Abstract
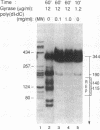
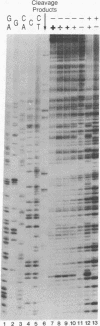
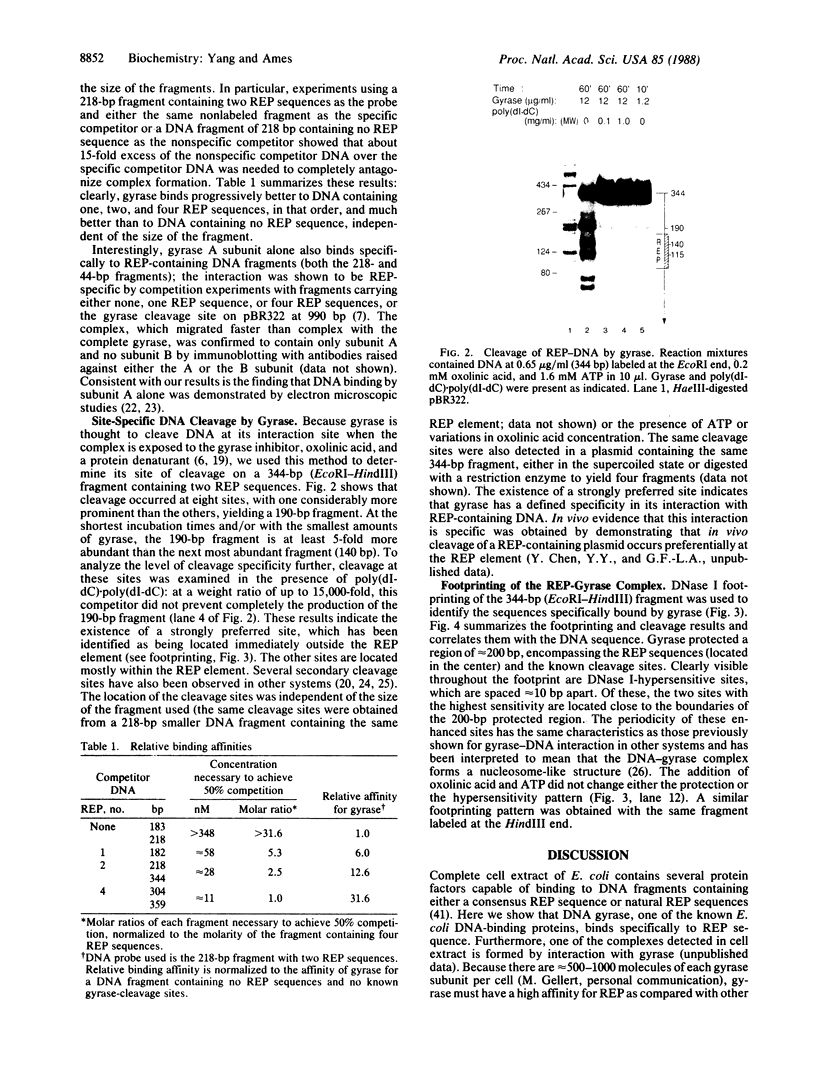
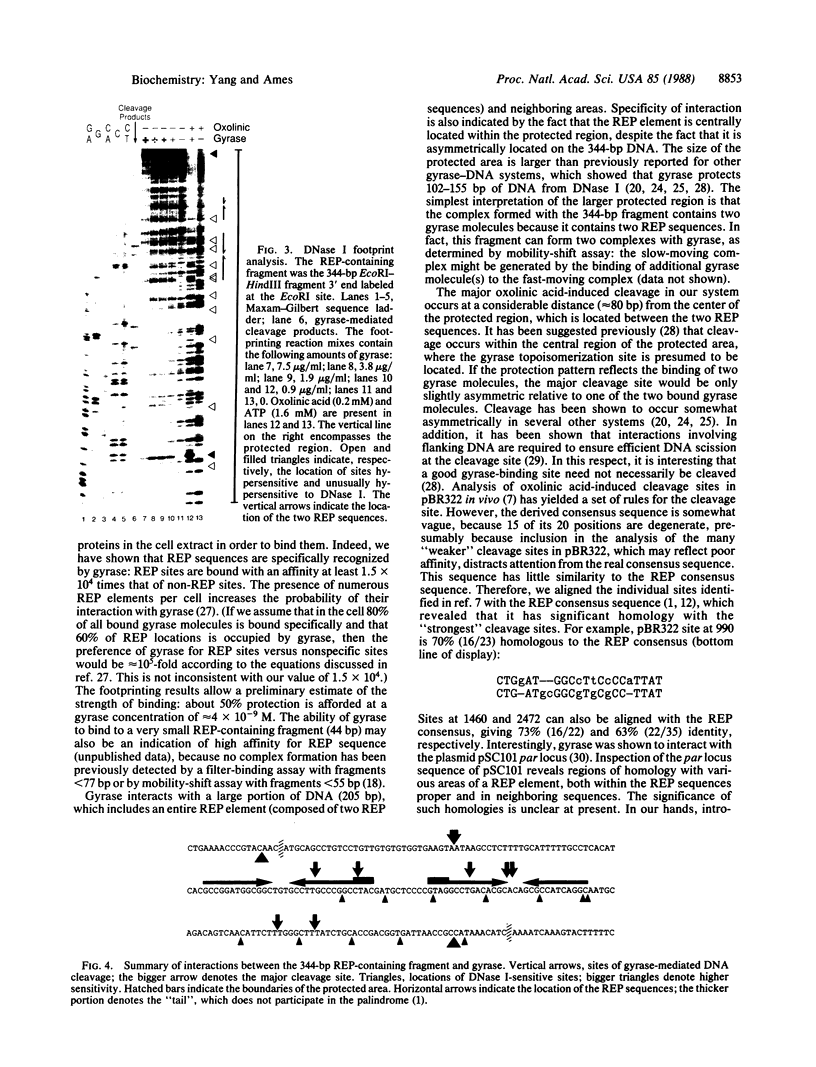
A family of repetitive extragenic palindromic (REP) sequences is composed of hundreds of copies distributed throughout the chromosome. Their palindromic nature and conservation suggested that they are specifically recognized by a protein(s). We have identified DNA gyrase [DNA topoisomerase (ATP-hydrolysing), EC 5.99.1.3] as one of the REP-binding proteins. Gyrase has at least a 10-fold higher affinity for DNA containing REP sequences than for DNA not containing REP sequences. Binding effectiveness correlates directly with the number of REP sequences in the DNA. DNase I footprinting shows that gyrase protects 205 base pairs on a REP-containing DNA fragment enclosing the REP sequences. In agreement with the above results, a comparison of the REP consensus sequence with the sequence of previously identified pBR322 "strong" gyrase cleavage sites reveals a high degree of homology. Because REP sequences are numerous and found throughout the genome, we suggest they have physiological functions mediated through their interaction with gyrase, such as being sites of action for the maintenance of DNA supercoiling. In addition, we speculate that these interactions may be of a structural nature, such as involvement in the higher-order structure of the bacterial chromosome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berrios M., Osheroff N., Fisher P. A. In situ localization of DNA topoisomerase II, a major polypeptide component of the Drosophila nuclear matrix fraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4142–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlison M. G., Spencer M. E., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the sucA gene encoding the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 1;141(2):351–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Heck M. M. Localization of topoisomerase II in mitotic chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1716–1725. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Multiple DNA-protein interactions governing high-precision DNA transactions. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1050–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.2943018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher L. M., Barot H. A., Cullen M. E. DNA gyrase complex with DNA: determinants for site-specific DNA breakage. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1411–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher L. M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Ohmori H., Gellert M. Site-specific interaction of DNA gyrase with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4165–4169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laroche T., Falquet J., Boy de la Tour E., Laemmli U. K. Metaphase chromosome structure. Involvement of topoisomerase II. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):613–629. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Clément J. M., Brutlag D., Hofnung M. A family of dispersed repetitive extragenic palindromic DNA sequences in E. coli. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1417–1421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Perrin D., Clement J. M., Szmelcman S., Dassa E., Hofnung M. Palindromic units from E. coli as binding sites for a chromoid-associated protein. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 6;206(2):323–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Perrin D., Saurin W., Hofnung M. Species specificity of bacterial palindromic units. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):371–373. doi: 10.1007/BF02603122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins N. P., Peebles C. L., Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. Purification of subunits of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase and reconstitution of enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1773–1777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K., Wang J. C. Mapping the topography of DNA wrapped around gyrase by nucleolytic and chemical probing of complexes of unique DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90435-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. DNA-DNA gyrase complex: the wrapping of the DNA duplex outside the enzyme. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):979–984. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90281-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshon D., Morris D. R. Sites of reaction of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase on pBR322 in vivo as revealed by oxolinic acid-induced plasmid linearization. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lother H., Lurz R., Orr E. DNA binding and antigenic specifications of DNA gyrase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):901–914. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A., Gellert M. Mechanistic aspects of DNA topoisomerases. Adv Protein Chem. 1986;38:69–107. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60526-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A., Gellert M. The DNA dependence of the ATPase activity of DNA gyrase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14472–14480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Scaffold attachment of DNA loops in metaphase chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 5;200(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90336-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Klevan L., Wang J. C., Griffith J. D. Gyrase . DNA complexes visualized as looped structures by electron microscopy. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4612–4617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Cozzarelli N. R. Contacts between DNA gyrase and its binding site on DNA: features of symmetry and asymmetry revealed by protection from nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1416–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Cozzarelli N. R. Site-specific cleavage of DNA by E. coli DNA gyrase. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito A., Naito S., Ikeda H. Homology is not required for recombination mediated by DNA gyrase of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(2):238–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00330674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbury S. F., Smith N. H., Robinson E. C., Hiles I. D., Higgins C. F. Stabilization of translationally active mRNA by prokaryotic REP sequences. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):297–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90433-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettijohn D. E. Structure and properties of the bacterial nucleoid. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):667–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rau D. C., Gellert M., Thoma F., Maxwell A. Structure of the DNA gyrase-DNA complex as revealed by transient electric dichroism. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 5;193(3):555–569. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90266-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Drlica K. DNA gyrase on the bacterial chromosome: DNA cleavage induced by oxolinic acid. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):287–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. R., Drlica K. Bacterial chromosome segregation: evidence for DNA gyrase involvement in decatenation. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1081–1088. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. J., Ames G. F., Smith N. H., Robinson E. C., Higgins C. F. Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences: a major component of the bacterial genome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. J., Prossnitz E., Ames G. F. Role of the intercistronic region in post-transcriptional control of gene expression in the histidine transport operon of Salmonella typhimurium: involvement of REP sequences. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):141–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosberg H. P. DNA topoisomerases: enzymes that control DNA conformation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;114:19–102. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70227-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E., Kornberg A. The partition locus of plasmid pSC101 is a specific binding site for DNA gyrase. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1889–1895. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Kojima T., Yamagishi J., Nakamura S. Quinolone-resistant mutations of the gyrA gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jan;211(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00338386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]