Abstract
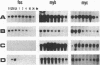
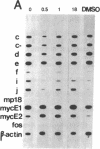
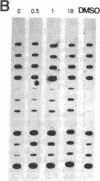
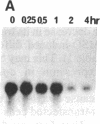
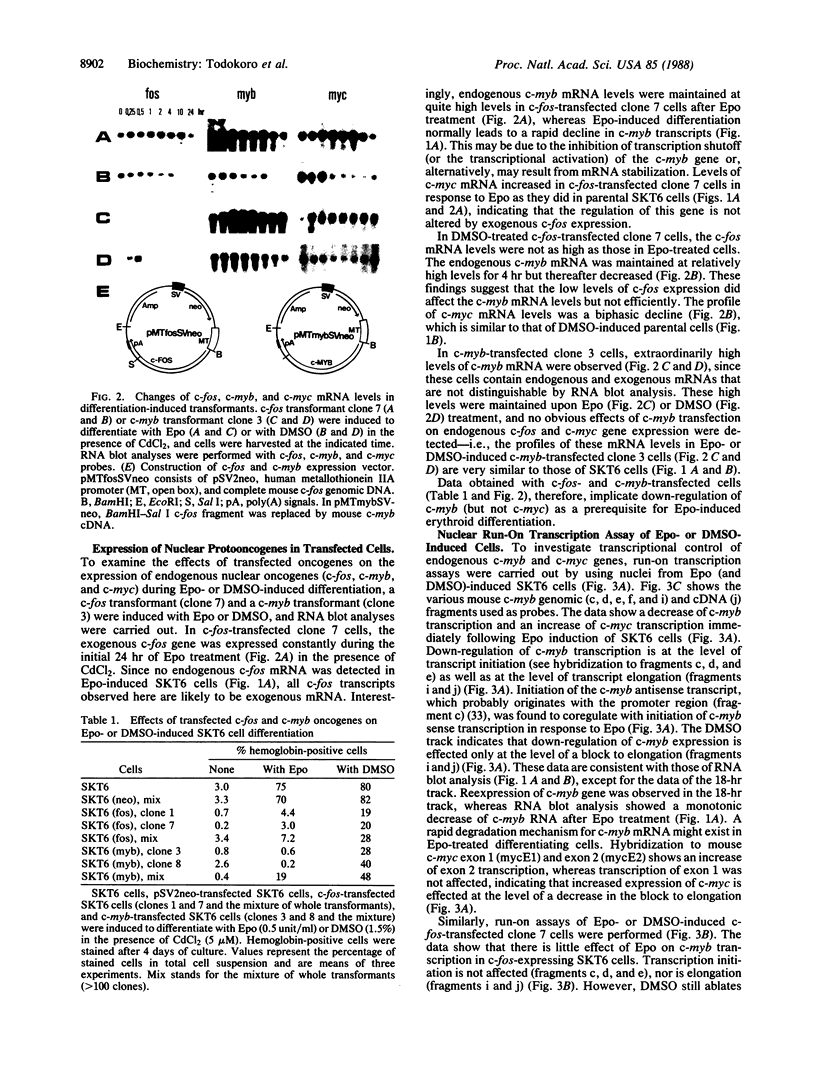
The role of nuclear protooncogenes during erythroid cell differentiation was examined by transfecting exogenous c-fos and c-myb genes into mouse erythroleukemia cells, which can be induced to differentiate either with erythropoietin (Epo) or dimethyl sulfoxide. Expression of exogenous c-myb or c-fos oncogene completely inhibited Epo-induced erythroid differentiation but only partially inhibited dimethyl sulfoxide-induced differentiation. Normally Epo-induced differentiation leads to a drastic decline of c-myb mRNA levels and an increase of c-myc transcripts in the early stage of differentiation. Cells expressing exogenous c-fos gene, however, maintained high levels of c-myb mRNA after Epo treatment. This high level of c-myb transcripts was found to be due to block of transcription shutoff (or transcriptional activation) rather than to mRNA stabilization. It is concluded that the down-regulation of endogenous c-myb gene expression is a prerequisite for commitment of Epo-induced erythroid differentiation and that expression of c-myb gene may be indirectly regulated by c-fos gene product. We also concluded that early down-regulation of c-myc gene expression is not essential for erythroid differentiation and that gene regulation of chemically induced erythroid differentiation may differ from that of Epo-induced differentiation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabretta B. Dissociation of c-fos induction from macrophage differentiation in human myeloid leukemic cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):769–774. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H. The molecular action of platelet-derived growth factor. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;45:183–216. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Cole M. D. Constitutive c-myc oncogene expression blocks mouse erythroleukaemia cell differentiation but not commitment. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):760–763. doi: 10.1038/320760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrovsky E., Kuehl W. M., Hollis G. F., Kirsch I. R., Bender T. P., Segal S. Expression of a transfected human c-myc oncogene inhibits differentiation of a mouse erythroleukaemia cell line. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):748–750. doi: 10.1038/322748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Oren M. Overproduction of p53 antigen makes established cells highly tumorigenic. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):158–160. doi: 10.1038/316158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R., de Blaquiere J. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA clones of the murine myb proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2003–2008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03884.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Metcalf D. Expression of myb, myc and fos proto-oncogenes during the differentiation of a murine myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):249–251. doi: 10.1038/310249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Cell-type specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression is regulated by at least three DNA sequence elements. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):885–897. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Itani T., Kiji Y., Ariga H. Possible function of the c-myc product: promotion of cellular DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2365–2371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes--primary structure of the metallothionein-II gene and a related processed gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):797–802. doi: 10.1038/299797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman H. M., Cheng G. H., Skoultchi A. I. Transfection of mouse erythroleukemia cells with myc sequences changes the rate of induced commitment to differentiate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6480–6484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. G., Gray H. E., Tötterman T., Pettersson U., Nilsson K. Drastically increased expression of MYC and FOS protooncogenes during in vitro differentiation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):223–227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki Y., Bos T. J., Davis C., Starbuck M., Vogt P. K. Avian sarcoma virus 17 carries the jun oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2848–2852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Curran T., Verma I. M. c-fos protein can induce cellular transformation: a novel mechanism of activation of a cellular oncogene. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Henning-Chubb C., Huberman E., Verma I. M. c-fos expression is neither sufficient nor obligatory for differentiation of monomyelocytes to macrophages. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Zokas L., Schreiber R. D., Verma I. M. Rapid induction of the expression of proto-oncogene fos during human monocytic differentiation. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90324-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake T., Kung C. K., Goldwasser E. Purification of human erythropoietin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5558–5564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Curran T., Müller D., Guilbert L. Induction of c-fos during myelomonocytic differentiation and macrophage proliferation. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):546–548. doi: 10.1038/314546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H., Weir L., Leder P. Enhancer-dependent expression of human kappa immunoglobulin genes introduced into mouse pre-B lymphocytes by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7161–7165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V., Kukowska J. Deregulated expression of c-myc by murine erythroleukaemia cells prevents differentiation. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):848–850. doi: 10.1038/322848a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quantin B., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor stimulates transcription of the c-jun proto-oncogene in rat fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):538–539. doi: 10.1038/334538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay R. G., Ikeda K., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Changes in gene expression associated with induced differentiation of erythroleukemia: protooncogenes, globin genes, and cell division. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6849–6853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ran W., Dean M., Levine R. A., Henkle C., Campisi J. Induction of c-fos and c-myc mRNA by epidermal growth factor or calcium ionophore is cAMP dependent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8216–8220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Sambucetti L. C., Curran T., Distel R. J., Spiegelman B. M. Common DNA binding site for Fos protein complexes and transcription factor AP-1. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):471–480. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Sinnett-Smith J. W. Bombesin induction of c-fos and c-myc proto-oncogenes in Swiss 3T3 cells: significance for the mitogenic response. J Cell Physiol. 1987 May;131(2):218–225. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavnezer E., Barkas A. E., Brennan L. A., Brodeur D., Li Y. Transforming Sloan-Kettering viruses generated from the cloned v-ski oncogene by in vitro and in vivo recombinations. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1073–1083. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1073-1083.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todokoro K., Ikawa Y. Sequential expression of proto-oncogenes during a mouse erythroleukemia cell differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 28;135(3):1112–1118. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todokoro K., Kanazawa S., Amanuma H., Ikawa Y. Specific binding of erythropoietin to its receptor on responsive mouse erythroleukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4126–4130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Sassone-Corsi P. Proto-oncogene fos: complex but versatile regulation. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):513–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma S. S., Gupta R. K., Kishore N., Sen Gupta J. A simple relationship between maximal aerobic power and body weight in Indian adolescent boys. Indian J Med Sci. 1986 Apr;40(4):93–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Bos T. J., Doolittle R. F. Homology between the DNA-binding domain of the GCN4 regulatory protein of yeast and the carboxyl-terminal region of a protein coded for by the oncogene jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3316–3319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J. A transcriptional arrest mechanism involved in controlling constitutive levels of mouse c-myb mRNA. Oncogene. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Dyson P. J., McMahon J. Multiple c-myb transcript cap sites are variously utilized in cells of mouse haemopoietic origin. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1643–1651. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]