical) surface fractions free of detectable Na+,K+-ATPase and glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase activities. Apical fractions exhibited higher diphenylhexatriene-fluorescence polarization values when compared with sinusoidal (basolateral) membrane fractions. When 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethyl 8-(cis-2-n-octylcyclopropyl)octanoate (A2C) was added to each fraction, Na+,K+-ATPase, but not glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity, was activated in the apical fraction. In contrast, further activation of both enzymes was not seen in sinusoidal fractions. The A2C-induced increase in apical Na+,K+-ATPase approached 75% of the sinusoidal level. Parallel increases in apical Na+,K+-ATPase were produced by benzyl alcohol and Triton WR-1339. All three fluidizing agents decreased the order component of membrane fluidity. Na+,K+-ATPase activity in each subfraction was identically inhibited by the monoclonal antibody 9-A5, a specific inhibitor of this enzyme. These findings suggest that hepatic Na+,K+-ATPase is distributed in both surface membranes but functions more efficiently and, perhaps, specifically in the sinusoidal membranes because of their higher bulk lipid fluidity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnen D. J., Brown W. R., Kloppel T. M. Secretory component: the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. What's in it for the gastroenterologist and hepatologist? Gastroenterology. 1985 Sep;89(3):667–682. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Stirling C. Distribution of transport proteins over animal cell membranes. J Membr Biol. 1984;77(3):169–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01870567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer B. L., Boyer J. L. Cytochemical localization of Na+, K+-ATPase in the rat hepatocyte. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1104–1108. doi: 10.1172/JCI109216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer B. L., Donovan C. B. A new method for the rapid isolation of basolateral plasma membrane vesicles from rat liver. Characterization, validation, and bile acid transport studies. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9295–9301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruscalupi G., Curatola G., Lenaz G., Leoni S., Mangiantini M. T., Mazzanti L., Spagnuolo S., Trentalance A. Plasma membrane changes associated with rat liver regeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 10;597(2):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90104-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan M. J., Anderson H. C., Palade G. E., Jamieson J. D. Intracellular sorting and polarized cell surface delivery of (Na+,K+)ATPase, an endogenous component of MDCK cell basolateral plasma membranes. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):623–631. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90888-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casperson G. F., Bourne H. R. Biochemical and molecular genetic analysis of hormone-sensitive adenylyl cyclase. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987;27:371–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.27.040187.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H., Farquhar M. G. Presence of adenylate cyclase activity in Golgi and other fractions from rat liver. I. Biochemical determination. J Cell Biol. 1976 Sep;70(3):660–670. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.3.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong P. L., Fortes P. A., Jameson D. M. Mechanisms of inhibition of (Na,K)-ATPase by hydrostatic pressure studied with fluorescent probes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14484–14490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conteas C. N., McDonough A. A., Kozlowski T. R., Hensley C. B., Wood R. L., Mircheff A. K. Mapping subcellular distribution of Na+-K+-ATPase in rat parotid gland. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):C430–C441. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.3.C430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. A., Kern F., Jr, Showalter R., Sutherland E., Sinensky M., Simon F. R. Alterations of hepatic Na+,K+-atpase and bile flow by estrogen: effects on liver surface membrane lipid structure and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4130–4134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst S. A., Palacios J. R., 2nd, Siegel G. J. Immunocytochemical localization of Na+,K+-ATPase catalytic polypeptide in mouse choroid plexus. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Feb;34(2):189–195. doi: 10.1177/34.2.3003182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H. A biochemical dissection of the functional polarity of the plasma membrane of the hepatocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 27;604(1):27–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90584-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBARG J. A., RUTENBURG A. M. The colorimetric determination of leucine aminopeptidase in urine and serum of normal subjects and patients with cancer and other diseases. Cancer. 1958 Mar-Apr;11(2):283–291. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195803/04)11:2<283::aid-cncr2820110209>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon L. M., Sauerheber R. D., Esgate J. A., Dipple I., Marchmont R. J., Houslay M. D. The increase in bilayer fluidity of rat liver plasma membranes achieved by the local anesthetic benzyl alcohol affects the activity of intrinsic membrane enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4519–4527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert J. J., Schenk D. B., Skelly H., Leffert H. L. Rat hepatic (Na+, K+)-ATPase: alpha-subunit isolation by immunoaffinity chromatography and structural analysis by peptide mapping. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):4156–4163. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar R., Mintz P. W., Swartz T. L., Birnbaumer L. Divalent cation-induced desensitization of glucagon-stimulable adenylyl cyclase in rat liver plasma membrane. GTP-dependent stimulation by glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11875–11882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Yguerabide J. The lateral mobility of the (Na+,K+)-dependent ATPase in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1256–1263. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakis G., Phillips M. J., Yousef I. M. The respective roles of membrane cholesterol and of sodium potassium adenosine triphosphatase in the pathogenesis of lithocholate-induced cholestasis. Lab Invest. 1980 Jul;43(1):73–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Noronha-Blob L., Sacktor B., Farquhar M. G. Microdomains of distinctive glycoprotein composition in the kidney proximal tubule brush border. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1505–1513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K., Papahadjopoulos D. Effects of phospholipid acyl chain fluidity, phase transitions, and cholesterol on (Na+ + K+)-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1071–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosower E. M., Kosower N. S., Wegman P. Membrane mobility agents. IV. The mechanism of particle-cell and cell-cell fusion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 1;471(2):311–329. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90259-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. Immunoferritin determination of the distribution of (Na+ + K+) ATPase over the plasma membranes of renal convoluted tubules. I. Distal segment. J Cell Biol. 1976 Feb;68(2):287–303. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. F., Ogden P., Simmons N. L. Autoradiographic localisation of [3H]ouabain bound to cultured epithelial cell monolayers of MDCK cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 22;644(2):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90391-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham P. S., Kashgarian M. The ultrastructural localization of transport ATPase in the rat liver at non-bile canalicular plasma membranes. Gastroenterology. 1979 May;76(5 Pt 1):988–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffert H. L., Schenk D. B., Hubert J. J., Skelly H., Schumacher M., Ariyasu R., Ellisman M., Koch K. S., Keller G. A. Hepatic (Na+,K+)-ATPase: a current view of its structure, function and localization in rat liver as revealed by studies with monoclonal antibodies. Hepatology. 1985 May-Jun;5(3):501–507. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura S., Eto S., Kato K., Tashiro Y. Ferritin immunoelectron microscopic localization of 5'-nucleotidase on rat liver cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):166–173. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J., Sztul E. S., Reuben A., Boyer J. L. Structural and functional polarity of canalicular and basolateral plasma membrane vesicles isolated in high yield from rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):991–1000. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mircheff A. K., Lu C. C. A map of membrane populations isolated from rat exorbital gland. Am J Physiol. 1984 Dec;247(6 Pt 1):G651–G661. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.247.6.G651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitoris B. A., Simon F. R. Renal cortical brush-border and basolateral membranes: cholesterol and phospholipid composition and relative turnover. J Membr Biol. 1985;83(3):207–215. doi: 10.1007/BF01868695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musil L. S., Baenziger J. U. Cleavage of membrane secretory component to soluble secretory component occurs on the cell surface of rat hepatocyte monolayers. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1725–1733. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poupon R. E., Evans W. H. Biochemical evidence that Na+,K+-ATPase is located at the lateral region of the hepatocyte surface membrane. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):374–378. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80567-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik L., Petzold G. L., Higgins J. A., Greengard P., Barrnett R. J. Hormone-sensitive adenyl cyclase: cytochemical localization in rat liver. Science. 1970 Apr 17;168(3929):382–384. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3929.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez H. J., Hogan W. C., Sinha S. K., Jacobson M. P., Klahr S. The K+-dependent phosphatase of rat kidney. Its properties and the effects of maneuvers that modify (Na+ + K+)-ATPase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 20;641(1):36–54. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90567-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman L. M., Hubbard A. L. A domain-specific marker for the hepatocyte plasma membrane. II. Ultrastructural localization of leucine aminopeptidase to the bile canalicular domain of isolated rat liver plasma membranes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1488–1496. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman L. M., Hubbard A. L. A domain-specific marker for the hepatocyte plasma membrane: localization of leucine aminopeptidase to the bile canalicular domain. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1548–1558. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosario J., Sutherland E., Zaccaro L., Simon F. R. Ethinylestradiol administration selectively alters liver sinusoidal membrane lipid fluidity and protein composition. Biochemistry. 1988 May 31;27(11):3939–3946. doi: 10.1021/bi00411a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y. Adenylate cyclase assay. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:35–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandermann H., Jr Regulation of membrane enzymes by lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 29;515(3):209–237. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter D. Fluidity and function of hepatocyte plasma membranes. Hepatology. 1984 Jan-Feb;4(1):140–151. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk D. B., Hubert J. J., Leffert H. L. Use of a monoclonal antibody to quantify (Na+,K+)-ATPase activity and sites in normal and regenerating rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14941–14951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk D. B., Leffert H. L. Monoclonal antibodies to rat Na+,K+-ATPase block enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5281–5285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner W., von Ilberg C., Kramer R., Seubert W. On the mechanism of Na+- and K+-stimulated hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate. 1. Purification and properties of a Na+-and K+-activated ATPase from ox brain. Eur J Biochem. 1967 May;1(3):334–343. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. The membrane actions of anesthetics and tranquilizers. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Dec;24(4):583–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Fuller S. D. Cell surface polarity in epithelia. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:243–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M., Pinkerton F., Sutherland E., Simon F. R. Rate limitation of (Na+ + K+)-stimulated adenosinetriphosphatase by membrane acyl chain ordering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4893–4897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., Yorek M. A. Membrane lipid composition and cellular function. J Lipid Res. 1985 Sep;26(9):1015–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling C. E. Radioautographic localization of sodium pump sites in rabbit intestine. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jun;53(3):704–714. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztul E. S., Biemesderfer D., Caplan M. J., Kashgarian M., Boyer J. L. Localization of Na+,K+-ATPase alpha-subunit to the sinusoidal and lateral but not canalicular membranes of rat hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1239–1248. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Omori K., Tashiro Y. Quantitative immunoferritin localization of leucine aminopeptidase on canine hepatocyte cell surface. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Jun;34(6):775–784. doi: 10.1177/34.6.3517150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda G., Oka H., Oda T., Ikeda Y. Subfractionation of rat liver plasma membrane. Uneven distribution of plasma membrane-bound enzymes on the liver cell surface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 17;413(1):52–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trams E. G., Lauter C. J. On the sidedness of plasma membrane enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 29;345(2):180–197. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90257-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier C., Louvard D., Maroux S., Desnuelle P. Structural and topological homology between porcine intestinal and renal brush border aminopeptidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 11;455(1):185–199. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziomek C. A., Schulman S., Edidin M. Redistribution of membrane proteins in isolated mouse intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Sep;86(3):849–857. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



