Abstract
The isolation and cloning of a full-length cDNA insert complementary to mRNA encoding human aromatase system cytochrome P-450 is reported. The insert contains an open reading frame encoding a protein of 503 amino acids. This gene is clearly a member of the cytochrome P-450 gene superfamily, because the sequence contains regions of marked homology to those of other members, notably a putative membrane-spanning region, I helix, Ozols, and heme-binding regions. The cDNA was inserted into a modified pCMV vector and expressed in COS-1 monkey kidney tumor cells. The expressed protein was similar in size to human placental aromatase system cytochrome P-450, as detected by immunoblot analysis, and catalyzed the aromatization of androstenedione, testosterone, and 16 alpha-hydroxyandrostenedione. This activity was inhibited by the known aromatase inhibitors, 4-hydroxyandrostenedione and econazole. Thus the several steps involved in the aromatization reaction appear to be catalyzed by a single polypeptide chain, which can metabolize the three major physiological substrates.
Full text
PDF


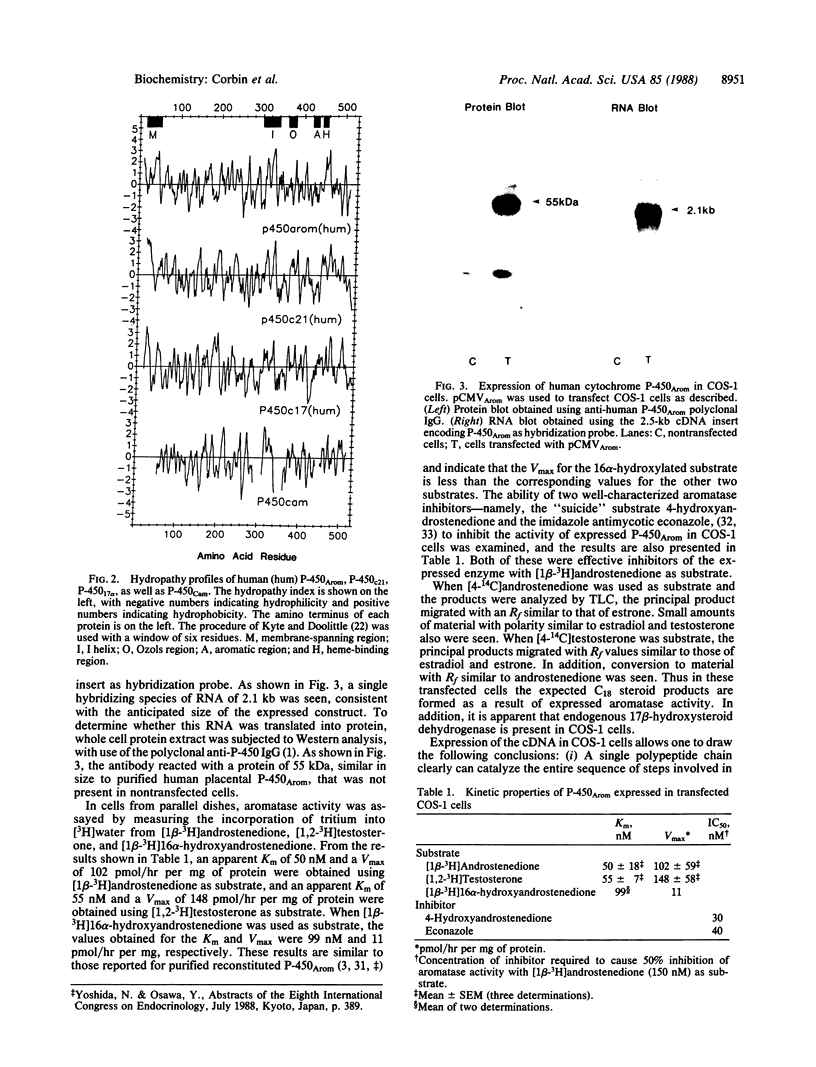

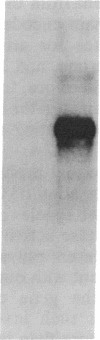
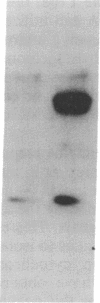
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman G. E., Smith M. E., Mendelson C. R., MacDonald P. C., Simpson E. R. Aromatization of androstenedione by human adipose tissue stromal cells in monolayer culture. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Aug;53(2):412–417. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-2-412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie A. M., Schwarzel W. C., Shaikh A. A., Brodie H. J. The effect of an aromatase inhibitor, 4-hydroxy-4-androstene-3,17-dione, on estrogen-dependent processes in reproduction and breast cancer. Endocrinology. 1977 Jun;100(6):1684–1695. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-6-1684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. A., Besman M. J., Sparkes R. S., Zollman S., Klisak I., Mohandas T., Hall P. F., Shively J. E. Human aromatase: cDNA cloning, Southern blot analysis, and assignment of the gene to chromosome 15. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):27–38. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., Shively J. E., Nakajin S., Shinoda M., Hall P. F. Amino terminal sequence analysis of human placenta aromatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 28;135(3):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90987-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. T., Corbin C. J., Saunders C. T., Merrill J. C., Simpson E. R., Mendelson C. R. Regulation of estrogen biosynthesis in human adipose stromal cells. Effects of dibutyryl cyclic AMP, epidermal growth factor, and phorbol esters on the synthesis of aromatase cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6914–6920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. T., Ledesma D. B., Schulz T. Z., Simpson E. R., Mendelson C. R. Isolation and characterization of a complementary DNA specific for human aromatase-system cytochrome P-450 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6387–6391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman J., Goto J. Mechanism of estrogen biosynthesis. Participation of multiple enzyme sites in placental aromatase hydroxylations. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4466–4471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- France J. T., Mason J. I., Magness R. R., Murry B. A., Rosenfeld C. R. Ovine placental aromatase: studies of activity levels, kinetic characteristics and effects of aromatase inhibitors. J Steroid Biochem. 1987 Aug;28(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(87)90371-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz I. B., Griswold M. D., Louis B. G., Dorrington J. H. Similarity of responses of cultured Sertoli cells to cholera toxin and FSH. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1976 Aug-Sep;5(3-4):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(76)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George F. W., Tobleman W. T., Milewich L., Wilson J. D. Aromatase activity in the developing rabbit brain. Endocrinology. 1978 Jan;102(1):86–91. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-1-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto J., Fishman J. Participation of a nonenzymatic transformation in the biosynthesis of estrogens from androgens. Science. 