Abstract
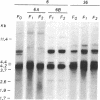
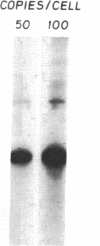
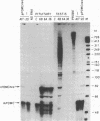
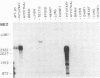
The product of a single gene encoding proopiomelanocortin (POMC) is differentially processed to produce corticotropin and alpha-melanotropin in anterior and intermediate pituitary cells, respectively. Hormonal control of POMC gene transcription and of corticotropin or alpha-melanotropin release is also tissue-specific; for example, glucocorticoids specifically inhibit anterior but not intermediate pituitary POMC transcription. Outside the pituitary gland, very low levels of POMC mRNAs are present in brain, testes, ovaries, and placenta. We have used transgenic mice to identify POMC 5' flanking sequences that are sufficient for tissue-specific expression and glucocorticoid regulation in anterior and intermediate pituitary cells. Three lines of transgenic mice were established, each carrying 50-75 copies (per cell) of a chimeric rPOMCneo gene constituted of rat POMC promoter sequences and of bacterial neomycin-resistance coding sequence. High levels of rPOMCneo transcripts were detected in pituitaries of mice from all three lineages. In situ hybridization revealed that the ratio of intermediate to anterior pituitary transcripts was similar for the transgene and endogenous POMC mRNA. rPOMCneo transcripts were not detected in any other tissue except at very low levels in the testes in two transgenic lines. Endogenous mouse POMC mRNA increased in response to depletion of plasma glucocorticoids (adrenalectomy) and decreased after glucocorticoid treatment; rPOMCneo transcripts were altered to the same extent by these treatments in all three lines. Intermediate pituitary and testicular rPOMCneo transgene expression was not altered by these treatments. Thus, no more than 769 base pairs of the rat POMC promoter are required for pituitary-specific expression and for specific glucocorticoid inhibition of the POMC gene in the anterior pituitary.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker B. L., Pek S., Midgley A. R., Jr, Gersten B. E. Identification of the corticotropin cell in rat hypophyses with peroxidase-labeled antibody. Anat Rec. 1970 Apr;166(4):557–567. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091660402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnberg N. C., Lissitzky J. C., Hinman M., Herbert E. Glucocorticoids regulate proopiomelanocortin gene expression in vivo at the levels of transcription and secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6982–6986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron J., Drouin J. Glucocorticoid inhibition of transcription from episomal proopiomelanocortin gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8903–8907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. L., Chang C. C., Krieger D. T., Bardin C. W. Expression and regulation of proopiomelanocortin-like gene in the ovary and placenta: comparison with the testis. Endocrinology. 1986 Jun;118(6):2382–2389. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-6-2382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. L., Mather J. P., Morris P. L., Bardin C. W. Expression of pro-opiomelanocortin-like gene in the testis and epididymis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5672–5675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civelli O., Birnberg N., Herbert E. Detection and quantitation of pro-opiomelanocortin mRNA in pituitary and brain tissues from different species. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6783–6787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouin J., Chamberland M., Charron J., Jeannotte L., Nemer M. Structure of the rat pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) gene. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 25;193(1):54–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouin J., Charron J., Gagner J. P., Jeannotte L., Nemer M., Plante R. K., Wrange O. Pro-opiomelanocortin gene: a model for negative regulation of transcription by glucocorticoids. J Cell Biochem. 1987 Dec;35(4):293–304. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240350404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberwine J. H., Roberts J. L. Glucocorticoid regulation of pro-opiomelanocortin gene transcription in the rat pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2166–2170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eipper B. A., Mains R. E. Structure and biosynthesis of pro-adrenocorticotropin/endorphin and related peptides. Endocr Rev. 1980 Winter;1(1):1–27. doi: 10.1210/edrv-1-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. R., Wan K. M., Ben-Ze'ev A., Penman S. Regulation of actin mRNA levels and translation responds to changes in cell configuration. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):182–189. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagner J. P., Drouin J. Opposite regulation of pro-opiomelanocortin gene transcription by glucocorticoids and CRH. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Apr;40(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90154-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagner J. P., Drouin J. Tissue-specific regulation of pituitary proopiomelanocortin gene transcription by corticotropin-releasing hormone, 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate, and glucocorticoids. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Oct;1(10):677–682. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-10-677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee C. E., Chen C. L., Roberts J. L., Thompson R., Watson S. J. Identification of proopiomelanocortin neurones in rat hypothalamus by in situ cDNA-mRNA hybridization. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):374–376. doi: 10.1038/306374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gizang-Ginsberg E., Wolgemuth D. J. Expression of the proopiomelanocortin gene is developmentally regulated and affected by germ cells in the male mouse reproductive system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1600–1604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeannotte L., Burbach J. P., Drouin J. Unusual proopiomelanocortin ribonucleic acids in extrapituitary tissues: intronless transcripts in testes and long poly(A) tails in hypothalamus. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Oct;1(10):749–757. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-10-749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeannotte L., Trifiro M. A., Plante R. K., Chamberland M., Drouin J. Tissue-specific activity of the pro-opiomelanocortin gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4058–4064. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. P., Tretjakoff I., Beaudet L., Peterson A. Expression and assembly of a human neurofilament protein in transgenic mice provide a novel neuronal marking system. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1085–1095. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacaze-Masmonteil T., de Keyzer Y., Luton J. P., Kahn A., Bertagna X. Characterization of proopiomelanocortin transcripts in human nonpituitary tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7261–7265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemer M., Lavigne J. P., Drouin J., Thibault G., Gannon M., Antakly T. Expression of atrial natriuretic factor gene in heart ventricular tissue. Peptides. 1986 Nov-Dec;7(6):1147–1152. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Transgenic mice. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):343–345. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintar J. E., Schachter B. S., Herman A. B., Durgerian S., Krieger D. T. Characterization and localization of proopiomelanocortin messenger RNA in the adult rat testis. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):632–634. doi: 10.1126/science.6740329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M., Herbert E. Complete amino acid sequence of mouse pro-opiomelanocortin derived from the nucleotide sequence of pro-opiomelanocortin cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):257–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]