Abstract
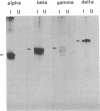
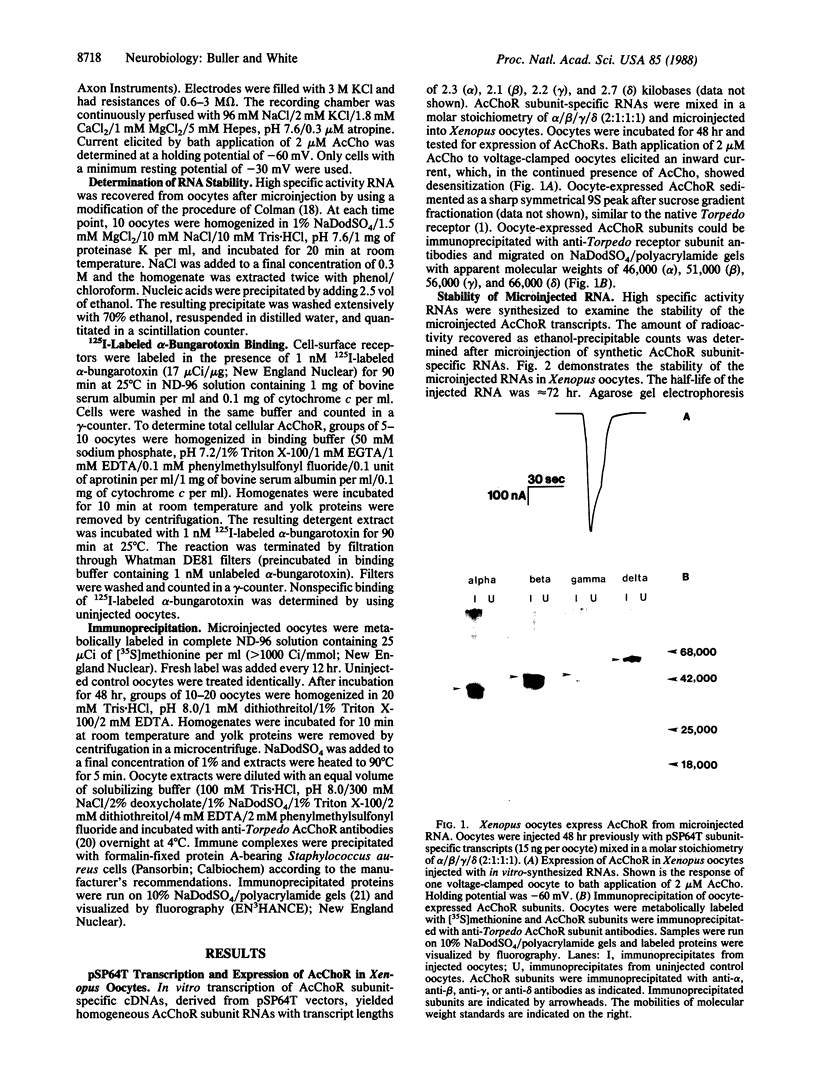
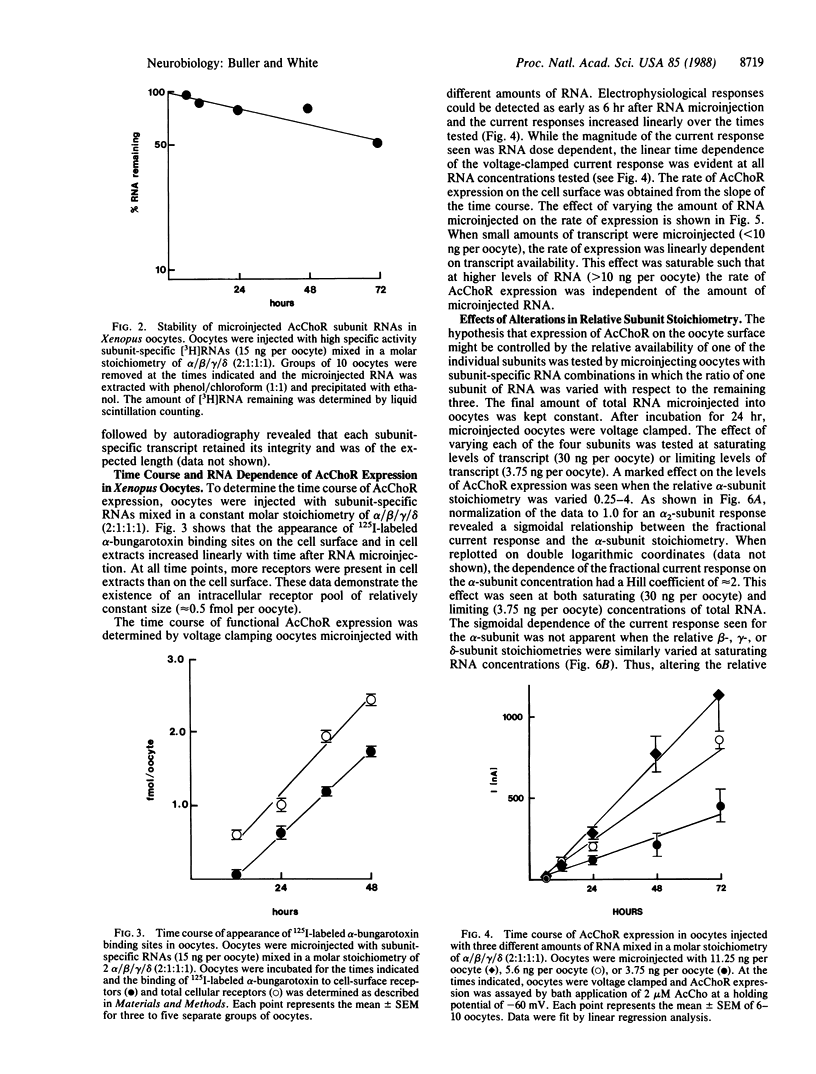
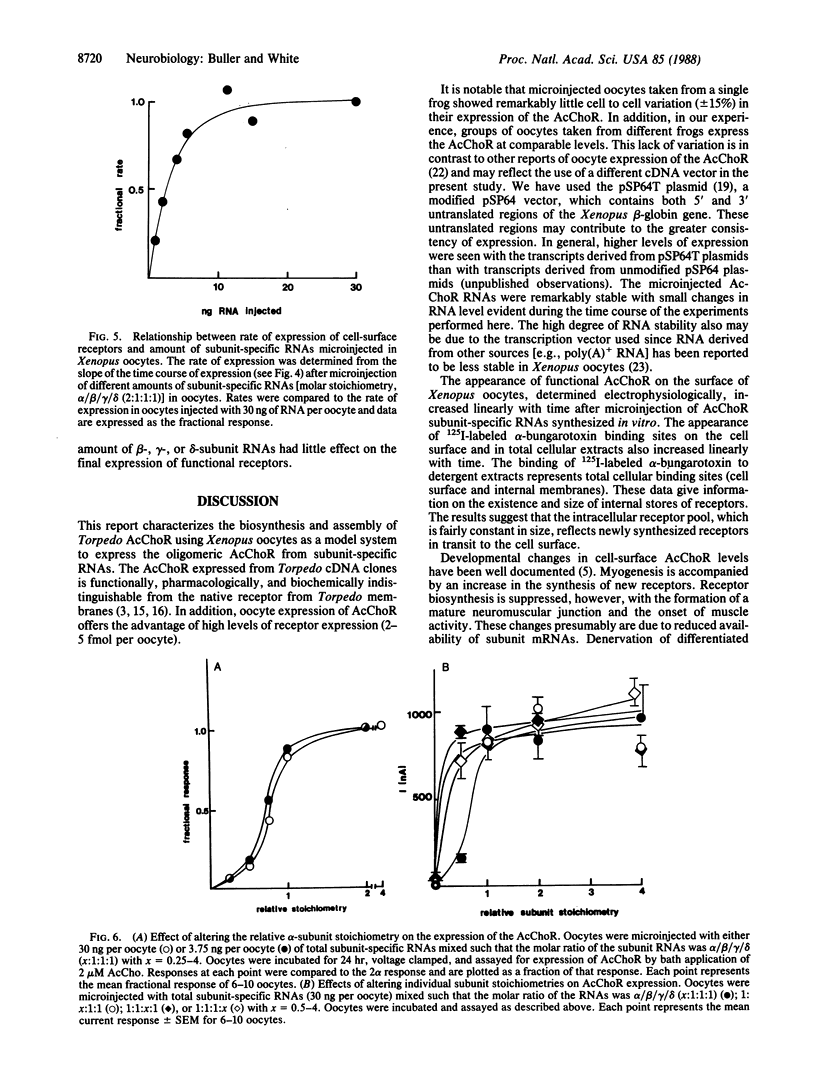
The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AcChoR) of Torpedo electroplax is a multisubunit transmembrane glycoprotein complex with a subunit stoichiometry of alpha 2 beta gamma delta. The RNAs for the separate subunits were transcribed in vitro from cDNAs inserted in pSP64T vectors and microinjected in Xenopus oocytes. Microinjected in vitro-transcribed RNAs were stable, with a half-life of 72 hr. Xenopus oocytes assembled functional AcChoRs from the subunit-specific RNAs. These receptors were inserted in the cell membrane and could be detected as early as 6 hr after RNA microinjection. The oocyte-expressed AcChoR subunits could be immunoprecipitated with anti-Torpedo AcChoR subunit antibodies. Expression of the AcChoR in oocytes proceeded linearly for 72 hr after microinjection. While the amount of RNA injected did not alter the linearity of the expression time course, the rate of receptor expression in oocytes showed a saturable dependence on RNA concentration. Varying the relative amount of alpha-subunit RNA microinjected into oocytes had a striking effect on receptor expression. This effect was specific for the alpha-subunit. These results suggest that transcript availability may control receptor expression in Xenopus oocytes. In addition, the availability of the alpha-subunit may be a limiting factor for receptor expression.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G. In vitro synthesis, glycosylation, and membrane insertion of the four subunits of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5598–5602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonanno A., Merlie J. P. Transcriptional regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes during muscle development. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11452–11455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T., Ballivet M., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor gamma subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T., Raftery M. A. Immunological comparison of acetylcholine receptors and their subunits from species of electric ray. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jun;181(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T. Stable expression of transfected Torpedo acetylcholine receptor alpha subunits in mouse fibroblast L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5967–5971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S., Goldman D., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Muscle acetylcholine receptor biosynthesis. Regulation by transcript availability. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4911–4916. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine sensitivity of muscle fiber membranes: mechanism of regulation by motoneurons. Science. 1970 Apr 17;168(3929):372–373. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3929.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M. Control of acetylcholine receptors in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jan;59(1):165–227. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Brenner H. R., Heinemann S. Acetylcholine receptor alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and delta-subunit mRNA levels are regulated by muscle activity. Neuron. 1988 Jun;1(4):329–333. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grampp W., Harris J. B., Thesleff S. Inhibition of denervation changes in skeletal muscle by blockers of protein synthesis. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):743–754. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Lane C. D., Woodland H. R., Marbaix G. Use of frog eggs and oocytes for the study of messenger RNA and its translation in living cells. Nature. 1971 Sep 17;233(5316):177–182. doi: 10.1038/233177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. A., Falls D. L., Dill-Devor R. M., Fischbach G. D. Acetylcholine receptor-inducing factor from chicken brain increases the level of mRNA encoding the receptor alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1983–1987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann O., Buonanno A., Geoffroy B., Robert B., Guénet J. L., Merlie J. P., Changeux J. P. Chromosomal localization of muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes in the mouse. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):866–868. doi: 10.1126/science.3022377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosaki T., Fukuda K., Konno T., Mori Y., Tanaka K., Mishina M., Numa S. Functional properties of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits expressed in various combinations. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 20;214(2):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy M. P., Earnest J. P., Young E. F., Choe S., Stroud R. M. The molecular neurobiology of the acetylcholine receptor. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:383–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.002123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina M., Tobimatsu T., Imoto K., Tanaka K., Fujita Y., Fukuda K., Kurasaki M., Takahashi H., Morimoto Y., Hirose T. Location of functional regions of acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit by site-directed mutagenesis. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):364–369. doi: 10.1038/313364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nef P., Mauron A., Stalder R., Alliod C., Ballivet M. Structure linkage, and sequence of the two genes encoding the delta and gamma subunits of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7975–7979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Miyata T., Numa S. Primary structure of alpha-subunit precursor of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):793–797. doi: 10.1038/299793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Hirose T., Asai M., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Primary structures of beta- and delta-subunit precursors of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequences. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):251–255. doi: 10.1038/301251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popot J. L., Changeux J. P. Nicotinic receptor of acetylcholine: structure of an oligomeric integral membrane protein. Physiol Rev. 1984 Oct;64(4):1162–1239. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.4.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D., Smith L. D. Differential capacity for translation and lack of competition between mRNAs that segregate to free and membrane-bound polysomes. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90372-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebbane R., Clokey G., Merlie J. P., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. Characterization of the mRNA for mouse muscle acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit by quantitative translation in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3294–3303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usdin T. B., Fischbach G. D. Purification and characterization of a polypeptide from chick brain that promotes the accumulation of acetylcholine receptors in chick myotubes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):493–507. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. M., Mayne K. M., Lester H. A., Davidson N. Mouse-Torpedo hybrid acetylcholine receptors: functional homology does not equal sequence homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4852–4856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshii K., Yu L., Mayne K. M., Davidson N., Lester H. A. Equilibrium properties of mouse-Torpedo acetylcholine receptor hybrids expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Oct;90(4):553–573. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.4.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L., LaPolla R. J., Davidson N. Mouse muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gamma subunit: cDNA sequence and gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3539–3555. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]