1977 Jan 7;195(4273):80–81. doi: 10.1126/science.831259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodin J. M., Siiteri P. K., MacDonald P. C. Source of estrogen production in postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Feb;36(2):207–214. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-2-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada N. Novel properties of human placental aromatase as cytochrome P-450: purification and characterization of a unique form of aromatase. J Biochem. 1988 Jan;103(1):106–113. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heap R. B., Hamon M., Allen W. R. Studies on oestrogen synthesis by the preimplantation equine conceptus. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1982;32:343–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellis J. T., Jr, Vickery L. E. Purification and characterization of human placental aromatase cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4413–4420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNatty K. P., Baird D. T., Bolton A., Chambers P., Corker C. S., McLean H. Concentration of oestrogens and androgens in human ovarian venous plasma and follicular fluid throughout the menstrual cycle. J Endocrinol. 1976 Oct;71(1):77–85. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0710077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson C. R., Simpson E. R. Regulation of estrogen biosynthesis by human adipose cells in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Aug;52(3):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson C. R., Wright E. E., Evans C. T., Porter J. C., Simpson E. R. Preparation and characterization of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies against human aromatase cytochrome P-450 (P-450AROM), and their use in its purification. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Dec;243(2):480–491. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90525-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naftolin F., Ryan K. J., Davies I. J., Reddy V. V., Flores F., Petro Z., Kuhn M., White R. J., Takaoka Y., Wolin L. The formation of estrogens by central neuroendocrine tissues. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1975;31:295–319. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571131-9.50012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Adesnik M., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F., Kemper B., Levin W. The P450 gene superfamily: recommended nomenclature. DNA. 1987 Feb;6(1):1–11. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Finzel B. C., Gunsalus I. C., Wagner G. C., Kraut J. The 2.6-A crystal structure of Pseudomonas putida cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16122–16130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roselli C. E., Horton L. E., Resko J. A. Distribution and regulation of aromatase activity in the rat hypothalamus and limbic system. Endocrinology. 1985 Dec;117(6):2471–2477. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E. R., Evans C. T., Corbin C. J., Powell F. E., Ledesma D. B., Mendelson C. R. Sequencing of cDNA inserts encoding aromatase cytochrome P-450 (P-450AROM). Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Aug;52(3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Gotoh O., Kawajiri K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Distinct organization of methylcholanthrene- and phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 genes in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkampf M. P., Mendelson C. R., Simpson E. R. Regulation by follicle-stimulating hormone of the synthesis of aromatase cytochrome P-450 in human granulosa cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Jul;1(7):465–471. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-7-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. A., Jr, Siiteri P. K. The involvement of human placental microsomal cytochrome P-450 in aromatization. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5373–5378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M. X., John M. E., Okamura T., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Bovine adrenocortical cytochrome P-450(17 alpha). Regulation of gene expression by ACTH and elucidation of primary sequence. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2475–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M. X., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Expression of bovine 17 alpha-hydroxylase cytochrome P-450 cDNA in nonsteroidogenic (COS 1) cells. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1258–1261. doi: 10.1126/science.3535074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]